b)![]()
A linearly polarized electromagnetic wave given as 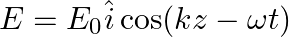 is incident normally on a perfectly reflecting infinite wall at
is incident normally on a perfectly reflecting infinite wall at  .
.
Assuming that the material of the wall is optically inactive, the reflected wave will be given as
a)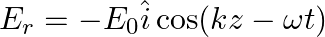
b)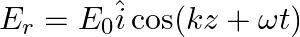
c)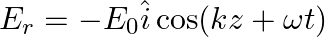
d)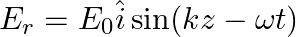
Assuming that the material of the wall is optically inactive, the reflected wave will be given as
a)
b)
c)
d)
A linearly polarized electromagnetic wave given as 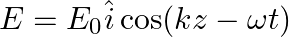 is incident normally on a perfectly reflecting infinite wall at
is incident normally on a perfectly reflecting infinite wall at  .
.
Assuming that the material of the wall is optically inactive, the reflected wave will be given as
a)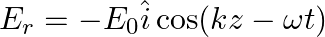
b)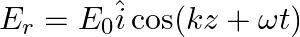
c)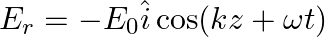
d)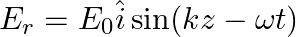
Assuming that the material of the wall is optically inactive, the reflected wave will be given as
a)
b)
c)
d)
