Solution:
Elements of group 14 (a) exhibit oxidation state of 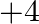 only (b) exhibit oxidation state of
only (b) exhibit oxidation state of 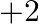 and
and 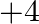 (c) form
(c) form 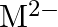 and
and 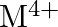 ion (d) form
ion (d) form 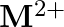 and
and 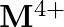 ions
ions
Solution: (b) Group 14 components have 4 valence electrons. Thus, bunch oxidation status is $+4$. In any case, the lower oxidation state turns out to be progressively steady because of the inactive...
An aqueous solution of borax is 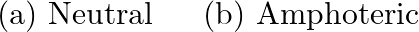

Solution: (b) Borax is a strong base salt (NaOH) and a feeble corrosive $\left(\mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{BO}_{3}\right)$. In this way, it is essential thing in nature.
Give one method for industrial preparation and one for laboratory preparation of CO and 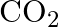 each.
each.
Solution: Carbon dioxide CO2 can be ready in the lab through the activity of weaken hydrochloric corrosive on calcium carbonate. Their response is as per the following: CO2 is industrially ready by...
Write balanced equations for: 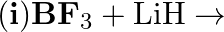 (ii)
(ii) 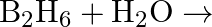 (iii)
(iii) 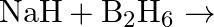 (iv)
(iv) 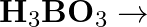 (v)
(v) 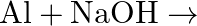 (vi)
(vi) 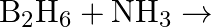
Solution: The balanced equations are as follow:
A certain salt 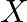 gives the following results. (i) Its aqueous solution is alkaline to litmus. (ii) It swells up to a glassy material
gives the following results. (i) Its aqueous solution is alkaline to litmus. (ii) It swells up to a glassy material 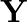 on strong heating. (iii) When conc.
on strong heating. (iii) When conc. 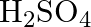 is added to a hot solution of
is added to a hot solution of 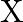 , a white crystal of an acid
, a white crystal of an acid 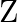 separates out Write equations for all the above reactions and identify X,
separates out Write equations for all the above reactions and identify X, 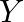 , and
, and 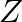 .
.
Solution: The salt given to litmus is antacid. $X$ is, subsequently, a salt with a solid base, and a feeble corrosive. When $X$ is warmed unnecessarily, it additionally enlarges to frame material...
When metal 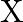 is treated with sodium hydroxide, a white precipitate (A) is obtained, which is soluble in excess of
is treated with sodium hydroxide, a white precipitate (A) is obtained, which is soluble in excess of 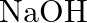 to give soluble complex (B). Compound (A) is soluble in dilute HCI to form compound (C). The compound (A) when heated strongly gives (D), which is used to extract the metal. Identify (X), (A), (B), (C) and (D). Write suitable equations to support their identities.
to give soluble complex (B). Compound (A) is soluble in dilute HCI to form compound (C). The compound (A) when heated strongly gives (D), which is used to extract the metal. Identify (X), (A), (B), (C) and (D). Write suitable equations to support their identities.
Solution: The given metal $X$ gives sodium hydroxide to a white accelerate, and the encourage breaks up surpassing sodium hydroxide. $X$ must, consequently, be made of aluminum. The acquired white...
(a) Classify the following oxides as neutral, acidic, basic or amphoteric. 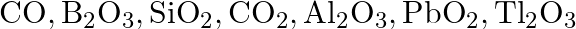 (B) Write suitable equations to show their nature.
(B) Write suitable equations to show their nature.
Solution: $\rightarrow$ CO $=$ Neutral $\rightarrow \mathrm{B}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}=$ Acidic Being acidic, it responds with bases to frame salts. It responds with $\mathrm{NaOH}$ to frame sodium...
What are allotropes? Sketch the structure of two allotropes of carbon namely diamond and graphite. What is the impact of structure on the physical properties of two allotropes?
Solution: Allotropy is the presence of a component in more than one structure, having diverse actual properties however similar substance properties. Diamond's solid 3-D construction makes it a...
How would you explain the lower atomic radius of Ga as compared to Al?
Solution: A tomic sweep (in pm) Aluminum Gallium In spite of the fact that Ga has more than one shell than Al, it is more modest in size than Al. This is on the grounds that the $3 \mathrm{~d}$...
Explain why is there a phenomenal decrease in ionization enthalpy from carbon to silicon?
Solution: Carbon ionizing enthalpy (the primary component in bunch 14 ) is exceptionally high $(1086 \mathrm{~kJ}/\mathrm{mol})$. That is normal on account of its little size. Nonetheless, there is...
Explain the following reactions (a) Silicon is heated with methyl chloride at high temperature in the presence of copper; (b) Silicon dioxide is treated with hydrogen fluoride; (c) CO is heated with ZnO; (d) Hydrated alumina is treated with aqueous 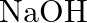 solution.
solution.
Solution: (a) Silicon is warmed with methyl chloride at high temperature within the sight of copper A class of organosilicon polymers called methyl-subbed chlorosilane $\mathrm{MeSiCl}_{3},...
What happens when (a) Borax is heated strongly (b) Boric acid is added to water (c) Aluminum is treated with dilute NaOH (d)  is reacted with ammonia?
is reacted with ammonia?
Solution: (a) Borax is warmed firmly Borax goes through different changes when warmed. It is losing atoms and expands of water right away. Then, at that point, it turns into a clear fluid, which...
Explain the structures of diborane and boric acid.
Solution: (a) Diborane $\mathrm{B}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{6}$ is a compound that does not have an electron. $\mathrm{B}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{6}$ just has 12 electrons $-6 \mathrm{e}^{-}$of $6 \mathrm{H}$...
Aluminium trifluoride is insoluble in anhydrous HF but dissolves when NaF is added. It precipitates out of the resulting solution when gaseous 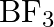 (boron trifluoride) is bubbled through. Give reasons.
(boron trifluoride) is bubbled through. Give reasons.
Solution: Hydrogen fluoride is a covalent compound with an exceptionally solid intermolecular clinging to hydrogen. Along these lines, it doesn't give particles and doesn't break up aluminum...
If B-CI bond has a dipole moment, explain why 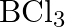 molecule has zero dipole moment.
molecule has zero dipole moment.
Solution: The $B-C l$ bond is normally polar as a result of the distinction in the electronegativities of $\mathrm{Cl}$ and $B$. However the particle of $\mathrm{BCl}_{3}$ is non-polar. That is on...
Suggest reasons why the B-F bond lengths in 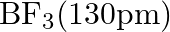 and
and 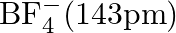 differ.
differ.
Solution; In $\mathrm{BF}_{3}$, the length of the $\mathrm{B}-\mathrm{F}$ bond is more limited than that of the $\mathrm{B}-\mathrm{F}$ bond in $\mathrm{BF}_{4}^{-} \cdot \mathrm{BF}_{3}$ is an...
Rationalize the given statements and give chemical reactions: – Lead (II) chloride reacts with 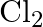 to give
to give 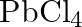 . – Lead (IV) chloride is highly unstable towards heat. – Lead is known not to form an iodide,
. – Lead (IV) chloride is highly unstable towards heat. – Lead is known not to form an iodide, 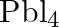 .
.
Solution: - Lead is an individual from bunch 14 of the occasional table. The two oxidation situations with bunch shows are $+2$ and $+4$. The $+2$ oxidation state turns out to be more steady when...
Explain the difference in properties of diamond and graphite on the basis of their structures.
Solution: Diamond: 1. It has a glasslike grid 2. In precious stone, every carbon molecule is sp3 hybridized and attached to four other carbon particles through a sigma bond. 3. It has an unbending...
What is the state of hybridisation of carbon in (a) 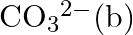 diamond (c) graphite?
diamond (c) graphite?
Solution: The condition of hybridization of carbon in: (a) $C O_{3}^{2-}$ c in $\mathrm{CO}_{3}^{2-}$ is sp $^{2}$ hybridized and is attached to 3 oxygen iotas. (b) Diamond Every precious stone...
Write the resonance structures of 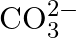 and
and 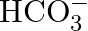 .
.
Solution: For $C O_{3}^{2-}$ There are just 2 resounding designs for the bicarbonate particle. For $\mathrm{HCO}_{3}^{-}$
Write reactions to justify amphoteric nature of aluminium
Solution: Amphoteric substances will be substances that display both acidic and essential characteristics. Since aluminum breaks up in the two acids and bases, it is said to have an amphoteric...
Describe the shapes of 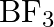 and
and 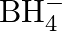 . Assign the hybridisation of boron in these species
. Assign the hybridisation of boron in these species
Solution: (I) $\mathbf{B} \boldsymbol{F}_{3}$ Boron will in general shape monomeric covalent halides in view of its little size and high electronegativity. These halides of boron generally have a...
Explain what happens when boric acid is heated .
Solution: After warming orthoboric corrosive at a temperature of $370 \mathrm{~K}$ or above, it is changed over into metaboric corrosive and, upon additional warming, yields boric oxide...
Is boric acid a protic acid? Explain.
Solution: Boric corrosive is a powerless monobasic corrosive which acts as a Lewis corrosive. In this way, it's anything but a protic corrosive. $\mathrm{B}(\mathrm{OH})_{3}+2 \mathrm{HOH}...
Consider the compounds, 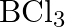 and
and 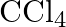 . How will they behave with water? Justify.
. How will they behave with water? Justify.
Solution: Since it is a Lewis corrosive, $\mathrm{BCl}_{3}$ promptly goes through hydrolysis to frame boric corrosive. $\mathrm{BCl}_{3}+3 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow 3...
Why does boron trifluoride behave as a Lewis acid?
Solution: The electronic arrangement of boron is $n s^{2} n p^{1}$. It contains 3 electrons in its valence shell. In this way, it can frame just 3 covalent bonds which imply that there are just 6...
How can you explain the higher stability of 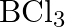 as compared to
as compared to 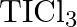 ?
?
Solution: Thallium and boron have a place with bunch 13 of the intermittent table and $+1$ oxidation state turns out to be more steady as we drop down the gathering. Boron is more steady than...
Discuss the pattern of variation in the oxidation states of (i) 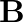 to
to 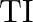 (ii)
(ii)  to
to 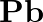
Solution: (I) $B$ to $\mathrm{TI}$ Gathering 13 components have their electronic design of $\mathrm{ns}^{2} \mathrm{np}^{1}$ and the oxidation state displayed by these components ought to be 3 ....
Thermodynamically the most steady type of carbon is (a) Diamond (b) Graphite (c) Fullerenes (d) Coal
Solution: (b) Graphite is thermodynamically the most steady type of carbon.
The kind of hybridization of boron in diborane is (a) sp (b)sp2 (c) sp3 (d) dsp2
Solution: (c) Boron in diborane is sp3 hybridized.
What do you comprehend by Catenation?
Solution: Catenation A few components or particles (like carbon) may interface with one another through solid covalent bonds to shape long chains or branches. This trademark is known as catenation....
What do you comprehend by Allotropy
Solution: Allotropy Allotropy is the presence of a component in more than one structure, having distinctive actual properties yet similar synthetic properties. The various types of a component are...
What do you comprehend by Inert pair impact
Solution: Inert pair impact As one actions down the gathering, s-block electrons decline their propensity to take part in substance holding. This impact is known as the dormant pair impact. The...
In a portion of the responses, thallium takes after aluminum, while in others it looks like with the gathering I metals. Backing this assertion by giving some proof.
Solution: Thallium is a piece of the intermittent table gathering 13. For this gathering, the most widely recognized oxidation state is + 3. Heavier individuals from this gathering, nonetheless,...
Clarify why would that be an incredible decline in ionization enthalpy from carbon to silicon?
Solution: Carbon ionizing enthalpy (the principal component in bunch 14) is exceptionally high (1086 kJ/mol). That is normal due to its little size. Nonetheless, there is a sharp decline in enthalpy...
Give reasons: Aluminium wire is utilized to make transmission links.
Solution: Aluminum wire is utilized to make transmission links. Aluminium wires are good conductors of electricity and also it is cheap metal easily available, light in weight and also very ductile....
Give reasons: Aluminum utensils ought not be kept in water for the time being.
Solution: Aluminum utensils ought not be kept in water for the time being. The oxygen in water responds to make a dainty layer of aluminum oxide with aluminum. This layer keeps further response from...
Give reasons: Aluminum compounds are utilized to make airplane body.
Solution: Aluminum compounds are utilized to make airplane body. Aluminum has a high protection from elastic and is light. It might likewise be alloyed to various metals like Si, Mg, Cu, Mn and Zn....
Give reasons: Diamond is utilized as a rough
Solution: Diamond is utilized as a rough Carbon is sp3 hybridized in Diamond. With the assistance of solid covalent bonds, every carbon molecule is bound to four other carbon iotas. These covalent...
Give reasons: Graphite is utilized as the grease.
Solution: Graphite is utilized as the grease. Graphite has a layered construction, and the powers of frail van der Waals tie various layers of graphite together. These layers might slide one over...
Give reasons: A combination of weaken NaOH and aluminum pieces is utilized to open channel.
Solution: A combination of weaken NaOH and aluminum pieces is utilized to open the channel. Sodium hydroxide and aluminum respond to shape aluminate (III) sodium tetra hydroxy and hydrogen gas....
Give reasons: Conc.HNO3 can be moved in an aluminum holder.
Solution: Conc.HNO3 can be shipped in an aluminum holder. As it responds with aluminum to frame a slight defensive oxide layer on the aluminum surface, concentrated HNO3 can be put away and shipped...
How is the exorbitant substance of CO2 answerable for a dangerous atmospheric devation?
Solution: Carbon dioxide is a gas that is vital for our endurance. The expanded CO2 content in the climate, nonetheless, represents a genuine danger. An increment in petroleum product ignition,...
Recommend an explanation with regards to why CO is toxic.
Solution: Given its capacity to frame a complex with hemoglobin, carbon monoxide is profoundly toxic. The previous hinders restricting with oxygen by Hb. Subsequently, an individual passes on...
What are electron lacking mixtures? Are BCl3 and SiCl4 electron insufficient species? Clarify.
solution: Electron-lacking mixtures are substance compounds with inadequate octets that will in general get at least 1 electrons to finish their octet setups. BCl3 BCl3 is a genuine illustration of...
Match the species given in Column I with the hybridisation given in Column II.
(i) is b (ii) is c (iii) is b (iv) is a (v) is b (vi) is c
Match the species given in Column I with properties given in Column II.
(i) is c (ii) is d (iii) is a (iv) is e (v) is b
Complete the following chemical equations : Z + 3 LiAiH4 → X + 3 Lif + 3AIF3 3X + 3O2 → B2O3 + 3H2O
BF3 + 3LiAlH4 → B2H6 + 3LiF + 3AlF3 3B2H6 + 3O2 → B2O3 + 3H2O
Identify the compounds A, X and Z in the following reactions : (i) A + 2HCL + 5H2O → 2NaCI + X X → HBO2 → Z
A is Borax, which produces Orthoboric acid when it combines with HCl in the presence of water (X). When Orthoboric acid is heated, Metaboric is formed, and when heated further, the chemical Z, i.e....
Explain the following : (vii) Tl (NO3)3 acts as an oxidising agent. (viii) Carbon shows catenation property but lead does not.
(vii) The +3 oxidation state of Tl is less stable than the +1 oxidation state due to the weak shielding effect of the inner electronic orbitals. Because Tl's oxidation state is +3 in Tl(NO3)3, it...
Explain the following : (v) Pb4+ acts as an oxidising agent but Sn2+ acts as a reducing agent. (vi) Electron gain enthalpy of chlorine is more negative as compared to fluorine.
(v); Due to the inert pair effect, the lower oxidation state, i.e. +2, is more stable than the higher one while travelling from top to bottom in the group. As a result of the inert pair effect, Pb...
Explain the following : (i) Gallium has a higher ionisation enthalpy than aluminium. (ii) Boron does not exist as B3+ ion
(i)The effective nuclear charge of Ga is somewhat greater than that of Al due to the poor shielding of valence electrons by the intervening 3d electrons. (ii) Boron's valence shell has three...
Aluminium dissolves in mineral acids and aqueous alkalies and thus shows amphoteric character. A piece of aluminium foil is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sodium hydroxide solution in a test tube and on bringing a burning matchstick near the mouth of the test tube, a pop sound indicates the evolution of hydrogen gas. The same activity when performed with concentrated nitric acid, the reaction doesn’t proceed. Explain the reason.
Aluminium interacts with both acid and base to produce hydrogen gas, which pops and burns in the air. As a powerful oxidising agent, nitric acid produces a thin coating of aluminium oxide on the...
Carbon and silicon both belong to the group 14, but despite the stoichiometric similarity, the dioxides, (i.e., carbon dioxide and silicon dioxide), differ in their structures. Comment.
Because of its tiny size, carbon can form stable p-p bonds with itself and other small atoms like oxygen and nitrogen. In carbon dioxide, each oxygen atom has a p-p overlapping double bond with the...
The +1 oxidation state in group 13 and +2 oxidation state in group 14 becomes more and more stable with increasing atomic number. Explain.
The likelihood of s orbital electrons to form bonds diminishes down the group from group 13 and 14 due to inadequate shielding of s orbital electrons by d and f orbitals. The inner pair effect is...
Give reasons for the following: (i) CCl4 is immiscible in water, whereas SiCl4 is easily hydrolyzed. (ii) Carbon has a strong tendency for catenation compared to silicon.
I Because water is polar and CCl4 is non-polar, CCl4 is insoluble in water. There are no vacant orbitals on the carbon atom to absorb the electrons given by oxygen in water. Because Si possesses an...
Explain why the following compounds behave as Lewis acids? (i) BCl3
Because it possesses 6 electrons in its outermost orbital and an empty p orbital, BCL3 is an electron-deficient compound. As a result, it functions as a Lewis acid, accepting a single pair of...
Draw the structure of boric acid showing hydrogen bonding. Which species is present in water? What is the hybridisation of boron in this species?
[B(OH)4]–species are formed when boric acid interacts with water. B(OH)3 + 2H2O → [B(OH)4]– + H3O+ Boron hybridization is sp3 in this species.
Explain the nature of boric acid as a Lewis acid in water.
Boric acid is a weak monobasic acid that accepts electrons from a hydroxyl ion to behave as a Lewis acid. B(OH)3 + 2H2O → [B(OH)4]– + H3O+ Boric acid accepts OH-, resulting in the production of the...
Draw the structures of BCl3.NH3 and AlCl3 (dimer).
Which of the following statements are correct. Answer based on Fig.11.1. (i) The two bridged hydrogen atoms and the two boron atoms lie in one plane; (ii) Out of six B–H bonds two bonds can be described in terms of 3 centre 2-electron bonds. (iii) Out of six B-H bonds, four B-H bonds can be described in terms of 3 centres 2 electron bonds; (iv) The four-terminal B-H bonds are two centre-two electron regular bonds.
The solutions are I (ii), and (iv).
Which of the following statements are correct? (i) Fullerenes have dangling bonds (ii) Fullerenes are cage-like molecules (iii) Graphite is a thermodynamically most stable allotrope of carbon (iv) Graphite is slippery and hard and therefore used as a dry lubricant in Machines
The correct answers are II and (iii).
Me3SiCl is used during polymerisation of organic silicones because (i) the chain length of organic silicone polymers can be controlled by adding Me3SiCl (ii) Me3SiCl blocks the end terminal of a silicone polymer (iii) Me3SiCl improves the quality and yield of the polymer (iv) Me3SiCl acts as a catalyst during polymerisationSolution:
The correct answers are I and (ii).
The linear shape of CO2 is due to _________. (i) sp3 hybridisation of carbon (ii) sp hybridisation of carbon (iii) pπ– pπ bonding between carbon and oxygen (iv) sp2 hybridisation of carbonSolution:
The correct answers are II and (iii).
The reason for the small radius of Ga compared to Al is _______. (i) poor screening effect of d and f orbitals (ii) increase in nuclear charge (iii) presence of higher orbitals (iv) higher atomic number
The correct answers are I and (ii).
Cement, the important building material is a mixture of oxides of several elements. Besides calcium, iron and sulphur, oxides of elements of which of the group (s) are present in the mixture? (i) group 2 (ii) groups 2, 13 and 14 (iii) groups 2 and 13 (iv) groups 2 and 14
Option II is the correct response.
. Dry ice is (i) Solid NH3 (ii) Solid SO2 (iii) Solid CO2 (iv) Solid N2
Option III is the correct response.
The most commonly used reducing agent is (i) AlCl3 (ii) PbCl2 (iii) SnCl4 (iv) SnCl2
Option IV is the correct response.
Quartz is extensively used as a piezoelectric material, it contains ___________. (i) Pb (ii) Si (iii) Ti (iv) Sn
Option II is the correct response.
A compound X, of boron, reacts with NH3 on heating to give another compound Y which is called inorganic benzene. The compound X can be prepared by treating BF3 with Lithium aluminium hydride. The compounds X and Y are represented by the formulas. (i) B2H6, B3N3H6 (ii) B2O3, B3 N3 H6 (iii) BF3, B3N3 H6 (iv) B3N3H6, B2H6
Option I is the correct response.
In the structure of diborane (i) All hydrogen atoms lie in one plane and boron atoms lie in a plane perpendicular to this plane. (ii) 2 boron atoms and 4 terminal hydrogen atoms lie in the same plane and 2 bridging hydrogen atoms lie in the perpendicular plane. (iii) 4 bridging hydrogen atoms and boron atoms lie in one plane and two terminal hydrogen atoms lie in a plane perpendicular to this plane. (iv) All the atoms are on the same plane.
Option II is the correct response.
Silicon has a strong tendency to form polymers like silicones. The chain length of silicone, a polymer can be controlled by adding (i) MeSiCl3 (ii) Me2SiCl2 (iii) Me3SiCl (iv) Me4Si
Option III is the correct response.
The geometry of a complex species can be understood from the knowledge of type of hybridisation of orbitals of the central atom. The hybridisation of orbitals of the central atom in [Be(OH)4] – and the geometry of the complex are respectively (i) sp3, tetrahedral (ii) sp3, square planar (iii) sp3d2, octahedral (iv) dsp2, square planar
Option I is the correct response.
