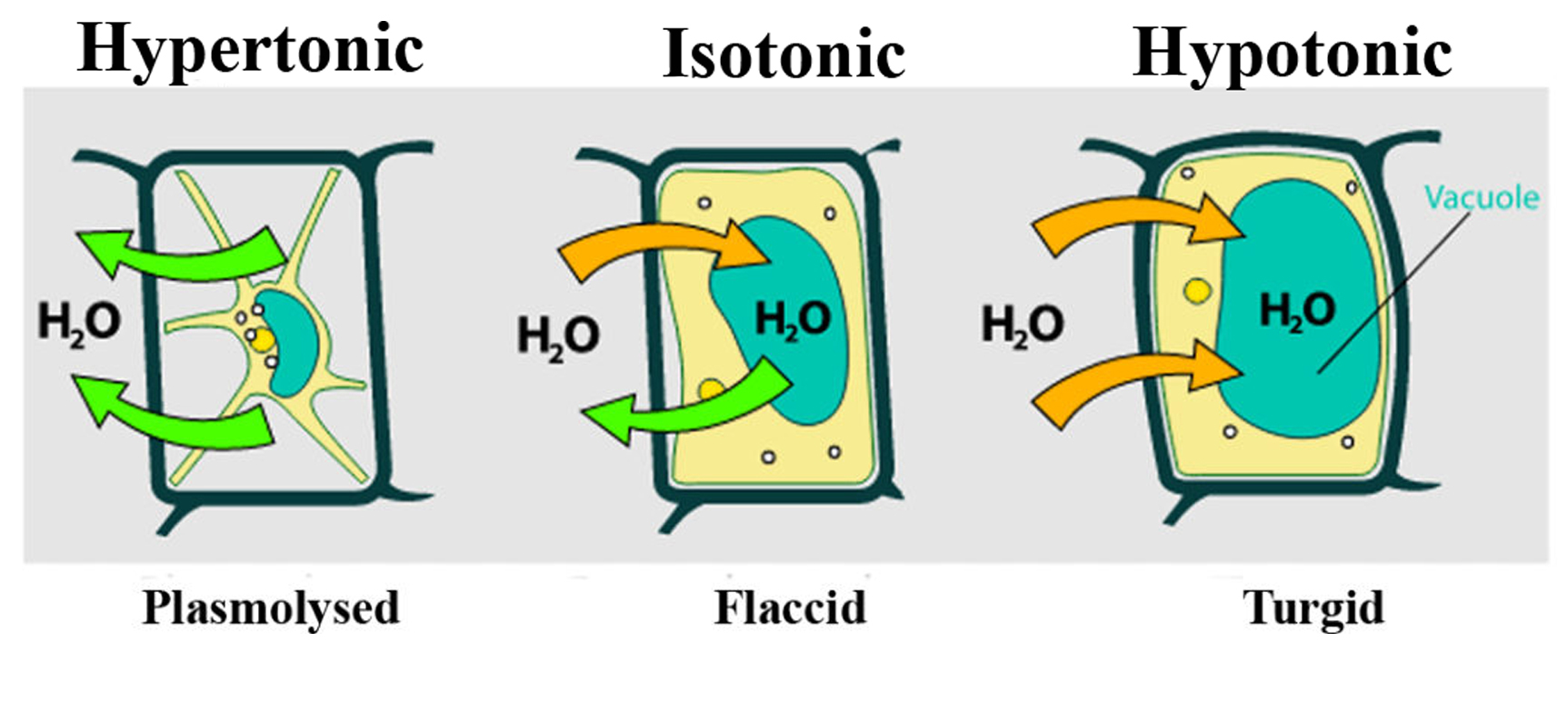
Solution: If a plant is kept in a solution having higher water potential, the following are the things that can happen-
a) When water leaves a plant’s cell and the cell membrane, the cell shrinks away from its cell wall, resulting in plasmolysis. Water travels out of the cell when it is placed in a hypertonic solution to the protoplasm (as seen in figure A). The cytoplasm loses water first, followed by the vacuole. The cell shrinks as a result, and the cell is said to be plasmolyzed.
b) A plant cell that is kept in a solution with a greater water potential absorbs water by endosmosis and becomes turgid or swelled (as observed in figure C). The inflated protoplast creates a wall pressure that equals the system’s water potential, causing endosmosis to cease.