Answer (4)
Sol. Since body does not move hence it is in equilibrium.
![]() frictional force which is less than or equal to limiting friction.
frictional force which is less than or equal to limiting friction.
Now ![]()
Hence ![]()
![]()
![]()
Answer (4)
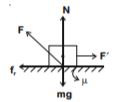
Sol. Since body does not move hence it is in equilibrium.
![]() frictional force which is less than or equal to limiting friction.
frictional force which is less than or equal to limiting friction.
Now ![]()
Hence ![]()
![]()
![]()
