Option (i) is the answer. Anomers are cyclic configurations of monosaccharides that differ in structure at carbon-1. I and II are anomers in this case because they differ solely in carbon-1.
Three cyclic structures of monosaccharides are given below which of these are anomers.
Which of the following reactions of glucose can be explained only by its cyclic structure?
(i) Glucose forms pentaacetate.
(ii) Glucose reacts with hydroxylamine to form an oxime.
(iii) Pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine.
(iv) Glucose is oxidised by nitric acid to gluconic acid
Option (iii) is the answer. The absence of a free -CHO group is indicated by the fact that glucose pentaacetate does not react with hydroxylamine. Only the cyclic nature of glucose may explain this...
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
(i) I, II, III
(ii) II, III
(iii) I, II
(iv) III
Option (i) is the answer. The -OH group is on the lowest asymmetric carbon on the right side of the I, II, and III structures, which is similar to (+) glyceraldehyde.
Structure of a disaccharide formed by glucose and fructose is given below. Identify anomeric carbon atoms in monosaccharide units.
(i) ‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘a’ carbon of fructose.
(ii) ‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘e’ carbon of fructose.
(iii) ‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘b’ carbon of fructose.
(iv) ‘f’ carbon of glucose and ‘f ’ carbon of fructose.
Option (iii) is the answer. Anomeric carbon is carbon that is next to an oxygen atom in the cyclic structure of glucose or fructose. 'a' and 'b' are next to the oxygen atom, as illustrated in the...
Three structures are given below in which two glucose units are linked. Which of these linkages between glucose, units are between C1 and C4 and which linkages are between C1 and C6?
(i) (A) is between C1 and C4, (B) and (C) is between C1 and C6
(ii) (A) and (B) are between C1 and C4, (C) is between C1 and C6
(iii) (A) and (C) is between C1 and C4, (B) is between C1 and C6
(iv) (A) and (C) is between C1 and C6, (B) is between C1 and C4
Option (iii) is the answer (A) and (C) are in the Cl-C4 range, while (B) is in the Cl-C6 range.
Proteins can be classified into two types on the basis of their molecular shape i.e., fibrous proteins and globular proteins. Examples of globular proteins are : (i) Insulin (ii) Keratin (iii) Albumin (iv) Myosin
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers Globulular protein is the structure that develops when a chain of polypeptides coils around to form a spherical shape. Insulin and albumin, for example, are...
Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose?
(i) Amylose
(ii) Amylopectin
(iii) Cellulose
(iv) Glycogen
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Amylopectin and glycogen are both glucose branching polymers.
Amino acids are classified as acidic, basic or neutral depending upon the relative number of amino and carboxyl groups in their molecule. Which of the following is acidic?
Option (ii) and (iv) are the answers. Acidic amino acids have more than one -COOH group one against the –NH2 group.
Lysine, is _______________.
(i) α-Amino acid
(ii) Basic amino acid
(iii) Amino acid synthesised in the body
(iv) β-Amino acid
Option (i), (ii) and (iii) are the answers. (a)Lysine is a kind of amino acid with the structural formula . (b) Because the number of NH2 groups (2) is more than the number of COOH groups, it is a...
Which of the following monosaccharides are present as five-membered cyclic structure (furanose structure)? (i) Ribose (ii) Glucose (iii) Fructose (iv) Galactose
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. The five-membered cyclic structure of ribose and fructose is shown (furanose structures). They have a five-membered ring, similar to the foran compound....
In fibrous proteins, polypeptide chains are held together by ___________.
(i) van der Waals forces
(ii) disulphide linkage
(iii) electrostatic forces of attraction
(iv) hydrogen bonds
Option (ii) and (iv) are the answers. Disulphide linkage and hydrogen bonding hold polypeptide chains together in fibrous proteins.
Which of the following are purine bases?
(i) Guanine
(ii) Adenine
(iii) Thymine
(iv) Uracil
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers. Purines are made up of a six-membered nitrogen-containing ring fused together with a five-membered nitrogen-containing ring. Purine bases guanine and adenine...
Which of the following terms are correct about enzyme?
(i) Proteins
(ii) Dinucleotides
(iii) Nucleic acids
(iv) Biocatalysts
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Enzymes are protein molecules that act as biocatalysts in the body's chemical reactions.
Name the sugar present in milk. How many monosaccharide units are present in it? What are such oligosaccharides called?
Lactose is the sugar found in milk. Glucose and galactose are two monosaccharides found in lactose. Disaccharides are oligosaccharides that include two monosaccharide units.
How do you explain the presence of all the six carbon atoms in glucose in a straight chain?
When glucose is heated with HI for a long time, n-hexane develops, implying that all six carbon atoms are connected in a straight chain.
In nucleoside, a base is attached at 1C position of the sugar moiety. A nucleotide is formed by linking the phosphoric acid unit to the sugar unit of a nucleoside. At which position of sugar unit is the phosphoric acid linked in a nucleoside to give a nucleotide?
When a nitrogenous base is connected to the 1' position of a five-carbon sugar, a nucleoside is produced. The 5' carbon of the sugar in a nucleoside molecule is bonded to the 5' carbon of the sugar...
Name the linkage connecting monosaccharide units in polysaccharides.
Glycosidic linkages connect the monosaccharide units of polysaccharides. When an oxide bond is created between two monosaccharide units with the loss of a water molecule, it is called a glycosidic...
Under what conditions glucose is converted to gluconic and saccharic acid?
When glucose is treated with a mild oxidising agent like Br2 water, it is transformed to gluconic acid, a six-carbon carboxylic acid. When glucose is treated with nitric acid, it is transformed to...
The letters ‘D’ or ‘L’ before the name of a stereoisomer of a compound indicates the correlation of configuration of that particular stereoisomer. This refers to their relationship with one of the isomers of glyceraldehyde. Predict whether the following compound has ‘D’ or ‘L’ configuration.
On the left side of the C5 carbon atom, the –OH group is connected. As a result, the provided compound is in the 'L' configuration.
Which sugar is called invert sugar? Why is it called so?
Invert sugar is another name for sucrose. It comes from sugarcane and sugarbeet and is a naturally occurring sugar. When sucrose is hydrolyzed, the sign of rotation changes from Dextro (+) to laevo...
Amino acids can be classified as α-, β-, -, δ- and so on depending upon the relative position of the amino group concerning the carboxyl group. Which type of amino acids forms polypeptide chain in proteins?
The sort of amino acids that make up a polypeptide chain are -amino acids and alpha-amino acids, where the amino acid is linked to the -carbon in the molecule.
α-Helix is a secondary structure of proteins formed by twisting of the polypeptide chain into right-handed screw-like structures. Which type of interactions is responsible for making the a-helix structure stable?
The –NH group of each amino acid residue hydrogen is bound to the –C=O of an adjacent turn of the helix, forming a right-handed screw helix shape.
Some enzymes are named after the reaction, where they are used. What name is given to the class of enzymes which catalyse the oxidation of one substrate with simultaneous reduction of another substrate?
Enzyme oxidoreductases is the name given to a group of enzymes that catalyse redox processes. Alcohol Dehydrogenase, for example, aids in the reduction of alcohol levels in the human body when...
During curdling of milk, what happens to sugar present in it?
The sugar found in milk, lactose, is transformed to lactic acid during curdling, which is produced by bacteria.
How do you explain the presence of five —OH groups in the glucose molecule?
When glucose is acetylated using acetic anhydride (CH3CO)2O in the presence of ZnCl2, glucose pentaacetate is formed, confirming the presence of five –OH groups.
Why does compound (A) give below not form an oxime?
The chemical in question is glucose pentaacetate. The presence of a free –C=O group in glucose indicates the presence of a free carbonyl group, as does the synthesis of oxime from glucose. Because...
Why must vitamin C be supplied regularly in diet?
Because vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin, any excess is eliminated from the body on a regular basis. Vitamin C cannot be stored in the body, thus it must be consumed on a regular basis.
Sucrose is dextrorotatory but the mixture obtained after hydrolysis is laevorotatory. Explain.
Sucrose's aqueous solution is dextrorotatory, rotating plane-polarized light entering the solution 66.5 degrees to the right. When sucrose is hydrolyzed with dilute acids or invertase enzyme, two...
Amino acids behave like salts rather than simple amines or carboxylic acids. Explain
An amino acid has both a –NH2 and a –COOH group. The –COOH group loses a proton [H]+ in aqueous solution of the amino acid, while the –NH2 acquires a proton to create a zwitterion, which is a...
Protein found in a biological system with a unique three-dimensional structure and biological activity is called a native protein. When a protein in its native form, is subjected to a physical change like change in temperature or a chemical change like change in pH, denaturation of protein takes place. Explain the cause.
Hydrogen bonds and other intermolecular interactions connect the amino acid residues in proteins. The hydrogen bonds are disrupted when a physical or chemical change occurs, and the native protein...
How do you explain the presence of an aldehydic group in a glucose molecule?
Bromine water can be used to treat glucose, which results in the carboxylic acid gluconic acid, which verifies the presence of an aldehyde group.
Evaluate the definite integrals as limit of sums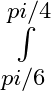 cosecx dx
cosecx dx
= = = = =
Evaluate the definite integrals as limit of sums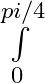 tanx dx
tanx dx
= = = = = =
Evaluate the definite integrals as limit of sums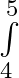 e^x dx
e^x dx
= = =
Evaluate the definite integrals as limit of sums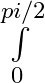 sin2x dx
sin2x dx
= = = = 0
Evaluate the definite integrals as limit of sums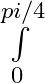 sin2x dx
sin2x dx
= = = = =
Evaluate the definite integrals as limit of sums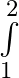 4x^3-5x^2 +6x+9 dx
4x^3-5x^2 +6x+9 dx
= = = = = = = = =
Evaluate the definite integrals as limit of sums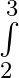 1/x dx
1/x dx
= = = = =
Evaluate the definite integrals as limit of sums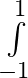 (x+1)dx
(x+1)dx
= = = = = =2
Evaluate the definite integrals as limit of sums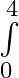 (x+e^2x)dx
(x+e^2x)dx
where and = = = = = = =
Evaluate the definite integrals as limit of sums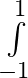 e^x dx
e^x dx
where and [ The series within brackets is a G.P. and ] = =
Evaluate the definite integrals as limit of sums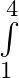 (x^2-x)dx
(x^2-x)dx
where Here, and = = = = = =
Evaluate the definite integrals as limit of sums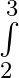 x^2 dx
x^2 dx
where Here, and = = = = =
Evaluate the definite integrals as limit of sums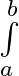 xdx
xdx
where Here, and = = = = = = =
Evaluate the definite integrals as limit of sums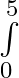 (x+1)dx
(x+1)dx
where and = = = = =
Evaluate the definite integrals as limit of sums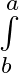 xdx
xdx
Since, where and = = = = = = =
Choose the correct answer in : ʃ√x^2-8x+7
= = = = Therefore, The correct option is option (D) .
Choose the correct answer in : ʃ√1+x^2
(A) (B) (C) (D) SOLUTION: = = = Therefore, The correct option is option (A) .
Integrate the functions: √1+(x^2/9)
= = = = =
Integrate the functions in √x^2+3x
= = = =
Integrate the functions in √1+3x-x^2
= = = = = = =
Integrate the functions in √x^2+4x-5
= = = =
Integrate the functions in √1-4x-x^2
= = = = = = =
Integrate the functions in √x^2+4x+1
= = = =
Integrate the functions in √x^2+4x+6
= = = =
Integrate the functions in √1-4x^2
= = = =
Integrate the functions in √4-x^2
= = =
Choose the correct option: The area bounded by the  -axis,
-axis, 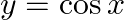 and
and 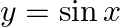 when
when 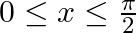
A. 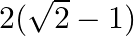
B. 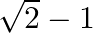
C. 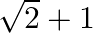
D. 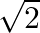
Solution: Given equations are $y=\cos x \ldots(1)$ And, $y=\sin x \ldots$ $\text { Required area }=\text { Area (ABLA) }+\text { area (OBLO) }$ $\begin{array}{l} =\int_{1}^{1} x d...
Choose the correct option: The area of the circle 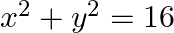 exterior to the parabola
exterior to the parabola 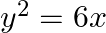 is
is
A. 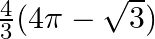
B. 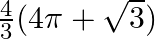
C. 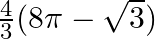
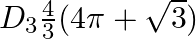
Solution: Given equations are $x^{2}+y^{2}=16 \dots \dots (1)$ $y^{2}=6x \dots \dots (2)$ The area bounded by the circle and parabola $=2[\text { Area }(\mathrm{OADO})+\text { Area...
Choose the correct option: Area bounded by the curve 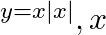 -axis and the ordinates
-axis and the ordinates 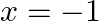 and
and 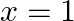 is given by [Hint:
is given by [Hint: 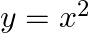 if
if 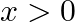 and
and 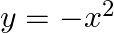 if
if 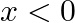 ]
]
A. 0
B. 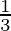
C. 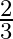
D. 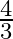
Solution: $\text { Required area }=\int_{-1}^{1} y d x$ $\begin{array}{l} =\int_{-1}^{1} x|x| d x \\ =\int_{-1}^{0} x^{2} d x+\int_{0}^{1} x^{2} d x \end{array}$ $\begin{array}{l}...
Choose the correct answer: Area bounded by the curve 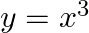 , the
, the 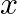 -axis and the ordinates
-axis and the ordinates 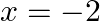 and
and 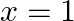 is
is
A. 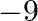
B. 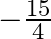
C. 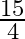
D. 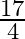
Solution: $\begin{array}{l} \text { Required area }=\int_{-2}^{1} y d x \\ =\int_{-2}^{1} x^{3} d x \\ =\left[\frac{x^{4}}{4}\right]_{-2}^{1} \end{array}$ $\begin{array}{l}...
Find the area of the region 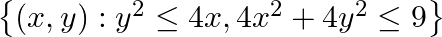
Solution: Eq. of parabola is $y^{2}=4 x$......(i) Eq. of circle is $4 x^{2}+4 y^{2}=9 \ldots \ldots$ (ii) From the diagram, the points of intersection of parabola (i) and circle (ii) are...
Using the method of integration find the area of the region bounded by lines: 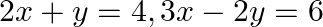 and
and 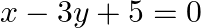
Solution: Given eqs. of lines are $\begin{array}{l} 2 x+y=4 \ldots(1) \\ 3 x-2 y=6 \ldots(2) \end{array}$ And, $x-3 y+5=0 \ldots$ (3) Area of the region bounded by the lines is the area of...
Using the method of integration find the area of the triangle ABC, coordinates of whose vertices are 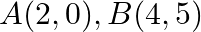 and
and 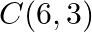
Solution: Vertices of $\triangle A B C$ are $A(2,0), B(4,5)$, and $C(6,3)$. Eq. of line segment $A B$ is $\begin{array}{l} y-0=\frac{5-0}{4-2}(x-2) \\ 2 y=5 x-10 \\ y=\frac{5}{2}(x-2) \end{array}$...
Find the area bounded by curves 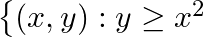 and
and 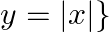
Solution: Area bounded by the curves, $\left\{(x, y): y \geq x^{2}\right.$ and $\left.y=|x|\right\}$, is represented by the shaded region as It can be observed that the required area is symmetrical...
Using the method of integration find the area bounded by the curve 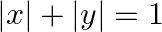 [Hint: the required region is bounded by lines
[Hint: the required region is bounded by lines 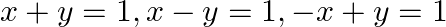 and
and 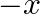
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com -y=11]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-5fcefea7abf57385227f72cfb8cccde1_l3.png)
Solution: Area bounded by the curve, $|x|+|y|=1$, is represented by the shaded region $\mathrm{ADCB}$ as The curve intersects the axes at points $A(0,1), B(1,0), C(0,-1)$, and $D(-1,0)$. It can be...
Find the area of the region enclosed by the parabola 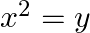 , the line
, the line 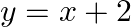 and
and 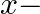 axis
axis
Solution: Area of the region enclosed by the parabola, $x^{2}=y$, the line, $y=x+2$, and $x$-axis is represented bv the shaded reaion $\mathrm{OABCO}$ as Point of intersection of the parabola,...
Find the area of the smaller region bounded by the ellipse 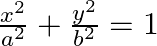 and the line
and the line 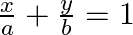
Solution: Area of the smaller region bounded by the ellipse, $\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1$, and the line, $\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{b}=1$ is represented by the shaded region BCAB as...
Find the area of the smaller region bounded by the ellipse 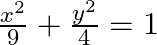 and the line,
and the line, 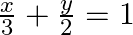
Solution: Area of the smaller region bounded by the ellipse, $\frac{x^{2}}{9}+\frac{y^{2}}{4}=1$, and the line, $\frac{x}{3}+\frac{y}{2}=1$ is represented by the shaded region BCAB as $\therefore$...
Find the area enclosed by the parabola 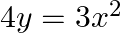 and the line
and the line 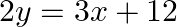
Solution: Area enclosed between the parabola, $4 y=3 x^{2}$, and the line, $2 y=3 x+12$, is represented by the shaded area OBAO as Points of intersection of the given curves are $A(-2,3)$ and...
Find the area enclosed between the parabola 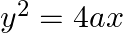 and the line
and the line 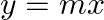
Solution: Area enclosed between the parabola, $y^{2}=4 a x$, and the line, $y=m x$, is represented by the shaded area $\mathrm{OABO}$ as Points of intersection of both the curves are $(0,0)$ and...
Find the area bounded by the curve 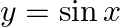 between
between 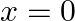 and
and 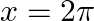
Solution: Graph of $y=\sin x$ can be drawn as $\therefore$ Required area $=$ Area OABO $+$ Area BCDB $\begin{array}{l} =\int_{0}^{\pi} \sin x d x+\left|\int_{k}^{2 \pi} \sin x d x\right| \\ =[-\cos...
Sketch the graph of 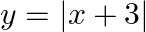 and evaluate
and evaluate 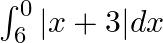
Solution: Given eq. is $y=|x+3|$ Corresponding values of $x$ and $y$ are given in the following table. $$\begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|l|l|l|l|l|} \hline$x$ & $-6$ & $-5$ & $-4$ & $-3$ & $-2$ & $-1$ & 0 \\...
Find the area of the region lying in the first quadrant and bounded by 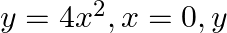
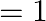 and
and 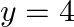
Solution: The area in the first quadrant is bounded by $y=4 x^{2}, x=0, y=1$, and $y=4$ is represented by the shaded area ABCDA as $\begin{aligned} \therefore \operatorname{Area} A B C D...
Find the area between the curves  and
and 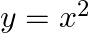
Solution: The area required is represented by the shaded area OBAO as The point of intersection of the curves $y=x$ and $y=x^{2}$ is A(1,1) Draw AC perpendicular to x-axis $\therefore$ Area...
Find the area under the given curves and given lines: (i) 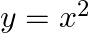 ,
, 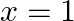 ,
, 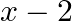 and x-axis (ii)
and x-axis (ii) 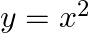 ,
,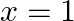 ,
, 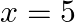 and x-axis.
and x-axis.
Solution: (i)The area required is represented by the shaded area ADCBA as $\begin{aligned} \text { Area } \mathrm{ADCBA} &=\int^{2} y d x \\ &=\int^{2} x^{2} d x \\...
Choose the correct answer: Area lying between the curves 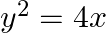 and
and 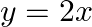 is:
is:
A. 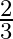
B. 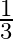
C. 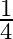
D. 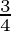
Solution: The area lying between the curve, $y^{2}=4 x$ and $y=2 x$, is represented by the shaded area OBAO as Points of intersection of these curves are $O(0,0)$ and $A(1,2)$. Draw AC perpendicular...
Choose the correct answer: Smaller area enclosed by the circle 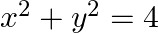 and the line
and the line 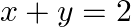 is
is
A. 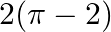
B. 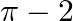
C. 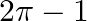
D. 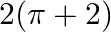
Solution: The smaller area enclosed by the circle, $x^{2}+y^{2}=4$, and the line, $x+y=2$, is represented by the shaded area ACBA as It is observed that, $\text { Area } A C B A=\text { Area } O A C...
Using integration find the area of the triangular region whose sides have the equations y 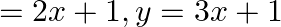 and
and 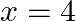
Solution: The eqs. of the sides of the triangle are $y=2 x+1, y=3 x+1$, and $x=4$. On solving these eqs., we get the vertices of triangle as $\mathrm{A}(0,1), \mathrm{B}(4,13)$, and $\mathrm{C}$...
Using integration finds the area of the region bounded by the triangle whose vertices are 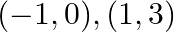 and
and 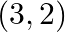
Solution: $\mathrm{BL}$ and $\mathrm{CM}$ are drawn perpendicular to $x$-axis. It is observed in the following figure that, Area $(\triangle \mathrm{ACB})=$ Area (ALBA) $+$ Area (BLMCB) - Area...
Find the area of the region bounded by the curves 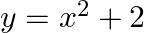 ,
,  ,
, 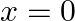 and
and 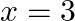 .
.
Solution: The area of the region bounded by the curves $y=x^{2}+2$, $y=x$, $x=0$ and $x=3$ is represented by the shaded area OCBAO as Therefore, Area of OCBAO = Area of ODBAO - Area of ODCO...
Find the area bounded by the curves 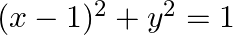 and
and 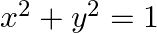
Solution: The area bounded by the curves $(x-1)^{2}+y^{2}=1$ and $x^{2}+y^{2}=1$ is reprsented by the shaded area as On solving the equations, $(x-1)^{2}+y^{2}=1$ and $x^{2}+y^{2}=1$, we get the...
Find the area of the circle 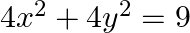 which is interior to the parabola
which is interior to the parabola 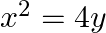 .
.
Solution: Required area is represented by the shaded area OBCDO On solving the given equation of circle, $4 x^{2}+4 y^{2}=9$, and parabola, $x^{2}=4 y$, we get $\mathrm{B}\left(\sqrt{2},...
Choose the correct answer: Area of the region bounded by the curve 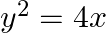 , y-axis and the line
, y-axis and the line 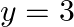 is
is
A.2
B.9\4
C.9\3
D.9\2
Solution: Area bounded by the curve, $y^{2}=4 x, y$-axis, and $y=3$ is represented as $\begin{aligned} \therefore \text { Area } \mathrm{OAB} &=\int_{0}^{3} x d y \\ &=\int_{0}^{3}...
Choose the correct answer: Area lying in the first quadrant and bounded by the circle 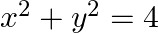 and the lines
and the lines 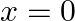 and
and 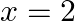 is
is
A.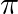
B.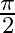
C.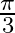
D.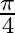
Solution: The area bounded by the circle and the lines, $x=0$ and $x=2$, in the first quadrant is represented as $\begin{aligned} \therefore \text { Area } \mathrm{OAB} &=\int_{0}^{2} y d x \\...
Find the area of the region bounded by the curve 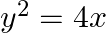
Solution: The region bounded by the parabola, $y^{2}=4 x$, and the line, $x=3$, is the area $\mathrm{OACO}$. Area of OACO is symmetrical about $x$-axis. $\therefore$ Area of $O A C O=2$ (Area of...
Find the area bounded by the curve 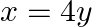 and the line
and the line 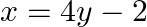
Solution: The area bounded by the curve, $x^{2}=4 y$, and line, $x=4 y-2$, is represented by the shaded area OBAO. Let's say $A$ and $B$ be the points of intersection of the line and parabola....
Find the area of the region bounded by the parabola  and the
and the 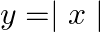 .
.
Solution: The area bounded by the parabola, $x^{2}=y$, and the line, $y=|x|$, can be represented as The given area is symmetrical about $y$-axis. $\therefore$ Area $\mathrm{OACO}=$ Area...
The area between 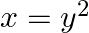 and
and 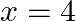 is divided into two equal parts by the line
is divided into two equal parts by the line  , find the value of a.
, find the value of a.
Solution: The line, $x=a$, divides the area bounded by the parabola and $x=4$ into two equal parts. $\therefore$ Area $O A D=$ Area $A B C D$ It is observed that the given area is symmetrical about...
Find the area of the smaller part of the circle  cutt off by the line
cutt off by the line 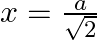
Solution: The area of the smaller part of the circle $x^{2}+y^{2}=a^{2}$ cutt off by the line $x=\frac{a}{\sqrt{2}}$ is the area of the ABCDA It can be observed that the area $A B C D$ is...
Find the area of the region in the first quadrant enclosed by x-axis, line 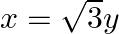 and the circle
and the circle 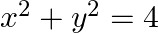
Solution: The area of the region bounded by the circle, $x^{2}+y^{2}=4, x=\sqrt{3} y$, and the $x$-axis is the area OAB. The point of intersection of the line and the circle in the first quadrant is...
Find the area of the region bounded by the ellipse 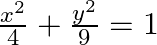
Solution: The given eq. of the ellipse can be represented as $\begin{array}{l} \frac{x^{2}}{4}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}=1 \\ \Rightarrow y=3 \sqrt{1-\frac{x^{2}}{4}} \end{array}$ It can be observed that the...
Find the area of the region bounded by the ellipse 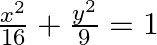
Solution: The given eq. of the ellipse, $\frac{{{x}^{2}}}{16}+\frac{{{y}^{2}}}{9}=1$ can be reprsented by It is observed that the ellipse is symmetrical about x-axis and y-axis. $\therefore$ Area...
Find the area of the region bounded by 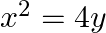 ,
, 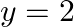 ,
, 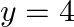 and the y-axis in the first quadrant.
and the y-axis in the first quadrant.
Solution: The area of the region bounded by $x^{2}=4y$, $y=2$, $y=4$ and the y-axis is the area of ABCD
Find the area of the region bounded by 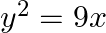 ,
, 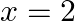 ,
, 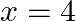 and the x-axis in the first quadrant.
and the x-axis in the first quadrant.
Solution: Area of the region bounded by the curve $y^{2}=9x$, $x=2$, $x=4$, \and the x-axis is the area of ABCD
Find the area of the region bounded by the curve 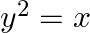 and the lines x=1, x=4 and the x-axis in the first quadrant.
and the lines x=1, x=4 and the x-axis in the first quadrant.
Solution:
Choose the correct option:
equals: (A) (B) (C) (D) SOLUTION: Let I = = It is in the form of since here and I = Therefore, The correct option is option (B) .
Choose the correct answer in :
equals to (A) (B) (C) (D) Ans. Let I = = ……….(i) Putting From eq. (i), I = = = Therefore, The correct option is option (B)...
Integrate the functions in-sin^(-1)(2x/1+x^2)
Putting = = = = = = = = = =
Assertion (A): (Fe(CN)6]3- ion shows magnetic moment corresponding to two unpaired electrons. Reason (R): Because it has d2sp3 type hybridisation.
(a) Assertion and Reason both are true, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (b) Assertion and Reason both are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (c) Assertion...
Integrate the functions in-e^(2x)sinx
Let I = = I = I = I = = 5I = I =
Integrate the functions in-(x-3)e^x/(x-1)^3
Let I = = = I = It is in the form of since here and = = . I =
Assertion (A): Complexes of MX6 and MX5L type (X and L are unidentate) do not show geometrical isomerism. Reason (R): Geometrical isomerism is not shown by complexes of coordination number 6.
(a) Assertion and Reason both are true, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (b) Assertion and Reason both are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (c) Assertion...
Integrate the functions in-e^x(1/x-1/x^2)
Let I = It is in the form of since here and I = =
Assertion (A): Linkage isomerism arises in coordination compounds containing ambidentate ligand. Reason (R): Ambidentate ligand has two different donor atoms.
(a) Assertion and Reason both are true, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (b) Assertion and Reason both are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (c) Assertion...
Assertion (A): [Cr(H2O)6]Cl2 and [Fe(H2O)6]Cl2 are reducing in nature. Reason (R): Unpaired electrons are present in their J-orbitals.
(a) Assertion and Reason both are true, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (b) Assertion and Reason both are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (c) Assertion...
Assertion (A): Toxic metal ions are removed by the chelating ligands. Reason (R): Chelate complexes tend to be more stable.
(a) Assertion and Reason both are true, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (b) Assertion and Reason both are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (c) Assertion...
Integrate the functions in-e^x(1+sinx/1+cosx)
Let I = = = = = It is in the form of since here and =
Integrate the functions in-xe^x/(1+x)^2
Let I = = = I = It is in the form of since here and I =
Integrate the functions in-e^x(sinx+cosx)
Let I = It is in the form of since here and I =
Match the compounds given in Column I with the oxidation state of cobalt present in it (given in Column II) and assign the correct code. with the oxidation state of cobalt present in it (given in Column II) and assign the correct code.
Solution: \[\left( c \right)\text{ }\left( A\text{ }\to \text{ }5 \right),\text{ }\left( B\text{ }\to \text{ }1 \right),\text{ }\left( C\text{ }\to \text{ }4 \right),\text{ }\left( D\text{...
Integrate the functions in-(x^2+1)logx
= = = = = =
Match the complex species given in Column I with the possible isomerism given in Column II and assign the correct code:
Solution: \[\left( d \right)\text{ }\left( A\text{ }\to 4 \right),\text{ }\left( B\to \text{ }1 \right),\text{ }\left( C\text{ }\to 2 \right),\text{ }\left( D\text{ }\to 3 \right)\] Isomerism...
Integrate the functions in-x(logx)^2
= = = = = = = =
Match the complex ions given in Column I with the hybridisation and number of unpaired electrons given in Column II and assign the correct code :
Solution: \[\left( a \right)\text{ }\left( A\text{ }\to \text{ }3 \right),\text{ }\left( B\text{ }\to 1 \right),\text{ }\left( C\text{ }\to \text{ }5 \right),\text{ }\left( D\to \text{ }2...
Integrate the functions in-tan^(-1)x
Let I = = = = = =
Match the coordination compounds given in Column I with the central metal atoms given in Column II and assign the correct code : Code : (i) A (5) B (4) C (1) D (2) (ii) A (3) B (4) C (5) D (1) (iii) A (4) B (3) C (2) D (1) (iv) A (3) B (4) C (1) D (2)
Solution: \[\left( b \right)\text{ }\left( A\text{ }\to 5 \right),\text{ }\left( B\text{ }\to \text{ }4 \right),\text{ }\left( C\text{ }\to \text{ }1 \right),\text{ }\left( D~\to 2 \right)\] ...
Integrate the functions in-xsec^(2)x
= = = = =
Integrate the functions in-xcos^(-1)x/√1-x^2
Let I = ……….(i) Putting I = = = = = = = = =
Match the complex ions given in Column I with the colours given in Column II and assign the correct code :
Solution: \[\left( b \right)\text{ }\left( A\text{ }\to 4 \right),\text{ }\left( B\text{ }\to \text{ }3 \right),\text{ }\left( C\text{ }\to \text{ }2 \right),\text{ }\left( D\text{ }\to \text{ }1...
Integrate the functions in-(sin^(-1)x)^2
Putting = = = = = = =
Integrate the functions in-xcos^(-1)x
Let I = ……….(i) Putting From eq. (i), I = = = = = = = Putting and = =
Name the type of isomerism when ambidentate ligands are attached to a central metal ion. Give two examples of ambidentate ligands.
Solution: Ambidendate ligands are those having diverse two restricting destinations. Example: Isothiocyanato Thiocyanato and Nitrite-N Nitrito-O The kind of isomerism when ambidentate ligands are...
CuSO4.5H2O is blue while CuSO4 is colourless. Why?
Solution: In CuSO4.5H2O, there are water particles that go about as ligands. The electrons will invigorate to higher d orbital and show tone. While, in CuSO4, there are no water particles to go...
Integrate the functions in-xtan^(-1)x
Let I = = = = = = = =
Give the electronic configuration of the following complexes based on Crystal Field Splitting theory. [CoF6]3–, [Fe(CN)6]4– and [Cu(NH3)6]2+.
Solution: \[{{[CO{{F}_{\mathbf{6}}}]}^{\mathbf{3}-}}:\text{ }C{{o}^{\mathbf{3}+}}~({{d}^{\mathbf{6}}})\]
Integrate the functions in-xsin^(-1)x
Let I = Putting I = = = = = = = = =
Which of the following complexes show linkage isomerism? (a) [CO(NH3)5(NO2)]2+ (b) [CO(H2O)5CO]3+ (c) [Cr(NH3)5SCN]2+ (d) [Fe(en)2Cl2]+
Solution: (a, c) NO2 and SCN are ambidentate ligands subsequently, show linkage isomerism.
Identify the correct statements for the behaviour of ethane-1, 2-diamine as a ligand. (a) It is a neutral ligand (b) It is a didentate ligand (c) It is a chelating ligand (d) It is a unidentate ligand
Solution: hence, option a, b and c are correct
Integrate the functions in- x^2logx
= = = = = =
Identify the optically active compounds from the following: (a) [Co(en)3]3+ (b) trans-[Co(en)2Cl2]+ (c) cis-[Co(en)2Cl2]+ (d) [Cr(NH3)5Cl]
Solution:
Integrate the functions in-xlog2x
= = = = = =
Integrate the functions in-xlogx
= = = = = =
Integrate the functions in- x^2e^x
= [Applying product rule] = = = = = = = =
Integrate the functions in- xsin3x
= = = = =
Integrate the functions in – xsinx
= = = = =
Choose the correct answer in each of the following:
equals: (A) (B) (C) (D) SOLUTION: Let I = = = …(i) Putting Putting this value in eq. (i), I = = I = = = = = = Therefore,The correct option is option...
Choose the correct answer in each of the following:
equals: (A) (B) (C) (D) SOLUTION: Let …….(i) = = = Therefore,The correct option is option (B).
Integrate the following function in- 1/(e^x-1)
Let I = …….(i) Putting From eq. (i), I = = = = = = = = = =
Integrate the following function in- 1/x(x^4-1)
Let I = = = …(i) Putting Putting this value in eq. (i), I = = I = = = = = =
Integrate the following function in- 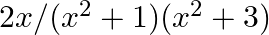
Let I = …….(i) Putting From eq. (i), I = = = = = = = = =
Integrate the following function in(x^2+1)(x^2+2)/(x^2+3)(x^2+4)
…….(i) Putting = …….(ii) = ….(iii) Let …….(iv) = = = = =
Integrate the following function in- cosx/(1-sinx)(2-sinx)
Let I = …….(i) Putting From eq. (i), I = = = = = = = = =
Integrate the following function in- 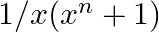
Let I = Multiplying both numerator and denominator by , I = = ……..(i) Putting From eq. (i), I = = = = = = = =
Integrate the following function in- 1/(x^4-1)
= Putting , = …..(i) Comparing the coefficients of A + B = 0 ……(ii) Comparing constants A – B = 1 …….(iii) On solving the eq. (ii) and (iii), we get A = B = Putting the values of A, B...
Integrate the following function in- 3x-1/(x+2)^2
Let I = …….(i) Putting Putting this value in eq. (i), I = = = = = = = = =
Integrate the following function in – 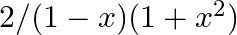
= …….(i) = = = = = = = =
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain the assertion. (ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explain the assertion. (iii) Both assertion and reason are the wrong statements. (iv) The assertion is correct statement and reason is the wrong statement. (v) The assertion is the wrong statement and reason is the correct statement.Assertion: Network polymers are thermosetting. Reason: Network polymers have high molecular mass.
Option (i) is correct During polymerisation, extensive cross linking results in the creation of a three-dimensional network that is rigid, insoluble, and infusible.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain the assertion. (ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explain the assertion. (iii) Both assertion and reason are the wrong statements. (iv) The assertion is correct statement and reason is the wrong statement. (v) The assertion is the wrong statement and reason is the correct statement. Assertion: For making rubber synthetically, isoprene molecules are polymerised. Reason: Neoprene (a polymer of chloroprene) is a synthetic rubber.
Option (v) is correct Natural rubber is made up of isoprene molecules, while neoprene, a synthetic rubber, is made up of chloroprene polymers.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain the assertion. (ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explain the assertion. (iii) Both assertion and reason are the wrong statements. (iv) The assertion is correct statement and reason is the wrong statement. (v) The assertion is the wrong statement and reason is the correct statement.Assertion: Polyamides are best used as fibres because of high tensile strength. Reason: Strong intermolecular forces (like hydrogen bonding within polyamides) lead to close packing of chains and increase the crystalline character, hence, provide high tensile strength to polymers.
Option (ii) is correct Polyamides, such as nylon, are the most often used fibres. Because of the strong intermolecular hydrogen connection, they have a high tensile strength.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain the assertion. (ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explain the assertion. (iii) Both assertion and reason are the wrong statements. (iv) The assertion is correct statement and reason is the wrong statement. (v) The assertion is the wrong statement and reason is the correct statement.Assertion: Most of the Synthetic polymers are not biodegradable. Reason: Polymerisation process induces toxic character in organic molecules.
Option (iv) is correct Enzymatic hydrolysis and environmental oxidation do not destroy the majority of synthetic polymers. Toxic characteristics are not produced via polymerization.
Match the polymers given in Column I with their repeating units given in Column II.
(i) is d (ii) is a (iii) is b (iv) is e (v) is c
Match the polymers given in Column I with the preferred mode of polymerisation followed by their monomers.
(i) is d (ii) is a (iii) is b
Match the polymers given in Column I with their main applications given in Column II.
(i) is d (ii) is e (iii) is a (iv) is f (v) is b (vi) is c
Match the polymers given in Column I with their commercial names given in Column II.
(i) is b (ii) is c (iii) is a (iv) is e (v) is d
Match the polymers given in Column I with their chemical names given in Column II.
(i) is c (ii) is a (iii) is b (iv) is e (v) is d
Which factor imparts crystalline nature to a polymer like nylon?
Intermolecular H –bonding exists between the two terminal groups –C=O and –NH, allowing one Nylon molecule to join another. Because intermolecular H –bonding is relatively strong, it can result in...
What is the structural difference between HDP and LDP? How does the structure account for different behaviour and nature, hence the use of a polymer?
HDP stands for high-density polymer with a linear structure, whereas LDP stands for low-density polymer with a branching structure. HDP has a greater melting point and is chemically inert, whereas...
Why does cis-polyisoprene possess elastic property?
The polymer may be stretched by applying force due to the presence of these weak forces. When the external force is released, the polymer recovers to its original condition, showing elastic...
How is the following resin intermediate prepared and which polymer is formed by this monomer unit?
The two starting monomers for this Resin intermediate are melamine and formaldehyde. Melamine polymer is the result of their condensed polymerization.
Can the enzyme be called a polymer?
The enzyme functions as a catalyst, speeding up biological processes. Proteins make up their structure. Proteins are polymers made up of monomeric units called amino acids. As a result, enzymes are...
Why are rubbers called elastomers?
Rubber may be stretched by applying force and then returned to its original shape once the force is removed. As a result, they are referred to as elastomers.
Identify the type of polymer given in the following figure.
This is a network or cross-linked polymer. Cross-linking connects two linear polymers.
Out of chain growth polymerisation and step-growth polymerisation, in which type will, you place the following.
In this illustration, a chain-growth polymerization process combines two monomers to produce a polymer. Only monomers react with each other to keep the chain expanding.
Which of the following complexes are heteroleptic? (a) [Cr(NH3)6]3+ (b) [Fe(NH3)4 Cl2]+ (c) [Mn(CN)6]4– (d) [Co(NH3)4Cl2]
Solution: (b, d) In complexes, [Fe(NH3)4Cl2]+ and [CO(NH3)4Cl2], metal is bonded to more than one sort of ligands subsequently, they are heteroleptic.
Which of the following complexes is homoleptic? (a) [Co(NH3)6]3+ (b) [Co(NH3)4 Cl2]+ (c) [Ni(CN)4]2– (d) [Ni(NH3)4Cl2]
Solution: (a, c) In complexes [Co(NH3)6]3+ and [Ni(CN)4]2-, both Co and Ni are connected to one sort of ligands just subsequently, they are homoleptic. hence, option a and c are correct
An aqueous pink solution of cobalt(II) chloride changes to deep blue on the addition of an excess of HCl. This is because____________. (a) [Co(H2O)6]2+ is transformed into [CoCl6]4– (b) [Co(H2O)6]2+ is transformed into [CoCl4]2– (c) tetrahedral complexes have smaller crystal field splitting than octahedral complexes. (d) tetrahedral complexes have larger crystal field splitting than octahedral complex.
Solution: (b, c) Aqueous pink arrangement of cobalt (II) chloride is because of electronic progress of electron from t2g to eg energy level of [Co(H2O)6]2+ complex. At the point when overabundance...
Which of the following polymers can have strong intermolecular forces? (i) Nylon (ii) Polystyrene (iii) Rubber (iv) Polyesters
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Nylon and polyester are thread-forming fibres with a high melting point and tensile strength. Intermolecular forces such as hydrogen bonding are strong.
Which of the following options are correct for [Fe(CN)6]3- complex? (a) d2sp3 hybridisation (b) sp3d2 hybridisation (c) Paramagnetic (d) Diamagnetic
Solution: hence, option a and c are correct for [Fe(CN)6]3- complex
Atomic number of Mn, Fe, Co and Ni are 25, 26 27 and 28 respectively. Which of the following outer orbital octahedral complexes have same number of unpaired electrons? (a) [MnCl6]3- (b) [FeF6]3- (c) [CoF6]3- (d) [Ni(NH3)6]2+
Solution: so, option a and c are the correct answer
Which of the following is an example of a synthetic rubber? (i) Polychloroprene (ii) Polyacrylonitrile (iii) Buna-N (iv) cis-polyisoprene
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. Polychloroprene and Buna-N are examples of a synthetic rubber
The atomic number of Mn, Fe and Co are 25, 26 and 27 respectively. Which of the following inner orbital octahedral complexions are diamagnetic? (a) [Co(NH3)6]3+ (b) [Mn(CN)6]3– (c) [Fe(CN)6]4– (d) [Fe(CN)6]3–
Solution: hence , a and c are the correct answer
IUPAC name of [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)] is (a) platinum diaminechloronitrite (b) chloronitrito-N-ammineplatinum (II) (c) diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum (II) (d) diamminechloronitrito-N-platinate (II).
Solution: (c) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)] is diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum (II)
What kind of isomerism exists between [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 (violet) and [Cr(H2O)5Cl)Cl2.H2O (greyish- green)? (a) Linkage isomerism (b) Solvate isomerism (c) Ionisation isomerism (d) Coordination isomerism
Solution: (b) The given mixtures have diverse number of water atoms inside and outside the organize circle.
Which of the following polymers are used as fibre? (i) Polytetrafluoroethane (ii) Polychloroprene (iii) Nylon (iv) Terylene
Option (iii) and (iv) are the answers. Because of strong intermolecular interactions such as H-bonding, nylon and terylene are employed as fibres, resulting in tight chain packing and therefore...
Which of the following polymers are thermoplastic? (i) Teflon (ii) Natural rubber (iii) Neoprene (iv) Polystyrene
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Teflon and polystyrene are thermoplastics because they can be melted and moulded anew.
Which of the following are characteristics of thermosetting polymers? (i) Heavily branched cross-linked polymers. (ii) Linear slightly branched long-chain molecules. (iii) Become infusible on moulding so cannot be reused. (iv) Soften on heating and harden on cooling, can be reused.
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. Thermosetting polymers have a lot of branching cross links. They can't be used again since they don't melt when heated and can't be remoulded.
Which of the following species is not expected to be a ligand? (a) NO (b) NH4– (c) NH2CH2CH2NH2 (d) CO
Solution: (b) Ligand should give a pair of electrons or inexactly held electron pair to metal and shape a M – L bond,
A chelating agent has two or more than two donor atoms to bind to a single metal ion. Which of the following is not a chelating agent? (a) Thiosulphate (b) Oxalato (c) Glycinato (d) Ethane-1, 2-diamine
Solution: (a) Thiosulphate or S2O3–isn't a chelating specialist since it is a monodentate ligand.
The compounds [Co(SO4)(NH3)5]Br and [CO(SO4)(NH3)5]Cl represent (a) linkage isomerism (b) ionization isomerism (c) coordination isomerism (d) no isomerism.
Solution: (d) [Co(SO4)(NH3)5]Br and [CO(SO4)(NH3)5]Cl address no isomerism since they are different compounds.
Due to the presence of ambidentate ligands coordination compounds show isomerism. Palladium complexes of the type [Pd(C6H5)2(SCN)2] and [Pd(C6H5)2(NCS)2] are (a) linkage isomers (b) coordination isomers (c) ionisation isomers (d) geometrical isomers
Solution: (a) The ligands having two distinctive holding locales are known as ambident ligands e.g., NCS, NO2, and so forth Here, NCS has two restricting locales at N and S. Subsequently, NCS...
The CFSE for octahedral [CoCl6]4– is 18,000 cm–1. The CFSE for tetrahedral [CoCl4]2– will be (a) 18,000 cm–1 (b) 16,000 cm–1 (c) 8,000 cm–1 (d) 20,000 cm–1
Solution:
Indicate the complex ion which shows geometrical isomerism. (a) [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]+ (b) [Pt(NH3)3 Cl] (c) [Co(NH3)6]3+ (d) [Co(CN)5(NC)]3–
Solution:
The correct IUPAC name of [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] is (a) diamminedichloridoplatinum (II) (b) diamminedichloridoplatinum (IV) (c) diamminedichloridoplatinum (I) (d) dichloridodiammineplatinum (IV)
Solution: (a) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] is diamminedichloridoplatinum (II) .
When 1 mol CrCl3.6H2O is treated with an excess of AgNO3, 3 mol of AgCl are obtained. The formula of the complex is : (a) [CrCl3 (H2O)3].3H2O (b) [CrCl2(H2O)4]Cl.2H2O (c) [CrCl(H2O)5]Cl2.H2O (d) [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3
Solution: (d) 3 mol of AgCl implies 3Cl are given in the arrangement henceforth, the equation of the complex will be [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3.
When 0.1 mol COCl3(NH3)5 is treated with excess of AgNO3, 0.2 mol of AgCl are obtained. The conductivity of solution will correspond to (a) 1:3 electrolyte (b) 1:2 electrolyte (c) 1:1 electrolyte (d) 3:1 electrolyte
Solution: (b) One mole of AgNO3 accelerates one mole of chloride particle. In the above response, when 0.1 mole COCl3(NH3)5 is treated with abundance of AgNO3, 0.2 mole of AgCl are obtained hence,...
The colour of the coordination compounds depends on the crystal field splitting. What will be the correct order of absorption of wavelength of light in the visible region, for the complexes, [Co(NH3)6]3+, [Co(CN)6]3–, [Co(H2O)6]3+ (a) [Co(CN)6]3–> [Co(NH3)6]3+>[Co(H2O)6]3+ (b) [Co(NH3)6]3+> [Co(H2O)6]3+> [Co(CN)6]3– (c) [Co(H2O)6]3+> [Co(NH3)6]3+> [Co(CN)6]3– (d) [Co(CN)6]3–> [Co(NH3)6]3+> [Co(H2O)6]3+
Solution:
Which of the following complexes formed by Cu2+ ions is most stable?
Solution: (b) The greater the value of log K, the more prominent will be strength of complicated compound shaped. For response, For this response, log K has most elevated worth among the...
Integrate the following function in
SOLUTION: = …….(i) [On dividing numerator by denominator] Let = = …….(ii) Comparing coefficients of : A + B = 2 …….(iii) Comparing constants: –A + B = 1 …….(iv) On solving eq. (iii) and...
Integrate the following function in
SOLUTION: = = …….(i) Comparing coefficients of : A + +B + C = 0 …….(ii) Comparing coefficients of : –B + 3C= 5 …….(iii) Comparing constants: –4A – 2B + 2C = 0 …….(iv) On solving eq. (i),...
Integrate the following function in
SOLUTION: = = …….(i) Comparing coefficients of : 2A + 2B + C = 0 …….(ii) Comparing coefficients of : 5A + B = 2 …….(iii) Comparing constants: 3A – 3B – C = –3 …….(iv) On solving eq. (i),...
Integrate the following function in
SOLUTION: = = = = = …….(i) Comparing coefficients of : A + C = 0 …….(ii) Comparing coefficients of : B – 2C= 3 …….(iii) Comparing constants: –2A + B + C = 5 …….(iv) On solving eq. (i),...
Integrate the following function in
SOLUTION: = …….(i) Comparing coefficients of : A + C = 0 …….(ii) Comparing coefficients of : A + B – 2C= 1 …….(iii) Comparing constants: –2A + 2B + C = 0 …….(iv) On solving eq. (i), (ii) and...
Integrate the following function in
SOLUTION: …….(i) Comparing coefficients of A + C = 0 …….(ii) Comparing coefficients of , –A + B = 1 …….(iii) Comparing constant terms, –B + C = 0 …….(iv) Solving eq. (ii), (iii) and (iv), we...
Integrate the (rational) function in
SOLUTION: = = = (Dividing numerator by denominator) = …….(i) Now = …….(ii) Comparing coefficients of on both sides –2A + B = …..(iii) Comparing constants A = 1 …….(iv) Solving eq....
Integrate the (rational) function in
SOLUTION: = = = = ….(i) Comparing coefficients of on both sides A + B = 2 …….(ii) Comparing constants 2A + B = 0 …..(iii) Solving eq. (ii) and (iii), we get A = and B = 4 Putting these...
Integrate the (rational) function in
SOLUTION: = …….(i) Comparing coefficients of : A + B + C = 0 …….(ii) Comparing coefficients of : –5A – 4B – 3C= 1 5A + 4B + 3C = –1 …….(iii) Comparing constants: 6A + 3B + 2C = 0 …….(iv) On...
Integrate the (rational) function in
SOLUTION: = …….(i) Comparing coefficients of : A + B + C = 0 …….(ii) Comparing coefficients of : –5A – 4B – 3C= 3 5A + 4B + 3C = –3 …….(iii) Comparing constants: 6A + 3B + 2C = –1 …….(iv) On...
Integrate the (rational) function in
SOLUTION: = = =
Integrate the (rational) function in
SOLUTION: …….(i) Comparing coefficients of on both sides A + B = 1 …..(ii) Comparing constants 2A + B = 0 …..(iii) Solving eq. (ii) and (iii), we get A = and B = 2 Putting these values of A...
