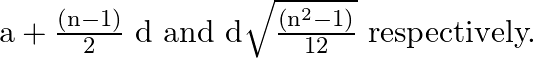Solution:
Given that the first ![]() terms of an A.P. whose first term is a and common difference is d Now we have to find mean and standard deviation
terms of an A.P. whose first term is a and common difference is d Now we have to find mean and standard deviation
Given AP in tabular form is shown below,
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|} \hline$x_{i}$ & $d_{i}=x_{i}-a$ & $d_{i}^{2}$ \\ \hline$a$ & 0 & 0 \\ \hline$a+d$ & $d$ & $d^{2}$ \\ \hline$a+2 d$ & $2 d$ & $4 d^{2}$ \\ \hline$a+3 d$ & $3 d$ & $9 d^{2}$ \\ \hline$-$ & $-$ & $-$ \\ \hline$a+(n-1) d$ & $(n-1) d$ & $(n-1)^{2} d^{2}$ \\ \hline \end{tabular}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-583e5e52b26d32788d27cb3bd749cd72_l3.png)
Assumed ![]() as mean.
as mean.
Given that the AP have ![]() terms. And it is known that the sum of all the terms of AP can be written as,
terms. And it is known that the sum of all the terms of AP can be written as,
![]()
Calculate the actual mean,
![]()
Substitute the corresponding values,
![]()
Above eq. can be written as
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \begin{aligned} &\bar{x}=\frac{[2 a+(n-1) d]}{2} \\ &\bar{x}=a+\frac{[(n-1) d]}{2} \\ &\bar{x}=a+\frac{(n-1)}{2} d \end{aligned}](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-31e945e1790366c7153507d8a0d547b0_l3.png)
The other two columns sums, i.e. ![]()
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \sum d_{i}=\sum\left(x_{i}-a\right)=d[1+2+3+\cdots+(n-1)]=d\left(\frac{n(n-1)}{2}\right)](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ea82e5d921f1061345ff60f95b4fa6db_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \sum \mathrm{d}_{\mathrm{i}}^{2}=\sum\left(\mathrm{x}_{\mathrm{i}}-\mathrm{a}\right)^{2}=\mathrm{d}^{2}\left[1^{2}+2^{2}+3^{2}+\cdots+(\mathrm{n}-1)^{2}\right]=\mathrm{d}^{2}\left(\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{n}-1)(2 \mathrm{n}-1)}{6}\right)](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-9583ea4fc094a02d038ed30dd198c4d9_l3.png)
The standard deviation is given by,
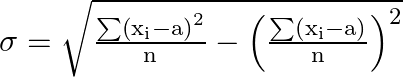
Substitute the corresponding values,
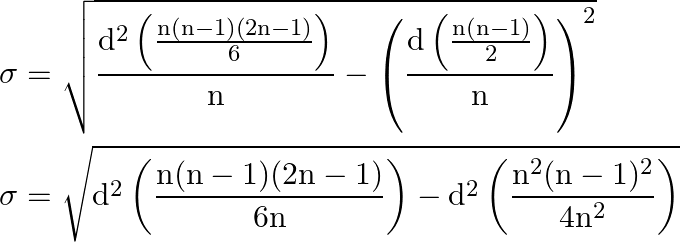
Cancel the like terms,
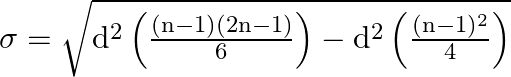
Take out the common terms
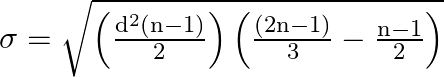
Taking the LCM,
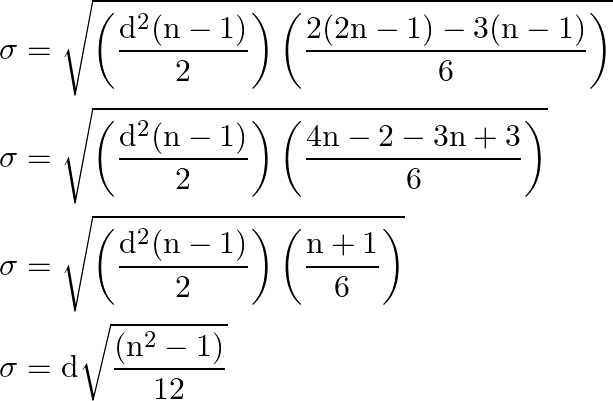
As a result the mean and standard deviation of the given AP is