What is the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure? Most people don’t know the answer to this question. This blog post will explain each term’s meaning and how they differ. And will also give some examples of why knowing these terms is essential. Learning about blood pressure can help you stay healthy! So keep reading to learn more.
What is Systolic Pressure?
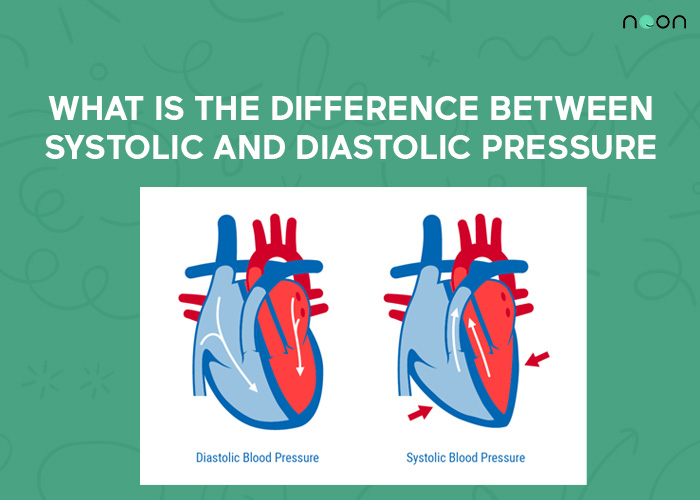
Systolic pressure is the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats and pumps blood through your body. A high systolic pressure, for example, can be a sign of hypertension or high blood pressure.
Untreated hypertension can lead to serious health problems like heart attack and stroke. That’s why it’s crucial to maintain a healthy lifestyle and see your doctor regularly to keep track of your blood pressure numbers. By understanding systolic pressure, you can take steps to keep your heart healthy and reduce your risk of developing severe health problems.
What is Diastolic Pressure?
Diastolic pressure is the pressure in your arteries when your heart relaxes between beats. Blood flow is at its lowest during this phase. Your diastolic blood pressure reading measures the amount of pressure in your arteries when your heart relaxes. This is the bottom number on a blood pressure reading, such as 120/80 mm Hg.
Average diastolic blood pressure is less than 80 mm Hg. If it’s consistently higher, you have high blood pressure, also called hypertension. High blood pressure puts you at greater risk for heart disease and stroke. Diastolic pressure may be affected by exercise, hot weather, and smoking.
What is the difference between Systolic and Diastolic pressure?
When your heart beats, it contracts and pushes blood into the arteries. This force creates pressure on the artery walls, called systolic pressure. During the relaxation phase of your heartbeat, when your heart is filling with blood, the pressure on the artery walls falls. This is called diastolic pressure.
Systolic pressure is always higher than diastolic pressure because it takes more force to push blood into the arteries than to fill them up. Your blood pressure reading gives both numbers: the systolic number (the first) followed by the diastolic number (the second).
A normal blood pressure reading is 120/80 mm Hg or lower. You have systolic hypertension if your systolic blood pressure is high (140 mm Hg or higher). You have diastolic hypertension if your diastolic blood pressure is high (90 mm Hg or higher).
These numbers are important because they can help to identify potential health problems. High systolic pressure, for example, can damage arteries and increase the risk of stroke, while high diastolic pressure can increase the risk of heart failure. If you have any concerns about your blood pressure, talk to your doctor.
Conclusion
In order to have a healthy body, it is important to keep both systolic and diastolic pressure at a certain level. You can learn more about other body parts by downloading the Noon Academy app. The app provides an in-depth understanding of your course and other useful concepts. It also offers practice questions and quizzes so you can ace your exams. Don’t wait any longer. Download the Noon Academy app today!