Why Thermometer Uses Mercury?
There are several kinds of thermometers, such as alcohol-in-glass or mercury-filled glass thermometers.
Mercury is a liquid that can move on the glass but does not adhere or stick to it.
Since mercury has a high coefficient of expansion, even a slight increase in temperature causes enough expansion to be noticed in the capillary of the calibrated portion of the thermometer. This is why mercury is utilized in thermometers.
Sensitivity and Range of a Thermometer
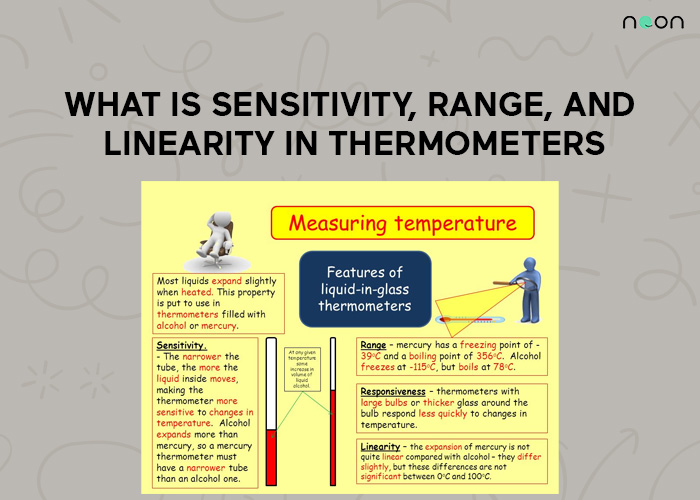
The smallest temperature change that can be observed or taken into account is referred to as a thermometer’s sensitivity. The lengthening of the mercury column with each degree of temperature rise is known as a thermometer’s sensitivity.
On the other hand, the difference between the highest and minimum temperature is referred to as a thermometer’s range. The conversion factor is in meters/degrees Celsius.
You need a thermometer that is sensitive to be able to measure temperature. When a thermometer is used on the body to measure its temperature at a temperature of 1/10 or 1/100 of a degree, it is considered to be sensitive.
A liquid in glass thermometer becomes sensitive when: For a slight change in temperature, the height of the liquid column changes more.
The capillary tube shouldn’t be too small and the bulb should be of a moderate size. Heat capacity rises with bulb size, and if the bore is too small, the liquid cannot flow freely.
- Using a thermometer with a smaller bulb can boost a thermometer’s sensitivity since a smaller bulb contains less mercury and absorbs heat more quickly.
- A glass lightbulb with a thinner wall allows heat to be transported directly to the bulb can also increase a thermometer’s sensitivity. Narrow-bore capillaries result in a greater change in the mercury column’s length.
The variation between the maximum and minimum temperatures that a thermometer can read is known as the range.
Liquid-in-glass thermometers typically measure temperatures between -10°C and 110°C.
A liquid-in-glass thermometer’s range is constrained by its length; however, this range can be expanded by:
- enlarging the capillary’s width, which results in a reduction in the amount of liquid that expands down the tube with each degree of temperature rise.
- reducing the bulb’s volume, which results in less liquid and less movement of the heated liquid down the capillary tube.
Linearity in Thermometers
When the liquid expands by the same amount for every degree Celsius increase in temperature, a liquid-in-glass thermometer is said to be linear.
This indicates that the scale will be marked in equal-sized degrees.
The scale would not be linear if the liquid did not grow in a uniform manner. It would need to be designated with sizes of varying degrees. It would be quite challenging to use and calibrate.
Thus, it is very essential that a thermometer is linear to ensure its usability.
Are you finding it challenging to prepare for your O-level Physics exam? Why not download the Noon app? The noon app offers valuable resources and interactive classes with experienced teachers that can help you prepare to ace your exams. Download the app today!