(a) aestivation
(b) placentation
(c) actinomorphic
(d) zygomorphic
(e) superior ovary
(f) perigynous flower
(g) epipetalous stamen
Solution:
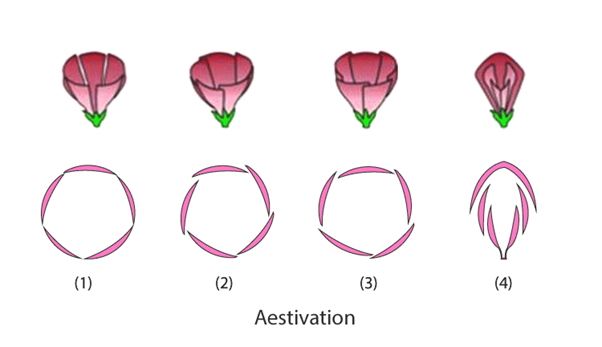
Aestivation is the arrangement of sepals or petals in a floral bud in relation to other members of the same whorl. There are several types of aestivation:
- Twisted – an appendage is twisted if one of its margins overlaps the neighbouring one in either a clockwise or anti-clockwise direction. Cotton is a good example.
- Valvate – A whorl is valvate when the petals or sepals slightly meet at the margin without overlapping. Calotropis is a good example.
- Imbricate – When petals or sepals overlap but not in a defined direction, as seen in gulmohar, it is imbricate.
- Vexillary – Vexillary aestivation occurs when the largest petal overlaps the two lateral petals, which overlap the two smallest anterior peels. Example – Bean flower
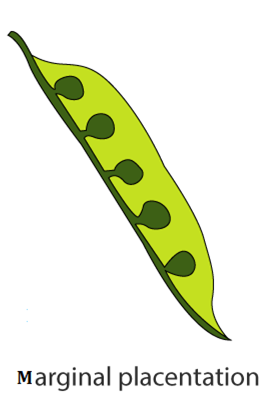
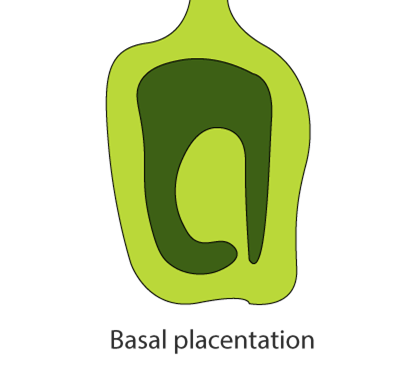
b) Arrangement of ovule within the ovary is known as placentation. They are of the following types:
- Marginal – The placenta forms a ridge that runs across the ovary’s ventral suture, and ovules are carried on the ridge in two rows. Example – Pea
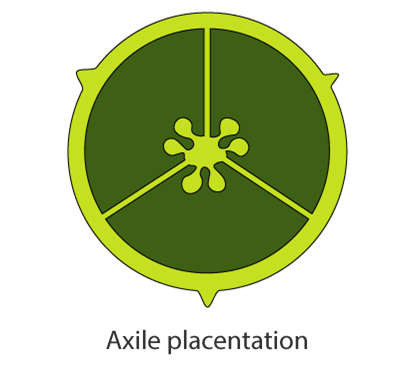
Axile – In a multilocular ovary, the placenta is axial and ovules are linked to it. Example – lemon
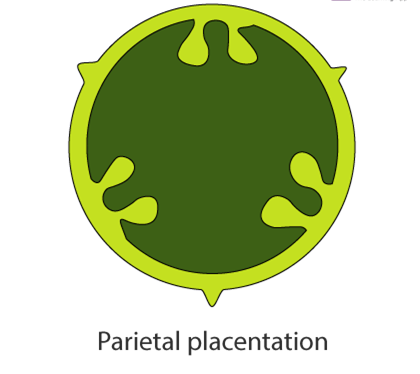
Parietal – Ovules form on the ovary’s inner wall or on the periphery. It is single-chambered at first, but as a false septum develops, it becomes two-chambered. Example- Mustard
Basal – A single ovule is linked to the placenta, which develops at the base of the ovary. Example – Marigold
Free central – Septa is missing, and ovules are borne on the central axis. Example – Primrose

c) Actinomorphic flowers are blooms that can be separated into two parts by any vertical plane. Example – Chilli
d) A zygomorphic flower is one that possesses bilateral symmetry and may be divided into two halves only in one plane. Example – Gulmohar
e) In a Hypogynous flower, the gynoecium is at the top, while the rest of the flower is below it. Superior ovary refers to the ovary in such a flower. Example – Brinjal
f)A perigynous flower is one in which the gynoecium is in the centre and the other parts of the flower are on the thalamus’s periphery. Half of the ovary is inferior. Rose g) Epipetalous stamen – Rather than being put directly over the thalamus, it bears a stamen that is borne over a petal. Brinjal is a good example.
