Solution: Benzene is a planar atom with electrons delocalized under or more the ring plane. Henceforth, it is a material wealthy in electrons. As an outcome, electron-inadequate species, i.e.,...
Organize benzene, n-hexane and ethyne in expanding request of their acidic conduct. Likewise, give a justification behind this conduct.
Solution: Acidic person of an animal groups is characterized based on the simplicity with which it can lose its H–iotas. The hybridization condition of carbon in the given compound is: As the s –...
Expansion of HBr to propene yields 2-bromopropane, while within the sight of benzoyl peroxide, a similar response yields 1-bromopropane. Clarify and give system.
Solution: The expansion of HBr to propene is an illustration of an electrophilic replacement response. Being a corrosive, the hydrogen bromide gives an electrophile, H+. This electrophile assaults...
What impact does fanning of an alkane chain has on its limit?
Solution: Alkanes experience Van-der Waals powers between atoms. The higher the alkane's force, the more prominent is the limit. As the atom stretching expands, the surface region diminishes which...
In the alkane H3C–CH2 – C(CH3)2 – CH2 – CH(CH3)2, distinguish 1°, 2°, 3° carbon particles and give the quantity of H iotas clung to every last one of these.
Solution: Essential carbon particles (1o): Carbon iotas clung to a solitary molecule of carbon are called essential iotas of carbon. The game plan given has comparing five 1o carbon iotas and...
How might you convert benzene into acetophenone
Solution: Benzene changed over to acetophenone
How might you convert benzene into p – nitrotoluene
Solution: Benzene changed over to p – nitrotoluene
How might you convert benzene into m-nitrochlorobenzene
Solution: Benzene changed over to m-nitrochlorobenzene
How might you convert benzene into p – nitrobromobenzene
Solution: Benzene changed over to p – nitrobromobenzene
Clarify why the accompanying framework isn’t fragrant?
Solution: Cyclo-octatetraene isn't planar yet is tub-molded. It is, in this manner, a non-planar framework having 8 n-electrons. In this manner, the atom isn't sweet-smelling as it doesn't contain a...
Clarify why the accompanying framework isn’t fragrant?
Solution: Because of the presence of sp3–hybridized carbon, the framework isn't planar. Further, it contains just four n-electrons, subsequently, the framework isn't fragrant on the grounds that it...
Clarify why the accompanying framework isn’t fragrant?
Solution: Because of the presence of a sp3-hybridized carbon, the framework isn't planar. It contains six n-electrons yet the framework isn't completely formed since all the six n-electrons don't...
What are the important conditions for any framework to be sweet-smelling?
Solution: The fundamental conditions for any fragrant framework are as per the following: (I) Firstly, the compound course of action or construction ought to be planar. (ii) The n-electrons are...
For what reason is benzene exceptionally steady however it contains three twofold bonds?
Solution: Benzene is a mixture of the resounding designs and it is displayed as: Every one of the six carbon molecules in benzene are hybridized to sp2.In benzene, every carbon particle's two...
Draw the cis and trans constructions of hex-2-ene. Which isomer will have higher b.p. what’s more, why?
Solution: Hex-2-ene is addressed as displayed beneath: Mathematical isomers of hex-2-ene are as per the following: A cis intensifies dipole second is equivalent to the amount of the C – CH3...
Compose synthetic conditions for the burning response of Toluene
Solution: Burning responses might be characterized as an oxygen or oxygen response of a compound.
Compose synthetic conditions for the burning response of Hexyne
Solution: Burning responses might be characterized as an oxygen or oxygen response of a compound.
Compose synthetic conditions for the burning response of Pentene
Solution: Burning responses might be characterized as an oxygen or oxygen response of a compound.
Compose synthetic conditions for the burning response of Butane
Solution: Burning responses might be characterized as an oxygen or oxygen response of a compound.
Propanal and pentan-3-one are the ozonolysis results of an alkene? What is the primary equation of the alkene?
Solution: From the given data, the two ozonolysis results of an alkene are pentan-3-one and propanal. Assume the alkene given is A. The converse of the ozonolysis response is the thing that we get,...
An alkene ‘A’ contains three C – C, eight C – H σ bonds and one C – C π bond. ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives two moles of an aldehyde of molar mass 44 u. Compose IUPAC name of ‘A’.
Solution: From the data given it gives two moles of an aldehyde of molar mass 44 u when ' A ' goes through ozonolysis. The arrangement of an aldehyde's two moles recommends that the presence of...
An alkene ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives a combination of ethanal and pentan-3-one. Compose construction and IUPAC name of ‘A’.
Throughout ozonolysis, an ozonide is created as a halfway that has a cyclic construction; it goes through cleavage to give the eventual outcomes. Ethanal and pentan-3-one are acquired from the...
Compose IUPAC names of the items acquired by the ozonolysis 1 – Phenylbut-1-ene
Solution: Ozonolysis of 1 – Phenylbut-1-ene is displayed as The resulting IUPAC names of the items are : Item (I) benzaldehyde, and Item (II) propanal
Compose IUPAC names of the items acquired by the ozonolysis 2-Ethylbut-1-ene
Solution: Ozonolysis of 2-Ethylbut-1-ene is displayed as: The resulting IUPAC names of the items are: Item (I) pentan-3-one, and Item (II) methanal
Compose IUPAC names of the items acquired by the ozonolysis 3, 4 – Dimethyl-hept-3-ene
Solution: Ozonolysis of 3, 4-Dimethylhept-3-ene is displayed as: The item names resulting to IUPAC are: Item (I) butan-2-one, and Item (II) Pentan-2-one
Compose IUPAC names of the items acquired by the ozonolysis Pent-2-ene
Solution: Ozonolysis of Pent-2-ene is displayed as: The accompanying Product IUPAC names are: Item (I) ethanal, and Item (II) propanal.
compose primary equations and IUPAC names for all potential isomers having the quantity of the twofold or triple bond as demonstrated C5H8 (one triple bond)
Solution: The resulting primary isomers are likely for C5H8 with one triple bond: The IUPAC name of Compound (I) is Pent-1-yne, Compound (II) is Pent-2-yne, and Compound (III) is...
Write the IUPAC names of
Solution: 4-Ethyldeca-1, 5, 8-triene is the necessary IUPAC name
Write the IUPAC names of
Solution: 5-(2-Methylpropyl)- decane is the necessary IUPAC name
Write the IUPAC name of
Solution: 2-Methyl phenol is the necessary IUPAC name
Write the IUPAC name of
Solution: 4-Phenyl but-1-ene is the necessary IUPAC name
Write the IUPAC name of
Solution: 1, 3-Butadiene or Buta-1,3-diene is the necessary IUPAC name
Write the IUPAC names of
Solution: Pen-1-ene-3-yne is the necessary IUPAC name
Write the IUPAC nameof ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{C}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{3}}}~\mathbf{CH}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{C}\text{ }{{(\mathbf{C}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{3}}})}_{\mathbf{2}}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c63b9b35d0c7e5500238909182cb534b_l3.png)
Solution: 2-Methylbut-2-ene is the necessary IUPAC name
How would you represent the arrangement of ethane during chlorination of methane?
Solution: The methane chlorination measure works through a free extreme chain instrument. Stage 1: Initiation: The outcome starts with the hemolytic cleavage of Cl – Cl bond as: Stage 2:...
Is there any change in the hybridisation of B and N atoms as a result of the following reaction? 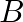 and
and 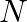
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[BF _{3}+ NH _{3} \rightarrow F _{3} B \cdot NH _{3}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f87a2a8a2c94b67d7949b58594c840a9_l3.png)
Ans.)
Answer: F3B.NH3 is a reaction product formed by the reaction of BF3 + NH3. As a result of changing the hybridization of the B-atom to sp3, the product NH3 is produced. The hybridization of N-atoms,...
Describe the change in hybridisation (if any) of the Al atom in the following reaction. ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[AlCl _{3}+C l^{-} \rightarrow A l C l_{4}^{-}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6a3539afdf8fa241be293a500542ae7d_l3.png)
Answer: The hybridization of Al atom alters from $sp ^{2}$ in $AlCl _{3}$ to $sp ^{3}$ in $AlCl _{4}^{-}$. In $AlCl _{3}$, Al contains 3 bond pairs of electrons and zero lone pair of electrons....
What is meant by hybridisation of atomic orbitals? Describe the shapes of 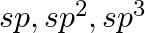 hybrid orbitals.
hybrid orbitals.
Answer: Intermixing orbitals of various energies to redistribute their energy and create new orbitals with equal energies and forms. The new orbitals are hybridized. In this way, two s orbitals...
Which out of 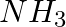 and
and 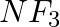 has higher dipole moment and why?
has higher dipole moment and why?
Answer: When comparing dipole moments, ammonia (1.47D) has a higher dipole moment than $NF_3$. (0.24D). Both molecules have a pyramidal molecular geometry, which is characteristic of this type of...
Displacement versus time curve for a particle executing SHM is shown. Identify the points marked at which
i) velocity of the oscillator is zero ii) speed of the oscillator is maximum Answer: (i) The oscillator's velocity is zero when the points A, C, E, and G are at their extreme positions. (ii) The...
Explain why BeH2 molecule has a zero dipole moment although the Be–H bonds are polar.
Answer: The dipole moment of a molecule with symmetrical and linear geometries is zero because they are vector in nature and the dipole of different bonds cancel with one another, whereas the dipole...
Apart from tetrahedral geometry, another possible geometry for CH4 is square planar with the four H atoms at the corners of the square and the C atom at its centre. Explain why CH4 is not square planar.
Answer: The square planar geometry has a bond angle of 90 degrees with the equilateral triangle geometry. In comparison to the tetrahedral bond angle, which is 109.5 0, this is less favourable. This...
Arrange the bonds in order of increasing ionic character in the molecules: LiF, 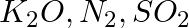 , and
, and 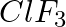 .
.
Answer: The differential in electronegativity between the atoms that make up a molecule determines the ionic character of that molecule. As a result, the greater the difference between two...
Explain with the help of suitable example polar covalent bond.
Answer: When two separate atoms join to form a covalent connection, their electrons are not shared equally. A more electronegative atom's nucleus attracts the bond pair. In this case, an...
Define electronegativity. How does it differ from electron gain enthalpy?
Answer: Sr. No Electronegativity Electron affinity 1 The electronegativity of an atom in a chemical compound refers to its proclivity to attract the shared pairs of electrons that are present in the...
Write the significance/applications of dipole moment.
Answer: The difference in electro-negativities of atom components causes polarisation in heteronuclear molecules. So one end gets a positive charge and the other gets a negative charge. Molecules...
 can be represented by structures 1 and 2 shown below. Can these two structures be taken as the canonical forms of the resonance hybrid representing
can be represented by structures 1 and 2 shown below. Can these two structures be taken as the canonical forms of the resonance hybrid representing  ? If not, give reasons for the same.
? If not, give reasons for the same.
Answer: The positions of the atoms remain constant in the canonical forms, while the positions of the electrons change. The positions of atoms shift in the specified canonical forms. As a result,...
Explain the important aspects of resonance with reference to the 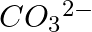 ion.
ion.
Answer: Although the properties of the carbonate ion cannot be described by a single structure, they can be described by two or more resonance structures. The carbonate ion's true structure is a...
Define Bond length.
Answer: “The equilibrium distance between the nuclei of two bound atoms in a molecule is defined as bond length.”
How do you express the bond strength in terms of bond order?
Answer: During the formation of a molecule, the extent of bonding that happens between two atoms is represented by the bond strength of the molecule. As the bond strength develops, the bond becomes...
Although geometries of NH3 and H2O molecules are distorted tetrahedral, bond angle in water is less than that of Ammonia. Discuss.
Answer: Ammonia's central atom (N) has 1 lone pair and 3 bond pairs. Water's central atom (O) has two lone pairs and two bond pairs. The two lone pairs on the O- atom of water reject the two bond...
Write the favourable factors for the formation of an ionic bond.
Answer: An ionic link is formed by moving electrons from one atom to another. This means that ionic bond formation is dependent on neutral atom flexibility. The lattice energy of the molecule...
Define the octet rule. Write its significance and limitations
Answer: "Atoms can combine either by transferring or sharing valence electrons to achieve the closest inert gas configuration," says the Octet Rule. Octet rule describes how chemical bonds occur...
Think about the components: Cs, Ne, I and F Identify the component that displays neither negative nor positive oxidation state?
Solution: Ne displays neither negative nor positive oxidation no. That is 0.
Think about the components: Cs, Ne, I and F Identify the component that displays both negative and positive oxidation states.
Solution: I displays both negative and positive oxidation no. That is - 1, +1, +3, +5 and +7.
Consider the elements: Cs, Ne, I and F Identify the element that exhibits only positive oxidation.
Solution: Cs displays just certain oxidation no. That is +1.
Think about the components: Cs, Ne, I and F Identify the component that displays just adverse oxidation.
Solution: F exhibits only negative oxidation number. That is -1.
Assign oxidation number to the underlined elements 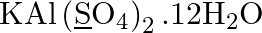
Solution: $\mathrm{KAl}\left(\underline{\mathrm{S}} \mathrm{O}_{4}\right)_{2} .12 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}$ Let expect oxidation number of S is x. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}...
Assign the oxidation number to the underlined component 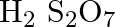
Solution: $\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}$ Let accept oxidation number of S is x. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Oxidation\text{ }number\text{ }of\text{ }O\text{ }=\text{...
Assign the oxidation number to the underlined component NaBH4
Solution: NaBH4 Let accept oxidation number of B is x. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Oxidation\text{ }number\text{ }of\text{ }Na\text{ }=\text{ }+1 \\ ~ \\ Oxidation\text{ }number\text{...
Assign the oxidation number to the underlined component CaO2
Solution: CaO2 Let expect oxidation number of O is x. \[Oxidation\text{ }number\text{ }of\text{ }Ca\text{ }=\text{ }+2\] Then, at that point, we have: \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}...
Assign the oxidation number to the underlined component K2MnO4
Solution: K2MnO4 Let expect oxidation number of Mn is x. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Oxidation\text{ }number\text{ }of\text{ }K\text{ }=\text{ }+1 \\ ~ \\ Oxidation\text{ }number\text{...
Assign the oxidation number to the underlined component H4P2O7
Solution: H4P2O7 Let expect oxidation number of P is x. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Oxidation\text{ }number\text{ }of\text{ }H\text{ }=\text{ }+1 \\ ~ \\ Oxidation\text{ }number\text{...
Assign the oxidation number to the underlined component NaHSO4
Solution: NaHSO4 Let expect oxidation number of S is x. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Oxidation\text{ }number\text{ }of\text{ }Na\text{ }=\text{ }+1 \\ ~ \\ Oxidation\text{ }number\text{...
Assign the oxidation number to the underlined component NaH2PO4
Solution: NaH2PO4 Let expect oxidation number of P is x. We realize that, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Oxidation\text{ }number\text{ }of\text{ }Na\text{ }=\text{ }+1 \\ ~ \\...
Thermodynamically the most steady type of carbon is (a) Diamond (b) Graphite (c) Fullerenes (d) Coal
Solution: (b) Graphite is thermodynamically the most steady type of carbon.
The kind of hybridization of boron in diborane is (a) sp (b)sp2 (c) sp3 (d) dsp2
Solution: (c) Boron in diborane is sp3 hybridized.
What do you comprehend by Catenation?
Solution: Catenation A few components or particles (like carbon) may interface with one another through solid covalent bonds to shape long chains or branches. This trademark is known as catenation....
What do you comprehend by Allotropy
Solution: Allotropy Allotropy is the presence of a component in more than one structure, having distinctive actual properties yet similar synthetic properties. The various types of a component are...
What do you comprehend by Inert pair impact
Solution: Inert pair impact As one actions down the gathering, s-block electrons decline their propensity to take part in substance holding. This impact is known as the dormant pair impact. The...
In a portion of the responses, thallium takes after aluminum, while in others it looks like with the gathering I metals. Backing this assertion by giving some proof.
Solution: Thallium is a piece of the intermittent table gathering 13. For this gathering, the most widely recognized oxidation state is + 3. Heavier individuals from this gathering, nonetheless,...
Clarify why would that be an incredible decline in ionization enthalpy from carbon to silicon?
Solution: Carbon ionizing enthalpy (the principal component in bunch 14) is exceptionally high (1086 kJ/mol). That is normal due to its little size. Nonetheless, there is a sharp decline in enthalpy...
Give reasons: Aluminium wire is utilized to make transmission links.
Solution: Aluminum wire is utilized to make transmission links. Aluminium wires are good conductors of electricity and also it is cheap metal easily available, light in weight and also very ductile....
Give reasons: Aluminum utensils ought not be kept in water for the time being.
Solution: Aluminum utensils ought not be kept in water for the time being. The oxygen in water responds to make a dainty layer of aluminum oxide with aluminum. This layer keeps further response from...
Give reasons: Aluminum compounds are utilized to make airplane body.
Solution: Aluminum compounds are utilized to make airplane body. Aluminum has a high protection from elastic and is light. It might likewise be alloyed to various metals like Si, Mg, Cu, Mn and Zn....
Give reasons: Diamond is utilized as a rough
Solution: Diamond is utilized as a rough Carbon is sp3 hybridized in Diamond. With the assistance of solid covalent bonds, every carbon molecule is bound to four other carbon iotas. These covalent...
Give reasons: Graphite is utilized as the grease.
Solution: Graphite is utilized as the grease. Graphite has a layered construction, and the powers of frail van der Waals tie various layers of graphite together. These layers might slide one over...
Give reasons: A combination of weaken NaOH and aluminum pieces is utilized to open channel.
Solution: A combination of weaken NaOH and aluminum pieces is utilized to open the channel. Sodium hydroxide and aluminum respond to shape aluminate (III) sodium tetra hydroxy and hydrogen gas....
Give reasons: Conc.HNO3 can be moved in an aluminum holder.
Solution: Conc.HNO3 can be shipped in an aluminum holder. As it responds with aluminum to frame a slight defensive oxide layer on the aluminum surface, concentrated HNO3 can be put away and shipped...
How is the exorbitant substance of CO2 answerable for a dangerous atmospheric devation?
Solution: Carbon dioxide is a gas that is vital for our endurance. The expanded CO2 content in the climate, nonetheless, represents a genuine danger. An increment in petroleum product ignition,...
Recommend an explanation with regards to why CO is toxic.
Solution: Given its capacity to frame a complex with hemoglobin, carbon monoxide is profoundly toxic. The previous hinders restricting with oxygen by Hb. Subsequently, an individual passes on...
Give a short portrayal of the standards of the accompanying procedures taking a model. Chromatography
Solution: Chromatography It is generally utilized for the partition and cleansing of natural mixtures. Rule: The guideline on which it works is that singular parts of a blend move at various speeds...
Give a short portrayal of the standards of the accompanying procedures taking a model. Distillation
Solution: Distillation This strategy is utilized to isolate non-unpredictable fluids from unstable pollutants. It is likewise utilized when the parts have an extensive distinction in their edges of...
Give a short portrayal of the standards of the accompanying procedures taking a model. Crystallization
Solution: Crystallization Crystallization is utilized to decontaminate strong natural mixtures. Standard: The guideline on which it works is the distinction in the dissolvability of the compound and...
Classify the following reactions in one of the reaction type studied in this unit. 
Solution: Substitution (nucleophilic) response since modification of particles happens.
Classify the following reactions in one of the reaction type studied in this unit. 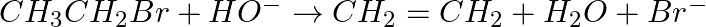
Solution: Elimination (bimolecular) response since response hydrogen and bromine are taken out to shape ethene.
Classify the following reactions in one of the reaction type studied in this unit.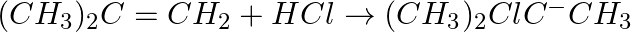
Solution: Addition (electrophilic) response since two reactant particles joins to shape a solitary item.
Classify the following reactions in one of the reaction type studied in this unit.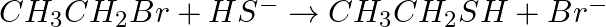
Solution: Substitution (nucleophilic) response since bromine bunch gets subbed by – SH bunch.
Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equations as nucleophiles or electrophiles: 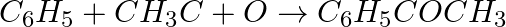
Solution: A nucleophile is a reagent that has an electron pair and will give it away. It is otherwise called a core adoring reagent. An electrophile is a reagent which needs an electron pair and is...
Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equations as nucleophiles or electrophiles: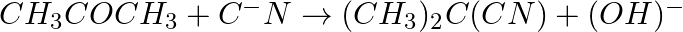
Solution: A nucleophile is a reagent that has an electron pair and will give it away. It is otherwise called a core adoring reagent. An electrophile is a reagent which needs an electron pair and is...
Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equations as nucleophiles or electrophiles: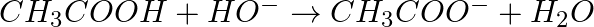
Solution: A nucleophile is a reagent that has an electron pair and will give it away. It is otherwise called a core adoring reagent. An electrophile is a reagent which needs an electron pair and is...
What are electrophiles and nucleophiles? Clarify with models.
Solution: A nucleophile is a reagent that has an electron pair and will give it away. It is otherwise called a core cherishing reagent. Ex: NC–, OH–, R3C–(carbanions), and so on An electrophile is a...
Which of the two: O2NCH2CH2O–or CH3CH2O–is relied upon to be more steady and why?
Solution: Since NO2 has a place with the electron-pulling out bunch, it shows – I impact. NO2 attempts to diminish the negative charge on the compound by pulling out the electrons toward it. This...
Draw recipes for the initial five individuals from each homologous series starting with the accompanying mixture H–CH=CH2
Solution: The initial five individuals from each homologous series starting with the given mixtures are H–CH=CH2: Ethene CH3–CH=CH2: Propene CH3–CH2–CH=CH2: 1-Butene CH3–CH2–CH2–CH=CH2: 1-Pentene...
Draw recipes for the initial five individuals from each homologous series starting with the accompanying mixture CH3COCH3
Solution: CH3COCH3: Propanone CH3COCH2CH3: Butanone CH3COCH2CH2CH3 : Pentan-2-one CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH3: Hexan-2-one CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 : Heptan-2-one
Draw recipes for the initial five individuals from each homologous series starting with the accompanying mixture H–COOH
Solution: The initial five individuals from each homologous series starting with the given mixtures are H–COOH: Methanoic corrosive CH3–COOH: Ethanoic corrosive CH3–CH2–COOH: Propanoic corrosive...
Which of the accompanying addresses the right IUPAC name for the mixtures concerned? But-3-yn-1-ol or But-4-ol-1-yne
Solution: Out of the two utilitarian gatherings present in the given compound, the alcoholic gathering is the central practical gathering. Consequently, the parent chain will have an – ol postfix....
Which of the accompanying addresses the right IUPAC name for the mixtures concerned? 2-Chloro-4-methylpentane or 4-Chloro-2-methylpentane
Solution: If the substituents in the chain are in identical positions, then, at that point, the lower number is given to the substituent bunch in sequential request. Along these lines, the right...
Which of the accompanying addresses the right IUPAC name for the mixtures concerned? 2,4,7-Trimethyloctane or 2,5,7-Trimethyloctane
Solution: The locant number should begin from the base. Here, 2,4,7 is lower than 2,5,7. Subsequently, the right IUPAC name would be 2,4,7-Trimethyloctane.
Which of the accompanying addresses the right IUPAC name for the mixtures concerned? 2,2-Dimethylpentane or 2-Dimethylpentane
solution: The prefix di shows that there are two methyl bunches in the chain. Along these lines, the right IUPAC name would be 2,2-Dimethylpentane.
What are the hybridisation conditions of every carbon molecule in the accompanying compound? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[C6H6\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-250e7c087123a8d0267c095925b18800_l3.png)
Solution: C6H6 All the 6 carbon particles in benzene are sp2 hybridized
What are the hybridisation conditions of every carbon molecule in the accompanying compound? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[CH2=CHCN\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-52ef84ac98a604743dfb23732dfbb165_l3.png)
Solution: C-1 is sp2 hybridized. C-2 is sp2 hybridized. C-3 is sp hybridized.
What are the hybridisation conditions of every carbon molecule in the accompanying compound? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( CH3 \right)2CO\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a2bea77220b7e99546204fa04a862cfa_l3.png)
Solution: C - 1 and C-3 are sp3 hybridized. C-2 is sp2 hybridized.
What are the hybridisation conditions of every carbon molecule in the accompanying compound? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[CH3CH=CH2\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6a2ef16862caa7e37fd3861c7df53de4_l3.png)
Solution: C-1 is sp3 hybridized. C-2 is sp2 hybridized. C-3 is sp2 hybridized.
What are the hybridisation conditions of every carbon molecule in the accompanying compound? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[CH2=C=O\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-3ffdae7fcb2301f4db1b66d768c446ab_l3.png)
Solution: C-1 is sp2 hybridized. C-2 is sp hybridized.
Lifetimes of the molecules in the excited states are often measured by using pulsed radiation source of duration nearly in the nanosecond range. If the radiation source has the duration of 2 ns and the number of photons emitted during the pulse source is 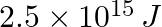 , calculate the energy of the source.
, calculate the energy of the source.
Frequency of radiation $\nu$ $\nu =\frac{1}{2.0\times 10^{-9}s}$ $\nu =5.0\times 10^{8}s^{-1}$ Energy (E) of source = Nhν Where, N is the no. photons emitted h is Planck’s constant ν denotes the...
The ejection of the photoelectron from the silver metal in the photoelectric effect experiment can be stopped by applying the voltage of 0.35 V when the radiation 256.7 nm is used. Calculate the work function for silver metal.
The energy associated with an incident photon (E) must equal the sum of its kinetic energy and the work function (W0) of the radiation, according to the rule of conservation of energy. E = W0 + K.E...
If the photon of the wavelength 150 pm strikes an atom and one of its inner bound electrons is ejected out with a velocity of 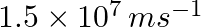 , calculate the energy with which it is bound to the nucleus.
, calculate the energy with which it is bound to the nucleus.
Energy of incident photon (E) is given by, $E=\frac{hc}{\lambda }$ $E=\frac{(6.626\times 10^{-34})(3\times 10^{8})}{(150\times 10^{-12})}=1.3252\times 10^{-15}\, J$ $\simeq 13.252\times 10^{-16}J$...
Emission transitions in the Paschen series end at orbit n = 3 and start from orbit n and can be represented as v =  (Hz) [1/3^2 – 1/n^ 2 ] Calculate the value of n if the transition is observed at 1285 nm. Find the region of the spectrum.
(Hz) [1/3^2 – 1/n^ 2 ] Calculate the value of n if the transition is observed at 1285 nm. Find the region of the spectrum.
Wavelength of the transition = 1285 nm =$1285 \times 10^{-9} m$(Given) $\nu =3.29\times 10^{15}(\frac{1}{3^{2}}-\frac{1}{n^{2}})$ Since$ \nu =\frac{c}{\lambda }$ =$\frac{3\times...
Calculate the wavelength for the emission transition if it starts from the orbit having radius 1.3225 nm and ends at 211.6 pm. Name the series to which this transition belongs and the region of the spectrum.
The radius of the n th orbit of hydrogen-like particles is given by, $r=\frac{0.529n^{2}}{Z}$ $r=\frac{5.29n^{2}}{Z}pm$ For radius (r1) = 1.3225 nm $=1.32225\times 10^{-9}m$ $=1322.25\times...
Dual behaviour of matter proposed by de Broglie led to the discovery of electron microscope often used for the highly magnified images of biological molecules and another type of material. If the velocity of the electron in this microscope is 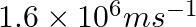 , calculate de Broglie wavelength associated with this electron.
, calculate de Broglie wavelength associated with this electron.
As per de Broglie’s equation, $\lambda =\frac{h}{m\nu }$ =$\frac{(6.626\times 10^{-34})}{9.103939\times 10^{-31}kg(1.6\times 10^{6}ms^{-1})}$ =$4.55\times 10^{-10}m\lambda =455pm$ Therefore, de...
Similar to electron diffraction, neutron diffraction microscope is also used for the determination of the structure of molecules. If the wavelength used here is 800 pm, calculate the characteristic velocity associated with the neutron.
From de Broglie’s equation, $\lambda =\frac{h}{m\nu }$ $\nu=\frac{h}{m\lambda}$ Where, v denotes the velocity of the neutron h is Planck’s constant m is the mass of the neutron λ is the wavelength...
If the velocity of the electron in Bohr’s first orbit is 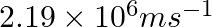 , calculate the de Broglie wavelength associated with it.
, calculate the de Broglie wavelength associated with it.
As per de Broglie’s equation, $\lambda =\frac{h}{m\nu}$ Where, λ is the wavelength of the electron h is Planck’s constant m is the mass of the electron v denotes the velocity of electron...
The velocity associated with a proton moving in a potential difference of 1000 V is 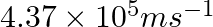 . If the hockey ball of mass 0.1 kg is moving with this velocity, calculate the wavelength associated with this velocity.
. If the hockey ball of mass 0.1 kg is moving with this velocity, calculate the wavelength associated with this velocity.
As per de Broglie’s expression, $\lambda =\frac{h}{m\nu }$ $ =\frac{(6.626\times 10^{-34})}{0.1kg(4.37\times 10^{5}ms^{-1})}$=$1.516\times 10^{-38}m$
If the position of the electron is measured within an accuracy of ± 0.002 nm, calculate the uncertainty in the momentum of the electron. Suppose the momentum of the electron is h/4πm × 0.05 nm, is there any problem in defining this value.
As per Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, ∆x.∆p >= h/4π Where, ∆x = uncertainty in the position of the electron ∆p = uncertainty in the momentum of the electron Substituting the given values in...
The bromine atom possesses 35 electrons. It contains 6 electrons in 2p orbital, 6 electrons in 3p orbital and 5 electrons in 4p orbital. Which of these electron experiences the lowest effective nuclear charge?
The nuclear charge that electrons (which are present in atoms containing multiple electrons) feel is determined by the distance between their orbital and the atom's nucleus. The smaller the...
Among the following pairs of orbitals which orbital will experience the larger effective nuclear charge? (i) 2s and 3s, (ii) 4d and 4f, (iii) 3d and 3p
The net positive charge acting on an electron in an atom's orbital with more than one electron is known as the nuclear charge. The distance between the orbital and the nucleus is inversely...
Indicate the number of unpaired electrons in: (a)P (b)Si (c)Cr (d)Fe (e)Kr
(a)Phosphorus (P): The atomic number of phosphorus is 15 Electronic configuration of Phosphorus: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 3 This can be represented as follows: From the diagram, it can be observed...
(a) How many sub-shells are associated with n = 4? (b) How many electrons will be present in the sub-shells having ms value of –1/2 for n = 4?
(a)n = 4 (Given) For some value of ‘n’, the values of ‘l’ range from 0 to (n – 1). Here, the possible values of l are 0, 1, 2, and 3 Therefore, a total of 4 subshells are possible when n=4: the s,...
For your agricultural field or garden you have developed a compost producing pit. Discuss the process in the light of bad odour, flies and recycling of wastes for a good product.
To avoid odours and insects, the compost pit should be covered. To avoid interfering with the breakdown of the wastes, non-biodegradable wastes should not be thrown into the compost pit. They should...
How can domestic waste be used as manure?
To begin, trash must be separated into biodegradable and non-biodegradable categories. Biodegradable materials, such as leaves and food wastes, are deposited in landfills alongside microorganisms...
A large number of fish are suddenly found floating dead on a lake. There is no evidence of toxic dumping but you find an abundance of phytoplankton. Suggest a reason for the fish kill.
Bacteria eat phytoplankton, and this process necessitates the presence of dissolved oxygen. As a result, the greater the number of Phytoplankton present, the greater the consumption of dissolved...
What would have happened if the greenhouse gases were totally missing in the earth’s atmosphere? Discuss.
The greenhouse gases in our atmosphere capture the sun's UV rays and heat up the earth. Without greenhouse gases, the earth will be unable to retain any heat, which is necessary for the existence of...
What do you mean by green chemistry? How will it help decrease environmental pollution?
The manufacturing process employs our current understanding of chemistry principles to produce, develop, and deploy chemical compounds and products that reduce the amount of harmful chemicals in the...
What are pesticides and herbicides? Explain giving examples.
A pesticide is a combination of two or more chemicals that is used to kill bugs. Plant diseases, weeds, insects, mollusks, and other pests that damage plants and cause them to die must all be...
Do you observe any soil pollution in your neighbourhood? What efforts will you make for controlling the soil pollution?
Pesticides and fertilisers are the most common contaminants that pollute soil. Because pesticides like DDT are not soluble in water, they remain in the soil for prolonged periods of time, polluting...
What do you mean by Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)?
The quantity of oxygen required by bacteria to breakdown organic materials in a given volume of water is known as biochemical oxygen demand. A BOD of less than 5 ppm indicates clean water, but a BOD...
Have you ever observed any water pollution in your area? What measures would you suggest to control it?
Water pollution is caused by human activities such as storm-water drainage, run-off from agricultural areas, wastewater treatment plant emissions, and so on. Industries and factories emit toxic...
What are the major causes of water pollution? Explain.
Water pollution happens when undesired and unwanted chemicals are introduced into water bodies, suffocating the aquatic life that lives there. The following are the primary sources of water...
What do you mean by ozone hole? What are its consequences?
Polar stratospheric clouds offer a surface for the reaction of hypochlorous acid and chlorine nitrate, which produces molecular chlorine after further reaction. Photolysis of HOCl and Molecular...
What are the reactions involved for ozone layer depletion in the stratosphere?
In the stratosphere, ozone is actually formed by the action of UV rays on Dioxygen molecules(O2). (i) O2(g) →UV O(g) +O(g) (ii) O2(g) + O(g) ↔UV O3(g) The second reaction demonstrates that the...
What are the harmful effects of photochemical smog and how can they be controlled?
Photochemical smog is oxidising in nature because it contains NO2 and O3, which cause rubber, stones, metals, and painted surfaces to corrode. Formaldehyde, PAN, and acrolein are also found in...
Write down the reactions involved during the formation of photochemical smog.
The interaction of sunlight with nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons produces photochemical smog. The major components of photochemical smog include formaldehyde, nitric oxide, ozone, PAN, and...
What is smog? How is classical smog different from photochemical smogs?
Smog is a combination of smoke and fog which causes air pollution. There are two types of smog: a) Photochemical smog b) Classical smog They can be differentiated as follows: Photochemical smog ...
Statues and monuments in India are affected by acid rain. How?
By interacting with water in the presence of ambient oxygen, nitrogen oxides (NO2, NO) and sulphur oxides (SO2 and SO3) produced by the combustion of coal, car gasoline, and other fossil fuels...
Explain tropospheric pollution in 100 words.
Tropospheric pollution is caused by the presence of undesirable chemicals in the troposphere's lowest layer. Nitrogen oxides, sulphur oxides, carbon, and hydrocarbons are the most common...
Define environmental chemistry.
The study of biological and chemical processes that occur in nature is referred to as environmental chemistry. It also investigates the chemical species' reactions, origins, impacts, and...
What is the maximum number of emission lines when the excited electron of a H atom in n = 6 drops to the ground state?
A total number of 15 lines (5 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1) will be obtained in this hydrogen emission spectrum. The total number of spectral lines emitted when an electron drops to the ground state from the...
How much energy is required to ionise a H atom if the electron occupies n = 5 orbit? Compare your answer with the ionization enthalpy of H atom (energy required to remove the electron from n =1 orbit).
The expression for the ionization energy is given by, $E_{n} =\frac{-(2.18\times 10^{-18})Z^{2}}{n^{2}}$ Where Z denotes the atomic number and n is the principal quantum number For the ionization...
What is the wavelength of light emitted when the electron in a hydrogen atom undergoes the transition from an energy level with n = 4 to an energy level with n = 2?
The $n_{i} = 4$ to$ n_{f}$= 2 transition results in a spectral line of the Balmer series. The energy involved in this transition can be calculated using the following expression: $E=2.18\times...
Electrons are emitted with zero velocity from a metal surface when it is exposed to radiation of wavelength 6800 Å. Calculate threshold frequency (ν0 ) and work function (W0 ) of the metal.
Threshold wavelength of the radiation $(\lambda _{0})= 6800 Å=6800\times 10^{-10}\, m$ Threshold frequency of the metal $(\nu _{0}) =\frac{c}{\lambda _{0}}=$ $\frac{3\times 10^{8}ms^{-1}}{6.8\times...
A 25-watt bulb emits monochromatic yellow light of the wavelength of 0.57µm. Calculate the rate of emission of quanta per second.
Power of the bulb,$ P = 25 Watt = 25\, Js^{-1}$ Energy (E) of one photon= $h\nu =\frac{hc}{\nu} $ Substituting these values in the expression for E: $E=\frac{(6.626\times 10^{-34})(3\times...
Electromagnetic radiation of wavelength 242 nm is just sufficient to ionise the sodium atom. Calculate the ionisation energy of sodium in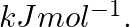
Ionization energy (E) of sodium =$ \frac{N_{A}hc}{\lambda }$ =$\frac{(6.023\times 10^{23}\, mol^{-1})(6.626\times 10^{-34})Js(3\times 10^{8})ms^{-1}}{242\times 10^{-9}m}$ =$4.947\times 10^{5}\, J\,...
A photon of wavelength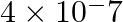 m strikes on metal surface, the work function of the metal is 2.13 eV. Calculate (i) the energy of the photon (eV), (ii) the kinetic energy of the emission, and (iii) the velocity of the photoelectron
m strikes on metal surface, the work function of the metal is 2.13 eV. Calculate (i) the energy of the photon (eV), (ii) the kinetic energy of the emission, and (iii) the velocity of the photoelectron 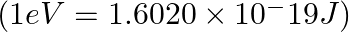 .
.
(i) Energy of the photon $(E)= h\nu =\frac{hc}{\lambda }$ Where, h denotes Planck’s constant, whose value is $6.626\times 10^{-34}\,Js$ c denotes the speed of light =$ 3\times 10^{8}\,m/s$...
What is the number of photons of light with a wavelength of 4000 pm that provides 1J of energy?
Energy of one photon (E) =$ h\nu$ Energy of ‘n’ photons $E_{n} = nh\nu \Rightarrow n=\frac{E_{n}\lambda }$ Where, \lambdaλ is the wavelength of the photons = 4000 pm = $4000\times 10^{-12}\, m$ c...
Find the energy of each of the photons which (i) correspond to light of frequency 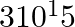 Hz. (ii) have a wavelength of 0.50 Å.
Hz. (ii) have a wavelength of 0.50 Å.
(i) The energy of a photon (E) can be calculated by using the following expression: $E= h\nu$ Where, ‘h’ denotes Planck’s constant, which is equal to $6.626\times 10^{-34}\, Js\nuν$ (frequency of...
Yellow light emitted from a sodium lamp has a wavelength (λ) of 580 nm. Calculate the frequency (ν) and wavenumber (ν ) of the yellow light.
Rearranging the expression, $\lambda =\frac{c}{\nu }$ the following expression can be obtained, $\nu =\frac{c}{ \lambda }$ ……….(1) Here, $\nu$ denotes the frequency of the yellow light c denotes...
Write the complete symbol for the atom with the given atomic number (Z) and atomic mass (A) (I)Z = 17, A = 35 (II)Z = 92, A = 233 (III)Z = 4, A = 9
(i)\({}_{17}^{35}C\) (ii)\({}_{92}^{233}C\) (iii)\({}_{4}^{9}C\)
(i) Calculate the total number of electrons present in one mole of methane. (ii) Find (a) the total number and (b) the total mass of neutrons in 7 mg of 14C. (Assume that mass of a neutron = 1.675 × 10–27 kg). (iii) Find (a) the total number and (b) the total mass of protons in 34 mg of NH3 at STP. Will the answer change if the temperature and pressure are changed?
(i) 1 molecule of methane contains 10 electrons (6 from carbon, 4 from hydrogen) Therefore, 1 mole of methane contains 10*NA = 6.022*1024 electrons. (ii) Number of neutrons in 14g (1 mol) of 14C =...
Dinitrogen and dihydrogen react with each other to produce ammonia according to the following chemical equation: N2 (g) + H2(g)→ 2NH3 (g) (i) Calculate the mass of 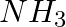 produced if
produced if 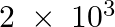 g
g 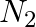 reacts with
reacts with 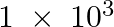 g of
g of 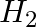 ? (ii) Will any of the two reactants remain unreacted? (iii) If yes, which one and what would be its mass.
? (ii) Will any of the two reactants remain unreacted? (iii) If yes, which one and what would be its mass.
(i) Balance the given equation: $N_{ 2 }\;(g) \; + \; 3H_{ 2 } \;(g) \; \rightarrow \; 2NH_{ 3 }\;(g) $ Thus, 1 mole (28 g) of N2 reacts with 3 mole (6 g) of H2 to give 2 mole (34 g)...
How are 0.50 mol 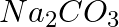 and 0.50 M
and 0.50 M 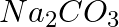 different?
different?
Molar mass of $Na_{ 2 }CO_{ 3 }$ = (2 × 23) + 12 + (3 × 16) = $106 g mol^{ -1 }$ 1 mole of $Na_{ 2 }CO_{ 3 }$ means 106 g of $Na_{ 2 }CO_{ 3 }$ Therefore, 0.5 mol of $Na_{ 2 }CO_{ 3 }$...
If 10 volumes of dihydrogen gas reacts with five volumes of dioxygen gas, how many volumes of water vapour would be produced?
2H2(g) +O2(g) →2H2O(g) 2 volumes of dihydrogen react with 1 volume of dioxygen to produce two volumes of vapour. Hence, 10 volumes of dihydrogen will react with five volumes of dioxygen to...
Which one of the following will have the largest number of atoms? (i) 1 g Au (s) (ii) 1 g Na (s) (iii) 1 g Li (s) (iv) 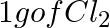 (g)
(g)
(i) 1 g Au (s) = $\frac{ 1 }{ 197 }$ mol of Au (s) = $\frac{ 6.022 \; \times \; 10^{ 23 } }{ 197 }$ atoms of Au (s) = $3.06 \times \; 10^{ 21 }$ atoms of Au (s) (ii) 1 g Na (s) = $\frac{ 1...
Calculate the molarity of a solution of ethanol in water, in which the mole fraction of ethanol is 0.040 (assume the density of water to be one).
Mole fraction of $C_{ 2 }H_{ 5 }OH$ = $\frac{Number \; of \; moles \; of \; C_{ 2 }H_{ 5 }OH}{Number \; of \; moles \; of \; solution}$ $0.040 = \frac{n_{C_{ 2 }H_{ 5 }OH}}{n_{C_{ 2 }H_{ 5 }OH} \; +...
What will be the mass of one 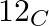 atom in g?
atom in g?
1 mole of carbon atoms =$ 6.023 \; \times \; 10^{ 23 }$atoms of carbon = 12 g of carbon Therefore, mass of $1 _{}^{ 12 }\textrm{ C }$ atom = $\frac{ 12 \; g }{ 6.022 \; \times \; 10^{ 23 }}$...
How many significant figures should be present in the answer of the following calculations? (i)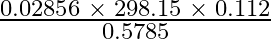 (ii) 5 × 5.365 (iii) 0.012 + 0.7864 + 0.0215
(ii) 5 × 5.365 (iii) 0.012 + 0.7864 + 0.0215
(i) $\frac{ 0.02856 \; \times \; 298.15 \; \times \; 0.112}{ 0.5785 }$ Least precise no. of calculation = 0.112 Therefore, no. of significant numbers in the answer = No. of significant numbers in...
Use the data given in the following table to calculate the molar mass of naturally occurring argon isotopes:
Molar mass of Argon: =$ [( 35.96755 \; \times \; \frac{ 0.337 }{ 100 }) + ( 37.96272 \; \times \; \frac{ 0.063 }{ 100 })+ ( 39.9624 \; \times \; \frac{ 99.600 }{ 100 })]$ =$ [0.121 + 0.024 + 39.802]...
Calculate the number of atoms in each of the following (i) 52 moles of Ar (ii) 52 u of He (iii) 52 g of He
(i) 52 moles of Ar 1 mole of Ar = $6.023 \; \times \; 10^{ 23 }$atoms of Ar Therefore, 52 mol of Ar = 52 × $6.023 \; \times \; 10^{ 23 }$atoms of Ar = $3.131 \; \times \; 10^{ 25 }$ atoms of Ar...
Calcium carbonate reacts with aqueous HCl to give CaCl2 and CO2 according to the reaction, CaCO3 (s) + 2 HCl (aq) → CaCl2(aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O(l) What mass of CaCO3 is required to react completely with 25 mL of 0.75 M HCl?
0.75 M of HCl ≡ 0.75 mol of HCl are present in 1 L of water ≡ $[(0.75 mol)\times(36.5 g mol–1 )]$ HCl is present in 1 L of water ≡ 27.375 g of HCl is present in 1 L of water Thus, 1000 mL of...
Chlorine is prepared in the laboratory by treating manganese dioxide (MnO2) with aqueous hydrochloric acid according to the reaction: 4 HCl (aq) + MnO2(s) → 2H2O (l) + MnCl2(aq) + Cl2 (g) How many grams of HCl react with 5.0 g of manganese dioxide?
1 mol of $MnO_{2}$ = 55 + 2 × 16 = 87 g 4 mol of HCl = 4 × 36.5 = 146 g 1 mol of $MnO_{2}$ reacts with 4 mol of HCl 5 g of $MnO_{ 2 }$will react with: =$ \frac{146 \; g}{87 \; g} \; \times \; 5...
In a reaction A + B2 → AB2 Identify the limiting reagent, if any, in the following reaction mixtures. (i) 300 atoms of A + 200 molecules of B (ii) 2 mol A + 3 mol B (iii) 100 atoms of A + 100 molecules of B (iv) 5 mol A + 2.5 mol B (v) 2.5 mol A + 5 mol B
Reagent limitation: It establishes the magnitude of a reaction. It is the first to be consumed in a reaction, causing the process to come to a halt and limiting the number of products produced. (i)...
If the speed of light is 3.0 × 10^8 m s^(–1), calculate the distance covered by light in 2.00 ns
Time taken = 2 ns = $2 \times10^{ -9 }$ s Now, Speed of light =$3 \times10^{ 8 } ms^{ -1 }$ So, Distance travelled in 2 ns = speed of light * time taken =$(3 \times10^{ 8 })(2 \times10^{ -9 })$ = $6...
The following data are obtained when dinitrogen and dioxygen react together to form different compounds:;(a) Which law of chemical combination is obeyed by the above experimental data? Give its statement. (b) Fill in the blanks in the following conversions: (i) 1 km = …………………. mm = …………………. pm (ii) 1 mg = …………………. kg = …………………. ng (iii) 1 mL = …………………. L = …………………. dm3
(a) If the mass of N2 is set at 28 g, the mass of O2 that will combine with it is 32 grammes, 64 grammes, 32 grammes, and 80 grammes. O2 has a mass-to-number ratio of 1: 2: 1: 5. As a result, the...
Round up the following upto three significant figures: (a) 34.216 (b) 10.4107 (c)0.04597 (d)2808
(a) The number after round up is: 34.2 (b) The number after round up is: 10.4 (c)The number after round up is: 0.0460 (d)The number after round up is: 2808
How many significant figures are present in the following? (a) 0.0027 (b) 209 (c) 6005 (d) 136,000 (e) 900.0 (f) 2.0035
(i) 0.0027: 2 significant numbers. (ii) 209: 3 significant numbers. (iii) 6005: 4 significant numbers. (iv) 136,000:3 significant numbers. (v) 900.0: 4 significant numbers. (vi) 2.0035: 5...
Express the following in the scientific notation: (i) 0.0048 (ii) 234,000 (iii) 8008 (iv) 500.0 (v) 6.0012
(a$) 0.0048= 4.8 \times10^{-3}$ (b) $234,000 = 2.34 \times10^{5}$ (c) $8008= 8.008 \times10^{3}$ (d) $500.0 = 5.000 \times10^{2}$ (e) $6.0012 = 6.0012 \times10^{0}$
A sample of drinking water was found to be severely contaminated with chloroform, CHCl3, supposed to be carcinogenic in nature. The level of contamination was 15 ppm (by mass). (i) Express this in per cent by mass. (ii) Determine the molality of chloroform in the water sample.
(a) $1 ppm = 1 part out of 1 million parts.$ Mass percent of 15 ppm chloroform in H2O= $\frac{15}{{{10}^{6}}}\times 100$ $\approx 1.5 \times{10}^{-3}%$ $ (b)$100 grams of the sample is having 1.5 ×...
What do you mean by significant figures?
The meaningful numbers that are known with certainty are known as significant figures. Significant numbers imply that the tested value is unknown. For example, if the experiment yielded 15.6 mL, 15...
Match the following prefixes with their multiples:
What is the SI unit of mass? How is it defined?
Kilogram is the SI unit of mass (kg) Mass: “Mass is defined as the mass equivalent to the mass of the international kilogramme prototype.”
Pressure is determined as force per unit area of the surface. The SI unit of pressure, pascal is as shown below: 1Pa = 1N m–2 If mass of air at sea level is 1034 g cm–2, calculate the pressure in pascal
As per definition, pressure is force per unit area of the surface. $P = \frac{F}{A}$ =$ \frac{1034\;g\;\times \;9.8\;ms^{-2}}{cm^{2}}\times \frac{1\;kg}{1000\;g}\times \frac{(100)^{2}\;cm^{2}}{1...
If the density of methanol is 0.793 kg 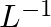 , what is its volume needed for making 2.5 L of its 0.25 M solution?
, what is its volume needed for making 2.5 L of its 0.25 M solution?
$Molar mass of CH_{3}OH$ = (1 * 12) + (4 * 1) + (1 * 16) =$32 g mol^{-1}$ = $0.032 kg mol^{-1}$ Molarity of the solution = $\frac{0.793\;kg\;L^{-1}}{0.032\;kg\;mol^{-1} }$ = 24.78 mol{L}^{-1}...
What is the concentration of sugar in mol
in mol  if its 20 g are dissolved in enough water to make a final volume up to 2L?
if its 20 g are dissolved in enough water to make a final volume up to 2L?
Molarity (M) is as given by, = $\frac{Number\;of\;moles\;of\;solute}{Volume\;of\;solution\;in\;Litres}$ =$\frac{\frac{Mass\;of\;sugar}{Molar\;mass\;of\;sugar}}{2\;L}$ =...
Considering the elements F, Cl, O and N, the correct order of their chemical reactivity in terms of oxidizing property is : (a) F > Cl > O > N (b) F > O > Cl > N (c) Cl > F > O > N (d) O > F > N > Cl
Answer: (b) F > O > Cl > N During a period, as we move from left to right, the non-metallic characteristics of the elements become more prominent. As a result, F > O > N.
Considering the elements B, C, N, F, and Si, the correct order of their non-metallic character is : a) B > C > Si > N > F b) Si > C > B > N > F c) F > N > C > B > Si d) F > N > C > Si > B
Answer: c) F > N > C > B > Si While moving from left to right in a period, the nonmetallic property of the elements reduces as we move from left to right in the period. As a result, F...
Considering the elements B, Al, Mg, and K, the correct order of their metallic character is : (a) B > Al > Mg > K (b) Al > Mg > B > K (c) Mg > Al > K > B (d) K > Mg > Al > B
Answer: d) K > Mg > Al > B During a period, the metallic nature of the components diminishes as we move from left to right in the period. As a result, Mg > Al. With each group we...
Which one of the following statements is incorrect in relation to ionization enthalpy? (a) Ionization enthalpy increases for each successive electron. (b) The greatest increase in ionization enthalpy is experienced on the removal of an electron from core noble gas configuration. (c) End of valence electrons is marked by a big jump in ionization enthalpy. (d) Removal of an electron from orbitals bearing lower n value is easier than from orbital having higher n value
Answer: (d) is a false statement When comparing orbitals with a lower value of 'n' to orbitals with a higher value of 'n,' it is easier to remove an electron from the lower value of 'n' orbital....
The size of isoelectronic species F–, Ne and Na+ is affected by (a) nuclear charge (Z ) (b) valence principal quantum number (n) (c) electron-electron interaction in the outer orbitals (d) none of the factors because their size is the same.
Answer: (a) Nuclear charge (Z) Because, in the case of isoelectronic species, the atomic size decreases as the number of nuclear charge increases (Z). e.g. the arrangement according to increasing...
“Anything that influences the valence electrons will affect the chemistry of the element”. Which of the factors given below is not affecting the valence shell? (a) Valence Principal quantum number (n) (b) Nuclear charge (Z) (c) Nuclear mass (d) Number of core electrons
Answer: Option c) Because the nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons, the mass of the nucleus has no effect on the valence shell. Protons, or nuclear charges, have an effect on the valence...
Which of the following statements related to the modern periodic table is incorrect? (a) The p-block has 6 columns because a maximum of 6 electrons can occupy all the orbitals in a p-shell. (b) The d-block has 8 columns because a maximum of 8 electrons can occupy all the orbitals in a d-subshell. (c) Each block contains a number of columns equal to the number of electrons that can occupy that subshell. (d) The block indicates the value of an azimuthal quantum number (l) for the last subshell that received electrons in building up the electronic configuration.
Answer: Correcting the incorrect statement is represented by option (b). It explains that "the d-block has 8 columns because a maximum of 8 electrons can occupy all of the orbitals in a d-subshell,"...
In the modern periodic table, the period indicates the value of : (a) atomic number (b) atomic mass (c) principal quantum number (d) azimuthal quantum number.
Answer: (c) The period in the Modern periodic table indicates the value of ‘n’ i.e. a principal quantum number. A periodic table's period reflects the value of a particular element's major quantum...
Predict the formulas of the stable binary compounds that would be formed by the combination of the following pairs of elements. (a) Lithium and oxygen (b) Magnesium and nitrogen (c) Aluminium and iodine (d) Silicon and oxygen (e) Phosphorus and fluorine (f) Element 71 and fluorine
Answer: i) $Li_2O$ is formed when the alkali metal lithium (with one valence electron) and group 16 element oxygen (with two valence electrons) mix. (ii) The alkaline earth metal magnesium (which...
The first 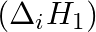 and the second
and the second 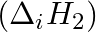 ionization enthalpies (in
ionization enthalpies (in  ) and the
) and the 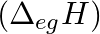 electron gain enthalpy (in
electron gain enthalpy (in 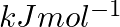 ) of a few elements are given below: Which of the above elements is likely to be : (a) the least reactive element. (b) the most reactive metal. (c) the most reactive non-metal. (d) the least reactive non-metal. (e) the metal which can form a stable binary halide of the formula MX2 (X=halogen). (f) the metal which can form a predominantly stable covalent halide of the formula MX (X=halogen)?
) of a few elements are given below: Which of the above elements is likely to be : (a) the least reactive element. (b) the most reactive metal. (c) the most reactive non-metal. (d) the least reactive non-metal. (e) the metal which can form a stable binary halide of the formula MX2 (X=halogen). (f) the metal which can form a predominantly stable covalent halide of the formula MX (X=halogen)?
Elements (\Delta _{i}H_{1})(ΔiH1) (\Delta _{i}H_{2})(ΔiH2) (\Delta _{eg}H)(ΔegH) 1 520 7300 -60 2 419 3051 -48 3 1681 3374 -328 4 1008 1846 -295 5 2372 5251 +48 6 738 1451 -40 Answer:...
Assign the position of the element having outer electronic configuration (i) 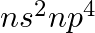 for
for  (ii) (n1)
(ii) (n1) 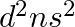 for
for 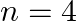 , and (iii)
, and (iii) 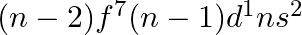 for
for 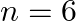 , in the periodic table.
, in the periodic table.
Answer: i) Since n = 6, the element is in period 6. f-block element because the last electron enters f-orbital. They are in the third group. So, 54 + 7 + 2 + 1 Equals 64. So Gadolinium is required....
Write the general outer electronic configuration of s-, p-, d- and f- block elements.
Answer: The general outer electronic configuration of s block elements is $ns ^{(1-2)}$. The general outer electronic configuration of p block elements is $ns ^{2} np ^{(1-6)}$. The general outer...
The increasing order of reactivity among group 1 elements is Li < Na < K < Rb Cl > Br > I. Explain.
Answer: Group 1 elements have only one valence electron. So they tend to expel this electron to form a stable inert gas. The ionization enthalpies of the elements drop in group 1. Expulsion of the...
Use the periodic table to answer the following questions. (a) Identify an element with five electrons in the outer subshell. (b) Identify an element that would tend to lose two electrons. (c) Identify an element that would tend to gain two electrons. (d) Identify the group having metal, non-metal, liquid as well as gas at the room temperature
Answer: (a) The electrical configuration of an element with 5 electrons in the outer subshell is ns2np5. The electrical configuration of the Halogen group is the same. As a result, the elements...
What are the major differences between metals and non-metals?
Answer: Metals lose electrons to produce cations. Metals have low ionization, negative electron, and electronegativities enthalpies. ionic compounds and basic oxides Non-metals readily take...
Would you expect the first ionization enthalpies for two isotopes of the same element to be the same or different? Justify your answer
Answer: The ionization enthalpy of any atom is determined by the number of protons and electrons in the atom. However, the isotopes of any element have the same number of electrons and protons as...
Describe the theory associated with the radius of an atom as it (a) gains an electron (b) loses an electron
Answer: a) An atom loses one electron when it expels one, but the nuclear charge remains the same. In an atom, electron-electron repulsion reduces. So the effective nuclear charge increases. As a...
How would you react to the statement that the electronegativity of N on the Pauling scale is 3.0 in all the nitrogen compounds?
Answer: Electronegativity is a property of any element that is subject to change. Electronegativity varies depending on the substance being studied. The following statement is erroneous: "The...
What is the basic difference between the terms electron gain enthalpy and electronegativity?
Answer: Electron gain enthalpy Electronegativity It is the common tendency of an atom to attract outside electrons It is the general tendency of an atom to attract shared pair of electrons It is the...
Would you expect the second electron gain enthalpy of O as positive, more negative or less negative than the first? Justify your answer
Answer: Oxygen is in p block element group 16. It is the first of 16 members. It is a non-metal found in the earth's crust. When an electron is added to an O atom, it releases energy. O has a...
Which of the following pairs of elements would have a more negative electron gain enthalpy? (i) O or F (ii) F or Cl
Answer: i) O and F are from the same period. As the electron is inserted in the same shell, the atomic size of O-atom is larger than F-atom. It has one less proton than F-atom. So an O-atom nucleus...
The first ionization enthalpy values (in kJ/mol) of group 13 elements are given below. How would you explain this deviation from the general trend?
B Al Ga In Tl 801 577 579 558 589 Answer The ionization enthalpy decreases with group size. B and Al agree. Ga has a higher ionization enthalpy than Al. Tend electrons in the inner shell of...
What are the various factors due to which the ionization enthalpy of the main group elements tends to decrease down a group?
Answer: The factors that cause the ionization enthalpy to drop as we travel down the main group are as follows: 1. “Inner shells increase in number as we proceed down the group.” The nucleus' inner...
How would you explain the fact that the first ionization enthalpy of sodium is lower than that of magnesium but its second ionization enthalpy is higher than that of magnesium?
Answer: Because magnesium has a larger 1st ionization enthalpy than sodium, Magnesium has bigger atoms than sodium. A higher effective nuclear charge than sodium, Magnesium So sodium requires less...
Among the second period elements the actual ionization enthalpies are in the order Li < B < Be < C < O < N < F < Ne. Explain Why {i}Be has higher ΔH than B (ii) O has lower ΔH than N and F?
Answer: i) The electron that can be evacuated from Be(beryllium) atom is 2s, but the electron that can be expelled from boron is 2p. 2s – electron, and nucleus attract more strongly than 2s –...
Energy of an electron in the ground state of the hydrogen atom is 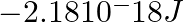 . Calculate the ionization enthalpy of atomic hydrogen in terms of J mol–1.
. Calculate the ionization enthalpy of atomic hydrogen in terms of J mol–1.
Answer: Given that, the electron of hydrogen is having $-2.18 * 10^{-18} J$ in the ground state. Thus, To eject an electron from the ground state in a $H ($ hydrogen $)-$ atom, a certain amount of...
What is the significance of the terms — ‘isolated gaseous atom’ and ‘ground state’ while defining the ionization enthalpy and electron gain enthalpy?
Answer: In the ground state of an isolated gaseous atom, ionisation enthalpy is required to eject an electron. Even though the atoms are far separated in the gaseous state, there are some attraction...
