The structure of the Brain:
The mind is a leading physical information processing center that acts as a control and command system.
Protected in the skull.
Covered by three membranes known as cranial meninges.
- Dura mater
- Arachnoid
- Pia mater
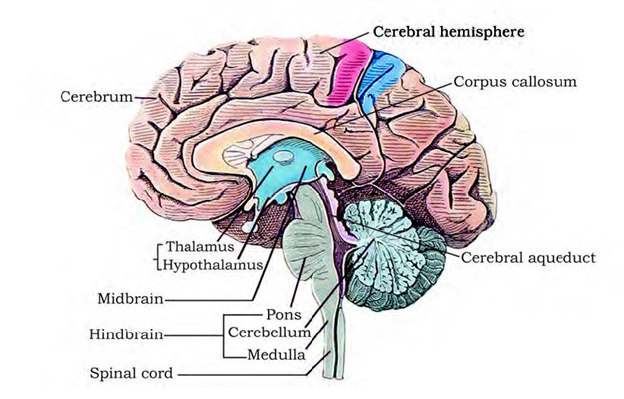
The three main regions of the brain are:
1. Forebrain:
It has three main components – the cerebrum, hypothalamus, and thalamus.
(A) The cerebrum forms the most important and major part of the entire brain.
Long divided into sections by deep separation, each part is known as the cerebral hemisphere. Both hemispheres are connected to the corpus callosum, which is the nerve endings. The cerebral hemispheres are not internal and the walls of the cerebrum have an internal medulla and an external cortex.
The cerebral cortex contains the body cells of neurons that give the appearance of gray matter; that is why it is called gray. The gray matter has many cracks and folds. The higher the number of convolutions, the greater the intelligence.
The cerebral cortex has sensory areas, motor areas and meeting places. These specific areas are responsible for complex functions namely communication, memory and internal organizations.
The cerebral medulla is made up of axons of nerve fibers, giving a white appearance, hence the name white. When a group of deep structures are connected within the cerebral hemispheres, which is the amygdala and hippocampus leading to the formation of a complex structure known as the limbic system or limbic lobe.
Role – Cerebrum is a center of memory, intelligence, knowledge, volunteerism and will.
(B) Thalamus: It is made of gray matter and is found higher than midbrain.
Role – transmits motor and nerve impulses to the brain and regulates the development of emotions, sensitivity to heat, pain and cold.
(C) Hypothalamus – Located at the base of the thalamus, it contains optic chiasma. It is the point at which the optic nerve fibers fall to the opposite sides. Behind this structure is the infundibulum, which is the gray color of the hypothalamus. It contains the pituitary gland.
Role – The hypothalamus has centers that regulate body temperature, hemeostasis, blood pressure, the center that controls appetite. The neurosecretory cells of the hypothalamus produce secreted substances or many hormones that are important in regulating the activity of pituitary hormones. Along with the limbic system, the hypothalamus also plays a role in regulating sexual function.
2. Mid Brain:
It contains cerebral peduncles and the corpora quadrigemina,
(A) Cerebral peduncles:
They are thick strands of fibers that connect the cerebrum with the cerebellum.
Role – Transfer sensory motor sensations between the rear brain and the frontal brain
(B) Corpora quadrigemina
Part of the spinal cord consists of two hard lobes called corpora quadrigemina where one group is referred to as the upper colliculi and the other end is referred to as the lower colliculi
Role – Corpora quadrigemina controls visual thinking and movement of the eye and head. They also control auditory thinking and head movement to identify and locate the sound source.
3. Hindbrain:
It contains the cerebellum, pons varolii and medulla oblongata
(A) Cerebellum:
Launched behind the upper part of the brain stem. The inner cerebellar cortex contains gray matter and the inner cerebellar medulla has a white matter. The cerebellum is connected to the medulla oblongata and the cerebrum by means of white matter fiber strips.
Role – Links body balance to muscle function. The intensity of muscle activity begins in the cerebrum. It controls the voluntary movement from the cerebrum.
(B) Pons varolii:
It is made up of a large number of white nerve fibres found above the medulla oblongata.
Role – Aligns between both lobes of the cerebellum. It has a respiratory control center called a pneumotaxic center.
(C) Medulla oblongata:
It has a round shape and is located at the base of the skull. It runs behind the brain like a spine. Any damage to this brain site can be fatal.
Role – Acts as the role of driving nerve impulses from the spinal cord to the brain. It controls all the functions of the internal organs, breathing and heartbeat.
