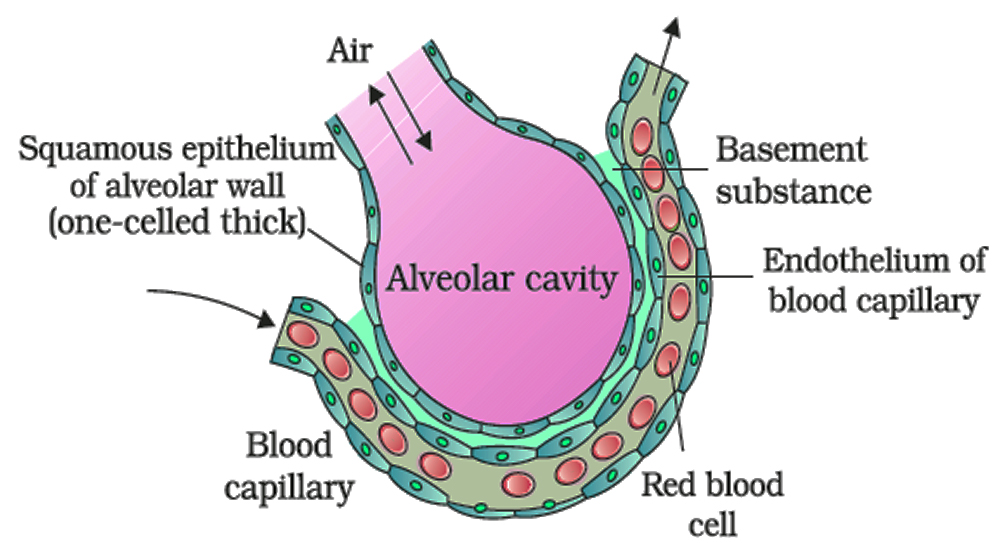
Solution: The alveoli present in the lungs are small air sacs that allow the fast exchange of gases. The alveolar membrane has a total thickness of less than a millimeter, and the outside surface of the membrane is in close proximity to the blood capillary connection.
A fine basement material distinguishes the endothelial membrane of blood capillaries and the alveolar membrane. The gases can easily diffuse through this thin barrier. The gas-diffusion is aided by higher levels of partial pressure of oxygen (![]() ) and lower levels of partial pressure of carbon dioxide (
) and lower levels of partial pressure of carbon dioxide (![]() ) in alveolar air that comes close to the blood capillaries. All of these structural advantages seen in alveoli are not found in any other respiratory system structure. As a result, the gas diffusion phenomenon occurs exclusively in the alveolar region and not elsewhere.
) in alveolar air that comes close to the blood capillaries. All of these structural advantages seen in alveoli are not found in any other respiratory system structure. As a result, the gas diffusion phenomenon occurs exclusively in the alveolar region and not elsewhere.