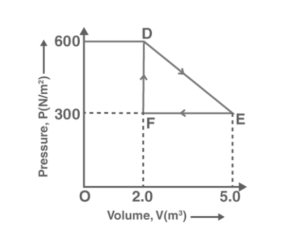
Solution:
From figure, DEF is the area of the gas’s total work done from D through E and F.
Area of ∆DEF = (1/2) x DE x EF
Where,
DF = Change in pressure = 600 N/m2 – 300 N/m2= 300 N/ m2
FE = Change in volume = 5.0 m3 – 2.0 m3= 3.0 m3
Area of ∆DEF = (1/ 2) x 300 x 3
On further evaluation, we get,
= 450 J
Hence, the total work done by the gas from D to E to F is 450 J
