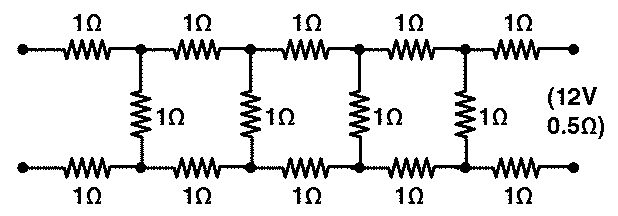
Solution:
Let the infinite network’s effective resistance be X. Because it is an endless network, adding three 1 resistance resistors will have no effect on the total resistance. X, in other words, will not change. If three resistors are added to the circuit, it will look like this.
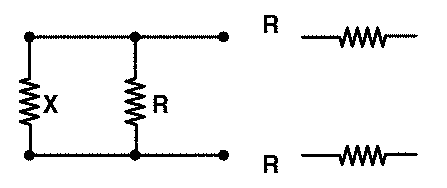
The equivalent resistance of this network is given by –
R’ = R + (equivalent resistance when X and R are parallel) + R
= R + [XR/(X+R)] + R
R’ = 2R + [XR/(X+R)]
Since it is an infinite network as given in the question, adding three resistors of 1 Ω resistance will not change the total resistance. Therefore,
R’ = X
⇒ 2R + [XR/(X+R)] = X
Since R = 1Ω we get
2 x 1 + [X x 1/(X+1)] = X
X2 – 2X -2 = 0
Solving this, we get –
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[X=\frac{-2\pm \sqrt{{{(-2)}^{2}}-4\times 1\times (-2)}}{2}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a555f262b1f62e851afb5c1fa9ce46fe_l3.png)
![]()
As we know. the value of resistance cannot be negative. Hence,
X= 1+√3 = 2.732 Ω
Given E = 12 V and r = 0.5 Ω
If the current drawn by the network is given by I, then
I = E / (X+r) = 12/(2.732+ 0.5)
I = 3.713 A
