a) the associated magnetic field is given as
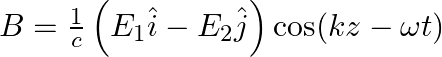
d) the given electromagnetic waves is plane polarised
An electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z-direction: 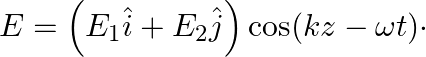 Choose the correct options from the following:
Choose the correct options from the following:
a) the associated magnetic field is given as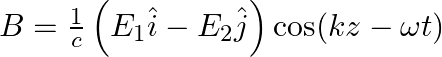
b) the associated magnetic field is given as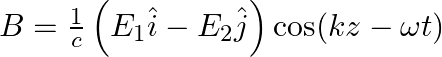
c) the given electromagnetic field is circularly polarised
d) the given electromagnetic waves is plane polarised
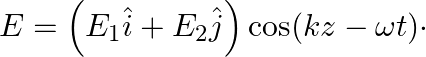 Choose the correct options from the following:
Choose the correct options from the following:a) the associated magnetic field is given as
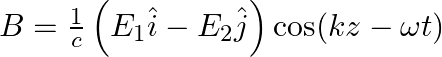
b) the associated magnetic field is given as
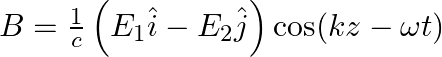
c) the given electromagnetic field is circularly polarised
d) the given electromagnetic waves is plane polarised
An electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z-direction: 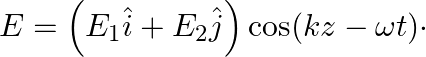 Choose the correct options from the following:
Choose the correct options from the following:
a) the associated magnetic field is given as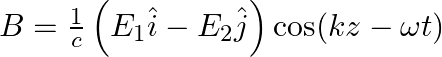
b) the associated magnetic field is given as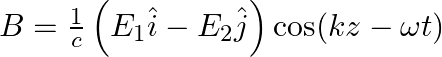
c) the given electromagnetic field is circularly polarised
d) the given electromagnetic waves is plane polarised
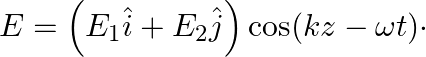 Choose the correct options from the following:
Choose the correct options from the following:a) the associated magnetic field is given as
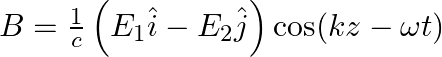
b) the associated magnetic field is given as
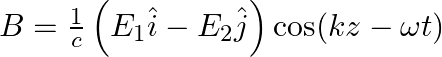
c) the given electromagnetic field is circularly polarised
d) the given electromagnetic waves is plane polarised
