Solution: The answer is (b) refraction of light by different layers of varying refractive indices Explanation: The refraction of light maintains the change in the position of the source of light....
Twinkling of stars is due to atmospheric
An element X of group 15 exists as a diatomic molecule and combines with hydrogen at 773 K in presence of the catalyst to form a compound, ammonia which has a characteristic pungent smell.
(a) Identify the element X. How many valence electrons does it have?
(b) Draw the electron dot structure of the diatomic molecule of X. What type of bond is formed in it?
Solution: Nitrogen is the correct answer, as it possesses five electrons in its outermost shell.
An element X of group 15 exists as a diatomic molecule and combines with hydrogen at 773 K in presence of the catalyst to form a compound, ammonia which has a characteristic pungent smell.
(c) Draw the electron dot structure for ammonia and what type of bond is formed in it?
Solution: Covalent bonding is formed by ammonia.
An element X which is a yellow solid at room temperature shows catenation and allotropy. X forms two oxides which are also formed during the thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate crystals and are the major air pollutants.
(e) Locate the position of the element in the Modern Periodic Table
Solution: The position of sulfur is Group 16 Period 3.
An element X which is a yellow solid at room temperature shows catenation and allotropy. X forms two oxides which are also formed during the thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate crystals and are the major air pollutants.
(c) Write the balanced chemical equation for the thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate crystals?
(d) What would be the nature (acidic/ basic) of oxides formed?
Solution: 2FeSO4 Fe2O3+SO2+SO3Sulphur oxides are acidic in nature
An element X which is a yellow solid at room temperature shows catenation and allotropy. X forms two oxides which are also formed during the thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate crystals and are the major air pollutants.
(a) Identify the element X
(b) Write the electronic configuration of X.
Solution: Element X is Sulphur2,8,6
Electropositive nature of the element(s) increases down the group and decreases across the period
(b) Electronegativity of the element decreases down the group and increases across the period
(c) Atomic size increases down the group and decreases across a period (left to right)
(d) Metallic character increases down the group and decreases across a period.
Based on the above trends of the Periodic Table, answer the following about the elements with atomic numbers 3 to 9.
(c) Name the element with the smallest atomic size
(d) Name the element which is a metalloid
Solution: (a)The electropositive character of the element(s) increases as it progresses through the group and diminishes as it progresses through time. (b) The element's electronegativity drops as...
Electropositive nature of the element(s) increases down the group and decreases across the period
(b) Electronegativity of the element decreases down the group and increases across the period
(c) Atomic size increases down the group and decreases across a period (left to right)
(d) Metallic character increases down the group and decreases across a period.
Based on the above trends of the Periodic Table, answer the following about the elements with atomic numbers 3 to 9.
(e) Name the element which shows maximum valency.
Solution: (a)The electropositive character of the element(s) increases as it progresses through the group and diminishes as it progresses through time. (b) The element's electronegativity drops as...
Electropositive nature of the element(s) increases down the group and decreases across the period
(b) Electronegativity of the element decreases down the group and increases across the period
(c) Atomic size increases down the group and decreases across a period (left to right)
(d) Metallic character increases down the group and decreases across a period.
Based on the above trends of the Periodic Table, answer the following about the elements with atomic numbers 3 to 9.
(a) Name the most electropositive element among them
(b) Name the most electronegative element
Solution: (a)The electropositive character of the element(s) increases as it progresses through the group and diminishes as it progresses through time. (b) The element's electronegativity drops as...
Mendeleev ′ predicted the existence of certain elements not known at that time and named two of them as Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminium.
(c) Classify these elements as metals, non-metals, or metalloids
(d) How many valence electrons are present in each one of them?
Solution: c) Gallium-Group 13 Period 4 is a periodic table of elements. The elements germanium and gallium are both metalloids; however, gallium is a metal. d) Germanium contains four electrons, but...
Mendeleev ′ predicted the existence of certain elements not known at that time and named two of them as Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminium.
(a) Name the elements which have taken the place of these elements
(b) Mention the group and the period of these elements in the Modern Periodic Table.
Solution: a) Eka-Silicon was replaced by germanium, while Eka-Aluminum was replaced by gallium. b) Gallium was replaced by germanium. b) Germanium-Group 14 Period 4 (Germanium-Group 14).
(a) In this ladder (Figure 5.2) symbols of elements are jumbled up. Rearrange these symbols of elements in the increasing order of their atomic number in the Periodic Table.
(b) Arrange them in the order of their group also.
Solution: a) H, He, Li, Be, B, C, N, O, F, Ne, Mg, Al Si, P, S, Cl, Ar, K, Ca b) Group 1:H, Li, Na, K Group 2: Be, Mg, Ca Group 13: B. Al Group 14: C, Si Group 15: N. P Group 16: 0, S Group 17: F. U...
Complete the following crossword puzzle in figure:
Across:
(1) An element with atomic number 12.
(3) Metal used in making cans and member of Group 14.
(4) A lustrous non-metal which has 7 electrons in its outermost shell.
Down:
(2) Highly reactive and soft metal which imparts yellow colour when subjected to flame and is kept in kerosene.
(5) The first element of the second Period
(6) An element which is used in making fluorescent bulbs and is the second member of Group 18 in the Modern Periodic Table
(7) A radioactive element which is the last member of the halogen family.
(8) Metal which is an important constituent of steel and forms rust when exposed to moist air.
(9) The first metalloid in Modern Periodic Table whose fibres are used in making bullet-proof vests
Solution: Across 1) Magnesium 3) Tin 4) Iodine Down 2) Sodium 5) Lithium 6) Neon 7) Astatine 8) Iron 9) Boron
Atomic number of a few elements are given below 10, 20, 7, 14
(c) Identify the Periods of these elements in the Periodic Table
(d) What would be the electronic configuration for each of these elements?
Solution: (c)Nitrogen and Neon belong to period 2. Calcium and silicon belongs to Period 3. (d)Electronic Configurations Neon-2,8 Calcium-2,8,8,2 Nitrogen-2,5 Silicon-2,8,4
Atomic number of a few elements are given below 10, 20, 7, 14
(e) Determine the valency of these elements
Solution: During the formation of chemical compounds or molecules, an element's valence or valency is measured in terms of its ability to combine with other atoms, which is known as its combining...
Atomic number of a few elements are given below 10, 20, 7, 14
(a) Identify the elements
Solution: (a)Elements are Neon (10) Calcium (20) Nitrogen (7) Silicon (14) (b)Neon belongs to group 18, Calcium belongs to group 2, Nitrogen belongs to group 7 and Silicon belongs to group 14.
An element X (atomic number 17) reacts with an element Y (atomic number 20) to form a divalent halide.
(a) Where in the periodic table are elements X and Y placed?
(b) Classify X and Y as metal (s), non-metal (s) or metalloid (s)
Solution: The answer of the following is: (a)X is in Group 17, period 3 and Y is in group 2 Period 4. (b)X is Non-metal and Y is metal
An element X (atomic number 17) reacts with an element Y (atomic number 20) to form a divalent halide.
(c) What will be the nature of oxide of element Y? Identify the nature of bonding in the compound formed
(d) Draw the electron dot structure of the divalent halide.
Solution: c) Y Oxide will be a fundamental element in nature. Ionic bonding results in the formation of a compound. d) The electron dot structure:
An element is placed in 2nd Group and 3rd Period of the Periodic Table, burns in presence of oxygen to form a basic oxide.
(c) Write the balanced equation when it burns in the presence of air
(d) Write a balanced equation when this oxide is dissolved in water.
Solution: The answer: (c) 2Mg+O2 $\to$ 2MgO (d) MgO+ H2O $\to$ Mg(OH)2
An element is placed in 2nd Group and 3rd Period of the Periodic Table, burns in presence of oxygen to form a basic oxide.
(e) Draw the electron dot structure for the formation of this oxide
Solution: Lewis structures, also known as Lewis dot formulas, Lewis dot structures, electron dot structures, or Lewis electron dot structures, are diagrams that depict the bonding between atoms in a...
An element is placed in 2nd Group and 3rd Period of the Periodic Table, burns in presence of oxygen to form a basic oxide.
(a) Identify the element
(b) Write the electronic configuration.
Solution: The answer is: (a) Element is Magnesium (b) Electronic Configuration-2,8,2
Properties of the elements are given below. Where would you locate the following elements in the periodic table?
An element whose thin oxide layer is used to make other elements corrosion-resistant by the process of “anodising”
Solution: The answer is Aluminium Group 13 Period 3
Properties of the elements are given below. Where would you locate the following elements in the periodic table?
(1) An element which is tetravalent and forms the basis of organic chemistry
(2) An element which is an inert gas with atomic number 2
Solution: The answer of the following: Carbon Group 14 Period 2Helium Group 18 Period 1
Properties of the elements are given below. Where would you locate the following elements in the periodic table?
(a) A soft metal stored under kerosene
(b) An element with variable (more than one) valency stored underwater.
Solution: The answer for the following are: Sodium Group 1 Period 3Phosphorus Group 15 Period 3
Give an account of the process adopted by Mendeleev ′ for the classification of elements. How did he arrive at “Periodic Law”?
Solution: Only 63 elements were known at the time of Mendeleev's discovery. Mendeleev looked into the relationship between chemical characteristics and the atomic manes of elements in the periodic...
Which group of elements could be placed in Mendeleev’s ′ Periodic Table without disturbing the original order? Give reason.
Solution: Inert gases could be included in Mendeleev's Periodic Table without causing any disruptions to the original order of elements. Noble gases, such as Helium, were known prior to Mendeleev's...
Identify the elements with the following property and arrange them in increasing order of their reactivity
(a) An element which is a soft and reactive metal
(b) The metal which is an important constituent of limestone
(c) The metal which exists in a liquid state at room temperature
Solution: (a) Sodium (b) Calcium (c) Mercury and order of reactivity : Hg < Ca < Na
Arrange the following elements in the increasing order of their metallic character Mg, Ca, K, Ge, Ga.
Solution: The arrangement in order required is Ge < Ga < Mg < Ca < K
Write the formula of the product formed when the element A (atomic number 19) combines with the element B (atomic number 17). Draw its electronic dot structure. What is the nature of the bond formed?
Solution: The letter K represents element A. (Potassium). It would be possible to have the electrical configuration of element A (atomic number 19) as 2, 8, 8, 1. Because it has only one valence...
Identify and name the metals out of the following elements whose electronic configurations are given below.
(a) 2, 8, 2
(b) 2, 8, 1
(c) 2, 8, 7
(d) 2, 1
Solution: The names of the following are: MagnesiumSodiumChlorineLithium Metals from the following are- Magnesium, Sodium, Lithium.
Arrange the following elements in increasing order of their atomic radii.
(a) Li, Be, F, N
(b) Cl, At, Br I
Solution: The elements in question are all members of the same group and are sorted from left to right. As a result, their atomic radii are increasing in order of magnitude. a)Li>Be>F>N b)...
Compare the radii of two species X and Y. Give reasons for your answer.
(a) X has 12 protons and 12 electrons
(b) Y has 12 protons and 10 electrons
Solution: From electron arrangement X -2, 8, 2 Y -2, 8 Because Y has fewer energy levels than X, the atomic radius of Y will be less than that of the latter.
Three elements A, B and C have 3, 4 and 2 electrons respectively in their outermost shell. Give the group number to which they belong in the Modern Periodic Table. Also, give their valencies.
Solution: A belongs to Group 13, B belongs to Group 14, and C belongs to Group 2. A belongs to Group 13 and B belongs to Group 14. The values of A, B, and C are 3, 4, and 2, respectively.
Write the formulae of chlorides of Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminium, the elements predicted by Mendeleev.
Solution: Eka-silicon is a kind of germanium (Ge). It belongs to group 4 of Mendeleev's periodic table, and as a result, it has a valency of four. GeCl4 is the chemical formula for its chloride....
In Mendeleev’s Periodic Table the elements were arranged in the increasing order of their atomic masses. However, cobalt with an atomic mass of 58.93 amu was placed before nickel having an atomic mass of 58.71 amu. Give a reason for the same.
Solution: It is possible to find instances in Mendeleev ′s Periodic Table in which elements with higher atomic masses are put before ones with lower atomic masses, and vice versa. As a result, items...
“Hydrogen occupies a unique position in Modern Periodic Table”. Justify the statement.
Solution: Because of the following factors, hydrogen holds a unique place in the Modern Periodic Table. The outer electronic configuration of hydrogen and alkali metals is comparable because both...
Can the following groups of elements be classified as Dobereiner’s triad?
(a) Na, Si, Cl
(b) Be, Mg, Ca
The atomic mass of Be 9; Na 23; Mg 24; Si 28; Cl 35; Ca 40 Explain by giving a reason.
Solution: Despite the fact that the atomic mass of Silicon is equal to the average of the atomic masses of Sodium and Chlorine, the elements do not have the same physical properties and hence cannot...
Elements have been arranged in the following sequence on the basis of their increasing atomic masses. F, Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl, Ar, K (a) Pick two sets of elements which have similar properties. (b) The given sequence represents which law of classification of elements?
Solution: a) Metals include sodium, magnesium, aluminum, and potassium. Halogens include the elements F and Cl. There are two sets of elements in total.b) Mendeleev's law of periodicity is...
The three elements A, B and C with similar properties have atomic masses X, Y and Z respectively. The mass of Y is approximately equal to the average mass of X and Z. What is such an arrangement of elements called as? Give one example of such a set of elements.
Solution: Triads are a type of arrangement of elements that is commonly found in nature. For example, the elements lithium, sodium, and potassium form a trio. These elements have atomic masses of...
On moving from left to right in a period in the periodic table, the size of the atom.
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) does not change appreciably
(d) first decreases and then increases
Solution: The answer is (b) decreases Explanation: When we move from left to right in a period, the radius of the atom shrinks, and as a result, the size of the atom reduces as well.
Which one of the following does not increase while moving down the group of the periodic table?
(a) Atomic radius
(b) Metallic character
(c) Valence
(d) Number of shells in an element
Solution: The answer is (c) Valence Explanation: In the periodic table, advancing down a group does not result in an increase in the number of valence electrons present.
Which one of the following depicts the correct representation of the atomic radius(r) of an atom?
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Solution: The answer is (b) (ii) and (iii) Explanation: Atomic radius, which is defined as the distance between the nucleus and the outermost orbital, is clearly displayed in photos ii) and iii),...
The element with atomic number 14 is hard and forms acidic oxide and a covalent halide. To which of the following categories does the element belong?
(a) Metal
(b) Metalloid
(c) Non-metal
(d) Left-hand side element
Solution: The answer is (b) Metalloid Explanation: Silicon has an electrical configuration of 2, 8, and 4 atoms. Considering that the outermost shell has just four electrons, it requires an...
Which of the following elements will form an acidic oxide?
(a) An element with atomic number 7
(b) An element with atomic number 3
(c) An element with atomic number 12
(d) An element with atomic number 19
Solution: The answer is (a) An element with atomic number 7 Explanation: The element with atomic number 7 has electron configuration 2,5, which means it has the ability to gain three electrons and...
Three elements B, Si and Ge are
(a) metals
(b) non-metals
(c) metalloids
(d) metal, non-metal, and metalloid respectively
Solution: The answer is (c) metalloids Explanation: Metalloids include the elements boron (B), silicon (Si), and germanium (Ge). Arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te), polonium (Po), and...
What type of oxide would Eka– aluminium form?
(a) 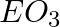
(b) 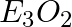
(c) 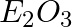
(d) EO
Solution: Answer is (c) E2O3 Explanation: Aluminum is Al with an oxidation state of +3, it may be converted into Al3+, and it has a valency of +3. $Al_2O_3$ will be formed as a result.Gallium and...
Arrange the following elements in the order of their increasing non-metallic character Li, O, C, Be, F
(a) F < O < C < Be < Li
(b) Li < Be < C < O< F
(c) F < O < C < Be < Li
(d) F < O < Be < C < Li
Solution: The answer is b) Explanation: Li is located on the left side of the current periodic table in the second period, followed by berrylium. Fluorine is located directly across from Neon. As a...
Arrange the following elements in the order of their decreasing metallic character Na, Si, Cl, Mg, Al
(a) Cl > Si >Al > Mg >Na
(b) Na >Mg >Al >Si > Cl
(c) Na > Al > Mg > Cl > Si
(d) Al > Na> Si > Ca> Mg
Solution: The answer is (b) Na >Mg >Al >Si > Cl Explanation: Na has one electron in its valence shell, magnesium has two, aluminium has three, and chlorine has seven electrons in its valence shell....
Which of the following are the characteristics of isotopes of an element?
(i) Isotopes of an element have the same atomic masses
(ii) Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number
(iii) Isotopes of an element show the same physical properties
(iv) Isotopes of an element show the same chemical properties
(a) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Solution: Option d) is the answer. Explanation: Isotopes are elements that have the same atomic number but have different atomic masses, and they are classified as such. Isotopes have the same...
Which of the following elements does not lose an electron easily?
(a) Na
(b) F
(c) Mg
(d) Al
Solution: Option b) is the answer Explanation: Sodium has one electron, magnesium has two, and aluminum has three electrons in its outermost shell, whereas fluorine has seven electrons in its...
Which of the following elements would lose an electron easily?
(a) Mg
(b) Na
(c) K
(d) Ca
Solution: The answer is (c) K Explanation: Magnesium and calcium are both members of the group I, while sodium and potassium are members of a different group (II). Given that K has only one electron...
Which among the following elements has the largest atomic radii?
(a) Na
(b) Mg
(c) K
(d) Ca
Solution: The answer is (c) K Explanation: Because atomic radii decrease from left to right during a period of time, K has the biggest atomic radii of all the elements. This is due to an increase in...
Which of the following gives the correct increasing order of the atomic radii of O, F and N?
a) O, F, N
(b) N, F, O
(c) O, N, F
(d) F, O, N
Solution: The answer is (d) F, O, N Explanation: As you move from left to right over a period, the radius of an atom grows. The atomic numbers (N7), O(8), and F(10) are listed in increasing sequence...
Which one of the following elements exhibit a maximum number of valence electrons?
(a) Na
(b) Al
(c) Si
(d) P
Solution:The answer is (d) P Explanation: The electronic configurations of Na, Al, Si, and P are 2,8,1, 2,8,3,2,8,4, and 2,8,5 for the elements in the periodic table. The number of valence electrons...
Which of the following is the outermost shell for elements of period 2?
(a) K shell
(b) L shell
(c) M shell
(d) N shell
Solution: The answer is (b) L shell Explanation: There are two shells in period 18, designated as K and L.
An element which is an essential constituent of all organic compounds belongs to
(a) group 1
(b) group 14
(c) group 15
(d) group 16
Solution: The answer is b) group 14 Explanation: Carbon is an essential ingredient of all organic molecules that are members of the 14th chemical group.
Where would you locate the element with electronic configuration 2,8 in the Modern Periodic Table?
(a) Group 8
(b) Group 2
(c) Group 18
(d) Group 10
Solution: The answer is (c) Group 18 Explanation: Because group 18 has all of its outermost shells entirely filled, any element having an electrical configuration falls into this category.
The elements A, B, C, D and E have atomic number 9, 11, 17, 12 and 13 respectively. Which pair of elements belong to the same group?
(a) A and B
(b) B and D
(c) A and C
(d) D and E
Solution: The answer is (c) A and C Explanation: Here A is Fluorine(Group 17), B is Sodium (Group 1), C is Chlorine (Group 17), D is Magnesium(Group 2) and E is Aluminium (Group 13). A and C are...
Which of the given elements A, B, C, D and E with atomic number 2, 3, 7, 10 and 30 respectively belong to the same period?
(a) A, B, C
(b) B, C, D
(c) A, D, E
(d) B, D, E
Solution: The answer is (b) B, C, D Explanation: The first period is dominated by the element with the highest atomic number, whereas the second period is dominated by elements B, C, and D.
Which of the following statement (s) about the Modern Periodic Table are incorrect
(i) The elements in the Modern Periodic Table are arranged based on their decreasing atomic number
(ii) The elements in the Modern Periodic Table are arranged based on their increasing atomic masses
(iii) Isotopes are placed in adjoining group (s) in the Periodic Table
(iv) The elements in the Modern Periodic Table are arranged based on their increasing atomic number
(a) (i) only
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iv) only
Solution: Answer: (b) (i), (ii) and (iii) Explanation:...
In Mendeleev’s Periodic Table, gaps were left for the elements to be discovered later. Which of the following elements found a place in the periodic table later
(a) Germanium
(b) Chlorine
(c) Oxygen
(d) Silicon
Solution: Answer: a) Germanium Explanation: Initially, Mendeleev designated unidentified elements as EKA- Boron, EKA- Aluminum, and EKA Silicon, which were later renamed Scandium, Gallium, and...
