[Fe( H2O)6 ]2+ and [ Fe( CN)6 ]2+ have H2O and CN- ligands respectively. CN- has a higher CFSE (crystal field splitting energy) than water because it is a strong field ligand. As a result,...
Write the electronic configurations of the elements with the atomic numbers 61, 91, 101 and 109.
A solution of [Ni(H2O)6]2+ is green but a solution of [Ni(CN)4]2– is colorless. Explain
[ Ni (H2O)6 ] is made up of the Ni+2 ion, which has a 3d8 electrical structure. Because H2O is a weak ligand, there are two unpaired electrons in this arrangement that cannot pair up. The d – d...
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[{{[\mathbf{Cr}{{(\mathbf{N}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{3}}})}_{\mathbf{6}}}]}^{\mathbf{3}+}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-39b74154417ca7572b9b77e89bc26feb_l3.png)
is paramagnetic while [Ni(CN)4]2– is diamagnetic. Explain why.
In [ Ni ( CN)4 ] 2−, Ni has an oxidation state of +2. Thus, it has d 8configuration.Ni 2+ : Because CN- is a strong field ligand, electrons in 3d orbitals couple. Ni 2+ undergoes dsp2 hybridization...
Name the members of the lanthanoid series which exhibit +4 oxidation states and those which exhibit +2 oxidation states. Try to correlate this type of behaviour with the electronic configurations of these elements.
In the parenthesis are the atomic numbers of the elements are given. Tb after forming Tb4+ attains a stable electronic configuration of [Xe] 4f7. Yb after forming Yb2+ attains a stable...
What is crystal field splitting energy? How does the magnitude of ∆o decide the actual configuration of d orbitals in a coordination entity?
The difference in energy between the two levels ( t2g and eg ) that have split from a degenerated d orbital due to the presence of a ligand is known as crystal-field splitting energy. It is...
Use Hund’s rule to derive the electronic configuration of Ce3+ ion, and calculate its magnetic moment on the basis of ‘spin-only’ formula.
Ce:1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p64f15d16s2 Ce3+:1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p64f1 Magnetic moment can be calculated by the formula: μ = [n(n+2)]1/2 Where, n = number of unpaired...
Which is the last element in the series of the actinoids? Write the electronic configuration of this element. Comment on the possible oxidation state of this element.
In the actinoid series, the last element is lawrencium, Lr. The atomic number of the element is 103 and its electronic configuration is [Rn] 5f14 6d1 7s2 . The most common oxidation...
What is the spectrochemical series? Explain the difference between a weak field ligand and a strong field ligand.
The Spectrochemical series is a set of common ligands arranged in ascending order of their crystal-field splitting energy (CFSE). CFSE readings are higher in strong field ligands. Weak field...
Draw a figure to show the splitting of d orbitals in an octahedral crystal field.
The chemistry of the actinoid elements is not so smooth as that of the lanthanoids. Justify this statement by giving some examples from the oxidation state of these elements.
Lanthanoids project 3 different oxidation states which are +2, +3, +4. Among these, the +3 oxidation state is the most common. Lanthanoids exhibit a limited number of oxidation states because of the...
What are inner transition elements? Decide which of the following atomic numbers are the atomic numbers of the inner transition elements : 29, 59, 74, 95, 102, 104.
Inner transition metals are the elements in which the last electron is entering in the f-orbital. The elements in which the 4f and the 5f orbitals are progressively filled are called f-block...
What are alloys? Name an important alloy which contains some of the lanthanoid metals. Mention its uses.
An alloy is defined as a solid solution of two or more elements present in a combined form in a metallic matrix. It can either be a partial solid solution or a complete solid solution. Alloys...
Indicate the steps in the preparation of: (i) KMnO4 from pyrolusite ore.
(i) Potassium permanganate ( KMnO4 ) can be prepared from pyrolusite (MnO2). The ore is fused with KOH in the presence of either atmospheric oxygen or an oxidising agent, such as KNO3 or...
Indicate the steps in the preparation of: (i) K2Cr2O7 from chromite ore. (ii) KMnO4 from pyrolusite ore.
(i) Potassium dichromate ( K2Cr2O7 ) is prepared from chromite ore (FeCr2O4) in the following steps. Step (1): Preparation of sodium chromate \[4FeC{r_2}{O_4} + 16NaOH + 7{O_2} \to...
Give examples and suggest reasons for the following features of the transition metal chemistry: (i) The highest oxidation state is exhibited in oxoanions of a metal.
(i) Oxygen is a strong oxidising agent due to its high electronegativity and small size. So, oxo-anions of a metal have the highest oxidation state. For example, in , the oxidation state of Mn is +7.
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entities on the basis of valence bond theory: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( i \right)\text{ }{{[Co{{({{C}_{2}}{{O}_{4}})}_{3}}]}^{3}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-efe43055f50042489c9d11ee26754efd_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( ii \right)\text{ }{{[Co{{F}_{6}}]}^{3-}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a46576bdb43c6d6939fb964ada245115_l3.png)
(i) Here, the oxidation state of cobalt is +3.Orbitals of Co 3+ ion : Oxalate is a field ligand with a low affinity. As a result, the electrons in the 3d orbital will not pair.Because there are six...
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entities on the basis of valence bond theory: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( i \right)\text{ }{{[Fe{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}}]}^{4}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c4239d4c20c9394384021fc803fa63f1_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( ii \right)\text{ }{{[Fe{{F}_{6}}]}^{3}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2cec302fc55db082efb330ec046bbe8e_l3.png)
(i) Here, the oxidation state of Fe is +3.Fe 2+ : Electronic configuration is 3d6Orbitals of Fe2+ ion : CN− is a strong field ligand, so it causes the unpaired 3d electrons to pair up: There are six...
What is the coordination entity formed when an excess of aqueous KCN is added to an aqueous solution of copper sulfate? Why is it that no precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained when ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[{{H}_{2}}S\left( g \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c8bf88a9a8a76dacccc6552af3570fa6_l3.png)
is passed through this solution?
As a result of the foregoing procedure, the coordination entity obtained is K2[Cu(CN)4 ].The above coordination entity does not ionize to produce Cu2+ ions since it is extremely stable. When...
Aqueous copper sulfate solution (blue in color) gives: (i) a green precipitate with aqueous potassium fluoride and (ii) a bright green solution with aqueous potassium chloride. Explain these experimental results.
The presence of [Cu( H2O)4]2+ ions in an aqueous CuSO4 solution gives it a blue colour. (i) As a result, when KF is introduced, H2O ligands are replaced by F- ligands, resulting in green [ CuF4 ]2+...
Write all the geometrical isomers of [Pt(NH3)(Br)(Cl)(py)] and how many of these will exhibit optical isomers?
None of the isomers exhibit optical isomerism.
Draw all the isomers (geometrical and optical) of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[{{[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}\left( en \right)]}^{+}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-3d4533747f86351d7cf03af6d4d2667f_l3.png)
Draw all the isomers (geometrical and optical) of: (i) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[{{[CoC{{l}_{2}}{{\left( en \right)}_{2}}]}^{+}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a90cf5dd5a070919003d67e7a6ddfc4f_l3.png)
(ii) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[{{[Co(N{{H}_{3}})Cl{{\left( en \right)}_{2}}]}^{2+}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-4265017b2224d863ef19cf033ef31c23_l3.png)
(i) (ii)
Draw the structures of optical isomers of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[{{[Cr{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}\left( en \right)]}^{+}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-826b87fdd17fb106f6e60bd3b147a0cf_l3.png)
Draw the structures of optical isomers of:
(i) [Cr(C2O4)3]3– (ii) [PtCl2(en)2]2+ Solution: (i) (ii)
How many geometrical isomers are possible in the following coordination entities? (i) [Cr(C2O4)3]3– (ii) [Co(NH3)3Cl3]
( i ) In [ Cr(C2O4)3] 3− no geometric isomers are present because it is a bidentate ligand. ( ii ) In [ Co( NH3)3 Cl3 ]two isomers are possible.
List various types of isomerism possible for coordination compounds, giving an example of each.
The various types of isomerism that can be observed in coordination compounds are 🙁 i ) Geometrical isomerism : ( ii ) Optical isomerism : (iii) Coordination isomerism :This kind of isomerism...
Using IUPAC norms write the systematic names of the following: (i) [Ni(NH3)6]Cl2 (ii) [Co(en)3]3+ (iii) [Ni(CO)4]
( i ) Hexaamminenickel(II) chloride ( ii ) Tris(ethane-1, 2-diammine) cobalt(III) ion ( iii ) Tetracarbonylnickel(0)
Using IUPAC norms write the systematic names of the following: (i) [Mn(H2O)6]2+ (ii) [NiCl4]2–
(i ) Hexaquamanganese(II) ion ( ii) Tetrachloridonickelate(II) ion
. Using IUPAC norms write the systematic names of the following: (i) [Ti(H2O)6]3+ (ii) [Co(NH3)4Cl(NO2)]Cl
(i ) Hexaquatitanium(III) ion ( ii ) Tetraamminichloridonitrito-N-Cobalt(III) chloride
Using IUPAC norms write the systematic names of the following: (i) [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 (ii) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NH2CH3)]Cl
( i ) Hexaamminecobalt(III) chloride ( ii ) Diamminechlorido(methylamine) platinum(II) chloride
Using IUPAC norms write the formulas for the following: (i) Tetrabromidocuprate(II) (ii) Pentaamminenitrito-N-cobalt(III)
( i ) [ Cu (Br)4] 2− ( ii ) [Co ( ONO )( NH3)5] 2+
Using IUPAC norms write the formulas for the following: (i) Potassium tri(oxalato)chromate(III) (ii) Hexaammineplatinum(IV)
(i ) K3 [ Cr ( C2O4)3] ( ii ) [ Pt (NH3)6] 4+
Using IUPAC norms write the formulas for the following: (i) Pentaamminenitrito-O-cobalt(III) (ii) Hexaamminecobalt(III) sulphate
(i ) [ Co (NO2) ( NH3)5] 2+ ( ii) [ Co( NH3)6]2 (SO4)3
Using IUPAC norms write the formulas for the following: (i) Diamminedichloridoplatinum(II) (ii) Potassium tetracyanidonickelate(II)
( i ) [ Pt ( NH3)2Cl2] ( ii) K2[ Ni(CN )4]
Using IUPAC norms write the formulas for the following: (i) Tetrahydroxidozincate(II) (ii) Potassium tetrachloridopalladate(II)
( i ) [Zn(OH)4]2 – ( ii ) K2[ Pd Cl4]
Specify the oxidation numbers of the metals in the following coordination entities:
Solution: (i) (ii) (iii)
Specify the oxidation numbers of the metals in the following coordination entities:
(i) 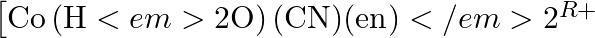
(ii) 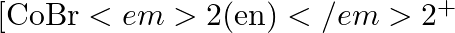
What is meant by unidentate, bidentate, and ambidentate ligands? Give two examples for each.
(a) Unidentate ligands: these are ligands with one donor site. Example Cl–, NH3 (b) Bidentate – these are ligands with two donor sites.Example – Ethane-1,2-diamine, Oxalate ion ( C2O42- ) (c)...
Explain with two examples each of the following: coordination entity, ligand, coordination number, coordination polyhedron, homoleptic and heteroleptic.
(a) Ligands are neutral chemicals or negative ions that are bonded to a metal atom in a coordination entity. Cl-, –OH as an exampleThey are electrically charged radicals or species. ( b )...
FeSO4 solution mixed with (NH4)2SO4 solution in 1:1 molar ratio gives the test of Fe2+ ion but CuSO4 solution mixed with aqueous ammonia in 1:4 molar ratio does not give the test of Cu2+ ion. Explain why.
When FeSO4is combined with (NH4)2SO4 in a 1: 1 molar ratio, a double salt is formed. FeSO4 (NH4)2SO4 .6H2O. This salt is in charge of supplying Fe 2+ . CuSO 4 in a 1:4 ratio with aqueous ammonia...
Explain the bonding in coordination compounds in terms of Werner’s postulates.
( a ) There are two types of valencies in metals: primary and secondary valencies. Primary valencies are satisfied by negative ions, and secondary valencies are filled by both neutral and negative...
Give examples and suggest reasons for the following features of the transition metal chemistry:
(i) The lowest oxide of transition metal is basic, the highest is amphoteric/acidic.
(ii) A transition metal exhibits highest oxidation state in oxides and fluorides.
(i) In the case of a lower oxide of a transition metal, the metal atom has a low oxidation state. This means that some of the valence electrons of the metal atom are not involved in bonding. As a...
Calculate the number of unpaired electrons in the following gaseous ions: Mn3+, Cr3+, V3+ and Ti3+. Which one of these is the most stable in aqueous solution?
Cr3+ is the most stable in aqueous solutions owing to a t2g3 configuration.
Which metal in the first series of transition metals exhibits +1 oxidation state most frequently and why?
In the first transition metal series, Cu exhibits +1 oxidation state very frequently because Cu has an electronic configuration of [Ar] 3d 10, that is, the completely filled d-orbital makes it...
What is meant by ‘disproportionation’? Give two examples of disproportionation reaction in aqueous solution.
It is found that sometimes a relatively less stable oxidation state undergoes an oxidation−reduction reaction in which it is simultaneously oxidised and reduced. This is called disproportionation....
The decomposition of 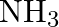 on platinum surface is zero order reaction. What are the rates of production of
on platinum surface is zero order reaction. What are the rates of production of 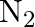 and
and 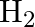 if
if 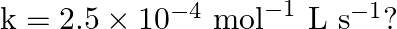
How would you account for the following? (i) The d1 configuration is very unstable in ions.
(i) The ions in d1 configuration tend to lose one more electron to get into stable d0 configuration. Also, the hydration or lattice energy is more than sufficient to remove the only electron present...
How would you account for the following?
(i) Of the d4 species, Cr2+ is strongly reducing while manganese(III) is strongly oxidising.
(ii) Cobalt(II) is stable in aqueous solution but in the presence of complexing reagents it is easily oxidised.
(i) Cr2+ is strongly reducing in nature. It has a d4 configuration. While acting as a reducing agent, it gets oxidized to Cr3+ (electronic configuration, d3). This...
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\text { For the reaction: } 2 A+B \rightarrow A_{2} B \text { is } k[A][B]^{2} \text { with } k=2.0 \times 10^{-6} \mathrm{~mol}^{-2} L^{2} \mathrm{~s}^{-1} \text {. }\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e9fea1165ffad66e28f91d69315a1de4_l3.png)
Calculate the initial rate of the reaction when ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com [\mathrm{A}]=0.1 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{~L}^{-1},[\mathrm{~B}]=0.2 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{~L}^{-1}](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d19cf8e34beaaae48c1bfcd427f9aa96_l3.png) . Calculate the rate of reaction after [A] is reduced to
. Calculate the rate of reaction after [A] is reduced to 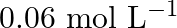
From the rate expression for the following reactions, determine their order of reaction and the dimensions of the rate constants.
(i) (ii) Solution: (i) (ii)
From the rate expression for the following reactions, determine their order of reaction and the dimensions of the rate constants.
Write the structure of the major organic product in each of the following reactions:
Solution:
Write the structure of the major organic product in each of the following reactions:
Solution: (i) (ii)
What happens when (i) methyl bromide is treated with sodium in the presence of dry ether, (Ii) methylchloride is treated with KCN.
(i) Ethane is generated when methyl bromide is reacted with sodium in the presence of dry ether. The Wurtz reaction is the name for this response. (ii)
What happens when (i) chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis, (ii) ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH
(i) Under normal circumstances, chlorobenzene does not hydrolyze. When heated in an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution at a temperature of 623 K and a pressure of 300 atm, it hydrolyzes to produce...
What happens when (i) n-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH, (ii) bromobenzene is treated with Mg in the presence of dry ether.
(i) The production of but-1-ene occurs when n-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH. A dehydrohalogenation process is what this is. (ii) Phenylmagnesium bromide is generated when bromobenzene...
Primary alkyl halide C4H9Br (a) reacted with alcoholic KOH to give compound (b). Compound (b) is reacted with HBr to give (c) which is an isomer of (a). When (a) is reacted with sodium metal it gives compound (d), C8H18 which is different from the compound formed when n-butyl bromide is reacted with sodium. Give the structural formula of (a) and write the equations for all the reactions.
The formula C4H9Br is used to make two main alkyl halides. They're n-butyl bromide and isobutyl bromide, respectively. Compound (a) is therefore either nbutyl bromide or isobutyl bromide. Compound...
The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in the presence of alcoholic KOH, alkenes are major products. Explain.
KOH almost entirely ionizes in an aqueous solution, yielding OH ions. Because the OH ion is a powerful nucleophile, it causes the alkyl chloride to undergo a substitution reaction, resulting in the...
p-Dichlorobenzene has higher m.p. and lower solubility than those of o- and m-isomers. Discuss.
The symmetrical nature of p-Dichlorobenzene is superior to that of the o- and m-isomers. As a result, it matches the crystal lattice better than the o- and m-isomers. As a result, breaking the...
Out of C6H5CH2Cl and C6H5CHClC6H5, which is more easily hydrolyzed by aqueous KOH?
The production of carbocation occurs during aqueous KOH hydrolysis. If the carbocation is stable, aqueous KOH can easily hydrolyze the compound. Now, C6H5 CH2Cl creates 1o– carbohydrate, whereas...
Arrange the compounds of each set in order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement: (i) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromopentane (ii) 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 3-Bromo-2- methylbutane (iii) 1-Bromobutane, 1-Bromo-2,2-dimethylpropane, 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1Bromo-3- methylbutane.
(i) The nucleophile approaches the carbon atom to which the leaving group is linked in an SN2 reaction. The reactivity for SN2 displacement reduces when the nucleophile is sterically inhibited. The...
What will be the mechanism for the following reaction?
Solution: The given reaction is CN- functions as a nucleophile, attacking the carbon atom that the Br is bonded to. The CN– ion is a nucleophile that can attack at both the C and N sites. In this...
Write the structure of the major organic product in each of the following reactions:
Solution:
Write the structure of the major organic product in each of the following reactions:
Solution:
Give the uses of freon 12, DDT, carbon tetrachloride and iodoform.
Freon -12 has a variety of applications. Freon-12 (dichlorodifluoromethane, CF2Cl2) is also known as CFC. It's found in deodorants, hair sprays, and other aerosol spray propellants. It's also...
Explain why (i) the dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride? (ii) alkyl halides, though polar, are immiscible with water? (iii) Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions?
(i) The Cl- atom in chlorobenzene is coupled to an sp2 hybridized carbon atom, whereas it is linked to an sp3 hybridized carbon atom in cyclohexyl chloride. The sp2 hybridized carbon atom is now...
How will you bring about the following conversions? (i) 1-Chlorobutane to n-octane (ii) Benzene to biphenyl.
(i) (ii)
How will you bring about the following conversions? (i) Bromomethane to propanone (ii) But-1-ene to but-2-ene
(i) (ii)
How will you bring about the following conversions? (i) Propene to propyne (ii) Ethanol to ethyl fluoride
(i) (ii)
How will you bring about the following conversions? (i) Propene to 1-nitropropane (ii) Toluene to benzyl alcohol
(i) (ii)
How will you bring about the following conversions? (i) Ethanol to but-1-yne (ii) Ethane to bromoethene
(i) (ii)
Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of the following halides with sodium ethoxide in ethanol and identify the major alkene: (i) 1-Bromo-1-methylcyclohexane (ii) 2-Chloro-2-methyl butane (iii) 2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane.
(i) 1−bromo−1−methylcyclohexane In the given molecule, all β-hydrogens are equivalent. As a result, only one alkene is produced when the given molecule is dehydrogenated. (ii) Different sets of...
Compare the chemistry of actinoids with that of the lanthanoids with special reference to: (i) oxidation state (ii) chemical reactivity.
(i) Oxidation states : The major oxidation state of lanthanoids is (+3). However, sometimes we also find oxidation states of +2 and +4. This occurs because of the extra stability of fully-filled and...
Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in SN2 reaction with –OH? (i) CH3Br or CH3I (ii) (CH3)3CCl or CH3Cl
(i) The order in which the halides react to an alkyl group is constant in the SN2 process. This is because as the size of the halide ion rises, it becomes a better leaving group. R-F << R-Cl...
Compare the chemistry of actinoids with that of the lanthanoids with special reference to:
(i) electronic configuration
(ii) atomic and ionic sizes
(i) Electronic configuration: The general electronic configuration for lanthanoids is [Xe]54 4f0-14 5d0-1 6s2 and that for actinoids is [Rn]86 5f1-14 6d0-1 7s2....
Compare the stability of +2 oxidation state for the elements of the first transition series.
From the table shown above we can deduce the following points: Mn shows maximum number of oxidation states, that ranges between +2 to +7.The number of oxidation states increases as we move on from...
What are ambident nucleophiles? Explain with an example.
The term ambident nucleophile refers to a nucleophile with two nucleophilic sites. These nucleophilic sites are targets for them to attack. For example, the nitrite ion. When the nitrite ion can...
Predict which of the following will be coloured in aqueous solution? Ti3+, V3+, Cu+, Sc3+, Mn2+, Fe3+ and Co2+. Give reasons for each.
Ions that have electrons in d-orbital will be the only ones that will impart colour and the ions with vacant d-orbital will remain colourless. All other ions, except Sc3+, will be coloured in...
Write the equations for the preparation of 1−iodobutane from: (i) 1-butanol (ii) 1-chlorobutane (iii) but-1-ene
(i) (ii) (iii)
For M2+/M and M3+/M2+ systems the EV values for some metals are as follows:
Cr2+/Cr = -0.9V Cr3/Cr2+ = -0.4 V
Mn2+/Mn = -1.2V Mn3+/Mn2+ = +1.5 V Fe2+/Fe = -0.4V Fe3+/Fe2+ = +0.8 V Use this data to comment upon: (i) the stability of Fe3+ in acid solution as compared to that of Cr3+ or Mn3+ and (ii) the ease with which iron can be oxidised as compared to a similar process for either chromium or manganese metal.
(i) The reduction potentials for the given pairs increase in the given order: Mn2+ / Mn < Cr2+ / Cr < Fe2+ /Fe So, the oxidation of Fe to Fe2+ is not as easy as the...
Write the isomers of the compound having formula C4H9Br.
(i) 1−Bromobutane (ii) 2−Bromobutane (iii) 1−Bromo−2−methylpropane (iv) 2−Bromo−2−methylpropane
A hydrocarbon C5H10does not react with chlorine in dark but gives a single monochloro compound C5H9Cl in bright sunlight. Identify the hydrocarbon.
C5H10 is a hydrocarbon with the chemical formula CnH2n, which belongs to the CnH2n group of hydrocarbons. As a result, it could be an alkene or a cycloalkane. Hydrocarbon cannot be an alkene because...
Describe the preparation of potassium permanganate. How does the acidified permanganate solution react with (i) iron(II) ions (ii) SO2 and (iii) oxalic acid?
Write the ionic equations for the reactions. The preparation of potassium permanganate can be done from pyrolusite (MnO2). The ore is fused with KOH in the presence of either atmospheric oxygen or...
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) CH3 C (p – Cl C6 H4 )2 CH(Br) CH3 (ii) (CH3 )3 C CH = C Cl C6 H4 I – p (i) 2−Bromo−3, 3−bis(4 − chlorophenyl) butane (ii) 1−chloro−1−(4−iodophenyl)−3,...
Describe the oxidising action of potassium dichromate and write the ionic equations for its reaction with:
(i) iodide (ii) iron(II) solution and (iii) H2S
In acidic medium, K2Cr2O7 behaves as a very strong oxidising agent. \[{K_2}C{r_2}{O_7} + 4{H_{2}}S{O_4} \to {K_2}S{O_{4}} + C{r_{2}}{(S{O_4})_{3}} + 4{H_2}O + 3[O]\;\] K2Cr2O7 gains electrons...
Describe the preparation of potassium dichromate from iron chromite ore. What is the effect of increasing pH on a solution of potassium dichromate?
Potassium dichromate is prepared from iron chromite ore through the following steps: Step 1: Preparation of sodium chromate: \[FeC{r_2}{O_4} + 16NaOH + 7{O_2} \to 8N{a_2}Cr{O_4} + 2F{e_2}{O_3} +...
How is the variability in oxidation states of transition metals different from that of the non transition metals? Illustrate with examples.
In transition elements, the oxidation state can vary from +1 to the highest oxidation state by the removal of all their valence electrons. Along with that. in transition elements, the oxidation...
What are interstitial compounds? Why are such compounds well known for transition metals?
Transition metals are large in size and they also contain many interstitial sites. These interstitial sites can be used to trap atoms of other elements (that have small atomic size), such as H, C, N...
Explain giving reasons:
(i) The transition metals generally form coloured compounds.(ii) Transition metals and their many compounds act as good catalyst. (i) Most of the complexes of transition metals are coloured as...
Explain giving reasons: (i) Transition metals and many of their compounds show paramagnetic behaviour.(ii) The enthalpies of atomisation of the transition metals are high.
i) Transition metals show paramagnetic behaviour. Paramagnetism is a phenomenon that arises due to the presence of unpaired electrons with each electron having a magnetic moment associated with...
What are the different oxidation states exhibited by the lanthanoids?
The most common oxidation state in the case of lanthanoids is +3 oxidation state. Thus, Ln(III) compounds are predominant. However, +2 and +4 oxidation states can also be found in the solution or in...
In what way is the electronic configuration of the transition elements different from that of the non transition elements?
Transition metals have a partially filled or incomplete d−orbital. Hence, the electronic configuration of transition elements is (n − 1)d1-10 ns0-2. The non-transition elements either do not...
What are the characteristics of the transition elements and why are they called transition elements? Which of the d-block elements may not be regarded as the transition elements?
Transition elements are those elements in which the atoms or ions (in stable oxidation state) contain partially filled or incomplete d-orbital. These elements are found in the d-block (as the...
Question 12.1: What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case. (v) Hemiacetal (vi) Oxime
Solution: (v) Hemiacetals are a type of α−alkoxyalcohols. A hemiacetal's overall structure. Aldehyde interacts with one molecule of monohydrated alcohol in the presence of dry HCl gas. (vi) Oxime:...
What is lanthanoid contraction? What are the consequences of lanthanoid contraction?
Across a period in the lanthanoid series, there is gradual increase in the atomic number which increases by one. With the increase in atomic number, the number of protons and electrons present in...
Name the oxometal anions of the first series of the transition metals in which the metal exhibits the oxidation state equal to its group number.
The name of the oxometal anions are as follows: (i) Chromate, CrO42- Oxidation state of Cr is + 6. (ii) Permanganate, MnO4- Oxidation state of Mn is + 7. (iii) Vanadate, VO3- Oxidation...
What may be the stable oxidation state of the transition element with the following d electron configurations in the ground state of their atoms: 3d3, 3d5, 3d8 and 3d4?
To what extent do the electronic configurations decide the stability of oxidation states in the first series of the transition elements? Illustrate your answer with examples.
Mn exhibits maximum oxidation states from +2 to +7 and it lies in the first half of the transition series. With an increase in atomic number of the elements, the stability of +2 oxidation state...
Explain briefly how +2 state becomes more and more stable in the first half of the first row transition elements with increasing atomic number?
In the given table, we can find the oxidation numbers of the elements in the first half of the first row of transition elements with increasing atomic number: Here, we can find that except Sc all...
Why are Mn2+ compounds more stable than Fe towards oxidation to their +3 state?
The electronic configuration of Fe2+ and Mn2+ ions are as follows: Fe2+ is [Ar]18 3d6. Mn2+ is [Ar]18 3d5. As it is known the half and completely filled orbitals have more...
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) Cl CH2 C ≡ C CH2 Br (iv) ( CCl 3) 3 CCl (i) 1 – Bromo – 4 – chlorobut – 2 – yne (ii) 2−(Trichloromethyl)−1,1,1,2,3,3,3−heptachloropropane
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) CH3 CH(Cl) CH(Br) CH3 (ii) CH F2 CBr ClF Solution: (i) 2−Bromo−3−chlorobutane (ii) 1−Bromo−1−chloro−1, 2, 2−trifluoroethane
Which one of the following has the highest dipole moment?
(i) CH2Cl2 (ii) CHCl3 (iii) CCl4 Solution: In CHCl3, the resultant of dipole moments of two C – Cl bonds is countered by the resultant of dipole moments of one CH bond and one C – Cl bond, as seen...
Write the structures of the following organic halogen compounds.
(i) 1 – Bromo – 4 – sec – butyl – 2 – methylbenzene (ii) 1 ,4 – Dibromobut – 2 – ene Solution: (i) (ii)
Write down the electronic configuration of:
The electronic configuration of the given elements in their respective oxidation states are: (i) Mn2+: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5 Or, [Ar]18 3d5 (ii) Th4+:...
Write down the electronic configuration of: (i) Co2+ (ii) Lu2+
The electronic configuration of the given elements in their respective oxidation states are: (i) Co2+: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d7 Or, [Ar]18 3d7 (ii) Lu2+:...
Write the structures of the following organic halogen compounds.
(i) 2 – Bromobutane (ii) 4 – tert – Butyl -3 –iodoheptane Solution: (i) (ii)
Write down the electronic configuration of:
The electronic configuration of the given elements in their respective oxidation states are: (i) Cu+: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 Or, [Ar]18 3d10 (ii) Ce+4 :...
Write the structures of the following organic halogen compounds.
(i) 1 -Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane (ii) 2 – (2 -Chlorophenyl) -1 –iodooctane Solution: (i) (ii)
Write down the electronic configuration of:
(i) Cr+3 (ii) Pm+3 The electronic configuration of the given elements in their respective oxidation states are: (i) Cr+3 : 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 Or, [Ar]18 3d3 (ii)...
Write the structures of the following organic halogen compounds.
(i) 2 -Chloro-3 -methylpentane (ii) p -Bromochlorobenzene Solution: (i) (ii)
Name the following halides according to the IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl ( primary, secondary, tertiary ), vinyl, or aryl halides.
(i) m-ClCH2C6H4CH2C(CH3)3 (ii) o-Br-C6H4CH(CH3)CH2CH3 Solution: (i) 1 – Chloromethyl – 3 − ( 2, 2 – dimethylpropyl ) benzene (Primary benzyl halide) (ii) 1 − Bromo − 2 – ( 1 − methylpropyl ) benzene...
Name the following halides according to the IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl ( primary, secondary, tertiary ), vinyl, or aryl halides
(i) CH3C(Cl)(C2H5)CH2CH3 (ii) CH3CH=C(Cl)CH2CH(CH3)2 Solution: (i) 3−Chloro−3–methylpentane (Tertiary alkyl halide) (ii) 3−Chloro−5−methylhex−2−ene (Vinyl halide)
Name the following halides according to the IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl ( primary, secondary, tertiary ), vinyl, or aryl halides
(i) CH3CH(CH3)CH(Br)CH3 (ii) CH3C(C2H5)2CH2Br Solution: (i) 2 − Bromo – 3 – methylbutane (Secondary alkyl halide) (ii) 1 − Bromo − 2 − ethyl − 2 – methylbutane (Primary alkyl...
Write structures of the compounds whose IUPAC names are as follows:
(i) Cyclopent – 3 – en – 1 – ol (ii) 4-Chloro-3-ethylbutan-1-ol. Solution: (i) (ii)
Write structures of the compounds whose IUPAC names are as follows:
(i) Cyclohexylmethanol (ii) 3 – Cyclohexylpentan – 3 – ol Solution: (i) (ii)
Write structures of the compounds whose IUPAC names are as follows:
(i) 1 – Ethoxypropane (ii) 2 – Ethoxy – 3 – methylpentane Solution: (i) structure of 1 – Ethoxypropane : (ii) Structure of 2 – Ethoxy – 3 – methylpentane...
Write structures of the compounds whose IUPAC names are as follows:
(i) 3 , 5 – Dimethylhexane – 1 , 3 , 5 – triol (ii) 2, 3 – Diethylphenol Solution: (i) (ii)
Write structures of the compounds whose IUPAC names are as follows:
(i) 2 – Methylbutan – 2 – ol (ii) 1–Phenylpropan–2–ol Solution: (i) (ii)
Give a mechanism for this reaction. (Hint: The secondary carbocation formed in step II rearranges to a more stable tertiary carbocation by a hydride ion shift from 3rd carbon atom)
Solution: The following procedure is involved in the above-mentioned steps of the reaction: Step 1: Protonation Step 2: Forming 2 ° carbonation by eliminating the water molecule Step 3: Rearranging...
Show how would you synthesize the following alcohols from appropriate alkenes?
(i) (ii) Solution: All the alcohols are formed by the hydration of alkenes in the acidic medium. The addition follows Markownikov’s rule. (i) 1-Methylcyclohexene can be used in the reaction. (ii)...
Write equations of the following reactions:(i) Bromination of anisole in ethanoic acid medium (ii) Friedel-Craft’s acetylation of anisole.
(i) (ii)
Write equations of the following reactions: (i) Friedel-Crafts reaction – alkylation of anisole.(ii) Nitration of anisole.
(i) (ii)
Write the mechanism of the reaction of HI with methoxymethane.
Step 1: Protonation of methoxymethane : Step 2: Nucleophilic attack of I – : Step 3: The methanol produced in the previous step is used to combine with another HI molecule, resulting in the...
Explain the fact that in aryl alkyl ethers.
(i) the alkoxy group activates the benzene ring towards electrophilic substitution and (ii) it directs the incoming substituents to ortho and para positions in the benzene ring. (i) The presence of...
Write the equation of the reaction of hydrogen iodide with:
(i) 1-propoxypropane (ii) methoxybenzene (iii) benzyl ethyl ether
Preparation of ethers by acid dehydration of secondary or tertiary alcohols is not a suitable method. Give reason.
The production of ethers with alcohol dehydration is a bimolecular process ( SN 2) that involves an alcohol molecule attacking a protonated alcohol molecule. The alkyl group should be free in the...
How is 1-propoxypropane synthesised from propan-1-ol? Write the mechanism of this reaction.
The process of dehydration is used to synthesize 1- propoxypropane from propan –1– ol. In the presence of protic acids (such as H2SO4, H3PO4), propan-1-ol dehydrates to yield 1 – propoxypropane....
How is 1-propoxypropane synthesized from propan-1-ol? Write the mechanism of this reaction.
Dehydration reaction can be used to synthesise 1- propoxypropane from propan –1– ol. In the presence of protic acids (such as H2SO4, H3PO4), propan-1-ol dehydrates to yield 1 –...
Illustrate with examples the limitations of Williamson synthesis for the preparation of certain types of ethers.
Williamson's synthesis is a flexible approach for making symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers. However, careful reactant selection is required for the synthesis of unsymmetrical ethers. Because the...
Write the names of reagents and equations for the preparation of the following ethers by Williamson’s synthesis:
(i) 2-Methoxy-2-methylpropane (ii) 1-Methoxyethane
Write the names of reagents and equations for the preparation of the following ethers by Williamson’s synthesis:
(i) 1-Propoxypropane (ii) Ethoxybenzene
Give IUPAC names of the following ethers:
1 -Ethoxy-4 -4 – dimethyl cyclohexane Ethoxybenzene
Give IUPAC names of the following ethers:
(i) 4-Nitroanisole(ii) 1-Methoxypropane
Give IUPAC names of the following ethers:
(i)1-Ethoxy-2-methylpropane(ii) 2-Chlorlo-l-methoxy ethane
Give a reason for the higher boiling point of ethanol in comparison to methoxymethane.
Because of the presence of the – OH group in ethanol, intermolecular H – bonding occurs, resulting in molecule interaction. To break these hydrogen bonds, more energy is required. Methoxymethane, on...
Give a reason for the higher boiling point of ethanol in comparison to methoxymethane.
Because of the presence of the –OH group in ethanol, intermolecular H–bonding occurs, resulting in molecule interaction. To break these hydrogen bonds, more energy is required. Methoxymethane, on...
Question 12.1: What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case. (iii) Semicarbazone (iv) Aldol
Solution: (iii) Semicabarbazone: Semicarbazone is made up of aldehydes and ketones, and it is generated when a ketone or aldehyde reacts with semicarbazide. The reaction type is condensation....
Question 12.1: What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case. (ii) Acetal
Acetal refers to gemdialkoxy alkanes with two groups of alkoxy at the terminal carbon atom. The alkyl group is...
15.1 What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case. (i) Cyanohydrin
Cyanohydrins are organic compounds having the formula RR'C(OH)CN, where R and R ‘ are alkyl or aryl groups. Aldehydes and ketones react with hydrogen cyanide in the presence of excess sodium cyanide...
Name the reagents used in the following reactions:
(i) Dehydration of propan-2-ol to propene.(ii) Butan-2-one to butan-2-ol. (i) Concentrated H2SO4 or H3PO4 (ii) catalytic hydrogenation or sodium borohydride (NaBH4) or lithium aluminium hydride...
Name the reagents used in the following reactions:
(i) Bromination of phenol to 2,4,6-tribromophenol.(ii) Benzyl alcohol to benzoic acid. (i) Bromine water (ii) Acidified potassium permanganate
Name the reagents used in the following reactions:
(i) Oxidation of primary alcohol to a carboxylic acid.(ii) Oxidation of primary alcohol to aldehyde. (i) NaBH4 or LiAlH4 to acidified KMnO4 (ii) Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)
How are the following conversions carried out?
(i) Ethyl magnesium chloride → Propan-1-ol.(ii) Methyl magnesium bromide → 2-Methylpropan-2-ol. (i) When ethyl magnesium chloride reacts with methane, an adduct is formed, resulting in propan–1–ol...
How are the following conversions carried out?
(i) Propene → Propan-2-ol.(ii) Benzyl chloride → Benzyl alcohol. (i) Propene is converted to propan–2–ol when it is treated with water in the presence of an acid catalyst. (ii) If benzyl chloride is...
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
The mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene takes place in the following three steps : Step 1 : Formation of ethyl oxonium by protonation of ethanol : Step 2 : Formation of a...
Explain the following with an example.
(i) Williamson ether synthesis.(ii) Unsymmetrical ether. (i) Williamson's ether synthesis is the process of obtaining ethers by treating an alkyl halide with a suitable sodium alkoxide. The sodium...
Explain the following with an example. (i) Kolbe’s reaction, (ii) Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
(i) Kolbe's reaction: When sodium phenoxide is heated with C02 at 400°C under 4-7 atmospheres and then acidified, the main result is 2-hydroxybenzoic acid (salicylic acid), with a minor amount of...
Give equations of the following reactions:
(i) Dilute HNO3 with phenol.(ii) Treating phenol with chloroform in the presence of aqueous NaOH. (i) (ii)
Give equations of the following reactions: (i) Oxidation of propan-1-ol with alkaline KMnO4solution, (ii) Bromine in CS2, with phenol.
(i) (ii)
Explain how does the –OH group attached to a carbon of benzene ring activates it towards electrophilic substitution.
Because the – OH group works as an electron-donating group, the electron density in the benzene ring increases. The resonance structure of phenol, as seen below, clearly demonstrates this. As a...
Explain why ortho nitrophenol is more acidic than ortho methoxyphenol.
An electron-withdrawing group is a nitro – group. The electron density in the O – H bond is reduced by the presence of this group in the ortho position. As a result, it is simpler to give away a...
Give two reactions that show the acidic nature of phenol. Compare the acidity of phenol with that of ethanol.
The acidic nature of phenol can be proven with the two reactions shown below : (i) Reaction with sodium: Phenol reacts with active metals like sodium to liberate Hydrogen gas. (ii) Reaction with...
Show how will you synthesize:
(i) 1-phenylethanol from a suitable alkene.(ii) cyclohexylmethanol using an alkyl halide by an SN2 reaction.(iii) pentan-1-ol using a suitable alkyl halide? (i) 1 – phenylethanol can be made by...
You are given benzene, conc.H2SO4and NaOH. Write the equations for the preparation of phenol using these reagents.
Write a chemical reaction for the preparation of phenol from chlorobenzene.
Chlorobenzene is mixed with NaOH (at 623 K and 320 atm pressure) to make sodium phenoxide, which is then acidified to produce phenol.
Write the mechanism of hydration of ethene to yield ethanol.
In the mechanism of hydration of ethene to create ethanol, three steps are involved. These are the actions to take: Step 1: Electrophilic action of H3O+ protonates ethene to create carbocation:...
Give the equations of reactions for the preparation of phenol from cumene.
Cumene is first oxidized in the presence of air to produce cumene hydroperoxide, which is then used to make phenol. The cumene hydroxide was then treated with dilute acid to produce phenol and...
While separating a mixture of ortho and para nitrophenols by steam distillation, name the isomer which will be steam volatile. Give reason.
o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol both have intramolecular H–bonding. Because intermolecular bonding exists in p–nitrophenol, the molecules are tightly bound together. As a result, o – nitrophenol is...
Give the structures and IUPAC names of monohydric phenols of molecular formula, C7H8O.
What is meant by the hydroboration-oxidation reaction? Illustrate it with an example.
The hydroboration–oxidation reaction is one in which borane is used to initiate the oxidation process. Propan–1–ol, for example, is made by subjecting propene to a hydroboration – oxidation...
Alcohols are comparatively more soluble in water than hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses. Explain this fact
Due to the presence of the –OH group, alcohols form H – bonds with water. As a result, alcohols are comparatively more soluble in water than hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses.
Explain why propanol has a higher boiling point than that hydrocarbon, butane.
Propanol undergoes intermolecular H-bonding due to the presence of the – OH group. Butane, on the other hand, does not have the same advantages. In order to dissolve the intermolecular hydrogen...
(i) Draw the structures of all isomeric alcohols of molecular formula C5H12O and give their IUPAC names. (ii) Classify the isomers of alcohols in question.
(a) CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-OH Pentan – 1 – ol (1 °) (ii) Primary alcohol: Pentan – 1 – ol ; 2 – Methylbutan – 1 – ol ; 3 – Methylbutan – 1 – ol ; 2, 2 – Dimethylpropan – 1 – ol Secondary alcohol:...
Write IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) 1 – Phenoxyheptane (ii) 2 – Ethoxybutane
Write IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) 1 – Methoxy – 2 – methyl propane (ii) Ethoxy benzene
Write IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) 2, 5 – Dimethylphenol (ii) 2, 6 – Dimethylphenol
Write IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) 2-Methylphenol (ii) 4 – Methyl phenol
Write IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) Butane – 2, 3 – diol (ii) Propane – 1, 2, 3 – triol
Write IUPAC names of the following compounds:
Solutions: (i) 2, 2, 4 -Trimethylpentan – 3 – ol (ii) 5 – Ethylheptane – 2, 4 – diol
How the following conversions can be carried out?
(i) tert-Butyl bromide to isobutyl bromide (ii) Aniline to phenylisocyanide Solutions: (i) (ii)
How the following conversions can be carried out?
(i) Chloroethane to butane (ii) Benzene to diphenyl Solutions: (i) (ii)
How the following conversions can be carried out?
(i) Chlorobenzene to p-nitrophenol (ii) 2-Bromopropane to 1-bromopropane Solutions: (i) (ii)
How the following conversions can be carried out?
(i) 2-Chloropropane to 1-propanol (ii) Isopropyl alcohol to iodoform Solution: (i) (ii)
How the following conversions can be carried out?
(i) Ethyl chloride to propanoic acid (ii) But-1-ene to n-butyliodide Solution: (i) (ii)
How the following conversions can be carried out?
(i) 2-Chlorobutane to 3, 4-dimethylhexane (ii) 2-Methyl-1-propene to 2-chloro-2-methylpropane Solution: (i) (ii)
How the following conversions can be carried out?
(i) Ethanol to propanenitrile (ii) Aniline to chlorobenzene Solution: (i) (ii)
How the following conversions can be carried out?
(i) Benzene to 4-bromonitrobenzene (ii) Benzyl alcohol to 2-phenylethanoic acid Solution: (i) (ii)
How the following conversions can be carried out?
(i) 1-Bromopropane to 2-bromopropane (ii) Toluene to benzyl alcohol Solution: (i) (ii)
How the following conversions can be carried out?
(i) Propene to propan-1-ol (ii) Ethanol to but-1-yne Solution: (i) (ii) OR
Predict conditions under which Al might be expected to reduce MgO.
After 13500C, the standard Gibbs free energy of formation of Al2O3 from Al is lower than that of MgO from Mg. As a result, Al can be expected to be able to reduce MgO at temperatures above 13500C.
Outline the principles of refining of metals by Vapour phase refining.
Vapour phase refining : It is a process of metal refining in which the metal is converted into a volatile compound, which is then decomposed to obtain the pure metal.(1) To accomplish this, the...
Outline the principles of refining of metals by Electrolytic refining.
It is the process of employing electricity to refine impure metals. The anode is impure metal, and the cathode is a thin sheet of pure metal in this process. The electrolyte is a metal-specific salt...
Outline the principles of refining of metals by Zone refining.
The premise behind this approach is that contaminants are more soluble in molten metal than in solid metal. A rotating circular heater slowly glides over an impure metal rod or bar in zone refining....
What is the role of graphite rod in the electrometallurgy of aluminium?
The anode in aluminium electrometallurgy is graphite, and the cathode iron is graphite lined. Electrolysis liberates O2, which combines with the graphite anode to produce CO2 and CO. If it hadn't...
Name the processes from which chlorine is obtained as a by-product. What will happen if an aqueous solution of NaCl is subjected to electrolysis?
Chlorine is obtained as a byproduct of the Down process. A fused mixture of CaCl2 and NaCl is electrolyzed at 873 K in this method. At the cathode, sodium is obtained, while Cl2 is released at the...
The choice of a reducing agent in a particular case depends on thermodynamic factor. How far do you agree with this statement? Support your opinion with two examples.
Ans: The graph of Gibbs energy ∆Gθ versus Temperature for the formation of solid oxides is shown above. This graph shows that if the ∆fGθ of a metal's oxide is more negative than the ∆fGθ of another...
Out of C and CO, which is a better reducing agent for ZnO?
At roughly 1673 K, ZnO is converted to Zn. The Gibbs free energy of formation of CO from C is smaller than the Gibbs free energy of formation of ZnO after 1073 K, and the Gibbs free energy of...
The value of ∆fG0 for formation of Cr2 O3 is – 540 kJmol−1 and that of Al2 O3 is – 827 kJmol−1 Is the reduction of Cr2 O3 possible with Al ?
Cr2O3 has a higher value of formation ( −540 kJ mol−1 ) than Al2O3 ( −827 kJ /mol ). Therefore, Al can reduce Cr2O3 to Cr. 2Al + (3/2)O2 ⇒ Al2O3 2Cr + (3/2)O2 ⇒ Cr2O3 Subtracting, 2Al +...
Why is zinc not extracted from zinc oxide through reduction using CO?
CO will not be able to reduce ZnO to Zn because the standard Gibbs free energy of formation of CO to CO2 is larger than that of Zn to ZnO. As a result, CO-assisted zinc oxide reduction is not...
How is leaching carried out in case of low grade copper ores?
When working with low-grade copper ores, bacteria or acids are utilised to leach the copper in the presence of air. Copper is introduced to the solution as Cu2+ ions in this method: Cu + 2H+ + ½...
What is the role of cryolite in the metallurgy of aluminium?
The basic functions of Na3AlF6 (Cryolite) are as follows: 1. Due to the presence of cryolite, the melting point of the solution drops from 2323 K to 1140 K. 2. Cryolite makes alumina a good...
Why copper matte is put in silica lined converter?
Cu2S and FeS are present in copper matte. When a hot blast of air passes through a molten matte in a silica coated converter, the matte's FeS oxidises to FeO. FeSiO3 (slag) is formed when FeO...
Differentiate between “minerals” and “ores”.
Minerals are substances that contain metals or metal compounds and are found in nature. Ores are rocks and minerals that can be mined for metals in a cost-effective and convenient manner. For...
How is ‘cast iron’ different from ‘pig iron”?
The iron obtained from a blast furnace is known as pig iron. It is 4 percent carbon and contains minor levels of additional impurities such as Si, P, S, and Mn.Cast iron is created by using a hot...
Giving examples, differentiate between ‘roasting’ and ‘calcination’.
Calcination is the process of converting carbonate and hydroxide ores to oxides by heating them to temperatures below their melting points while avoiding or limiting the presence of air.This...
How can you separate alumina from silica in a bauxite ore associated with silica? Give equations, if any.
The following steps are used to separate alumina from silica in bauxite ore that contains silica:To begin, the powdered ore is digested in a concentrated NaOH solution at 473 523 K and 35 36 bar...
Describe a method for refining nickel.
Mond's procedure is a nickel refinement technology. Heat is applied to nickel in the presence of carbon monoxide in this process, resulting in nickel tetracarbonyl, a volatile complex. Ni + 4CO ⇒...
What is the criterion followed while selecting the stationary phase of chromatography?
The stationary phase is chosen so that the constituents of the mixture have varying degrees of solubility in it. As a result, distinct elements move at different speeds through the phase, allowing...
