Answer (4)
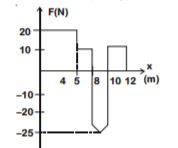
Sol.
Using work-energy theorem
![]() work
work ![]() area under
area under ![]() graph
graph
From ![]() to
to ![]()
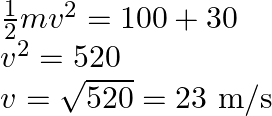
From ![]() to
to ![]()
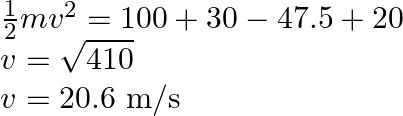
Hence appropriate option is ![]() and
and ![]()

Answer (4)
Sol.
Using work-energy theorem
![]() work
work ![]() area under
area under ![]() graph
graph
From ![]() to
to ![]()
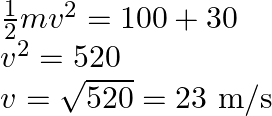
From ![]() to
to ![]()
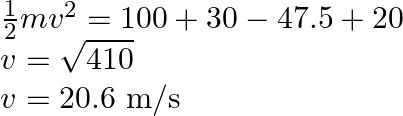
Hence appropriate option is ![]() and
and ![]()