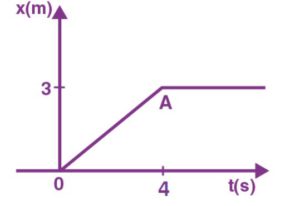
When t<0, the particle’s distance travelled is zero. As a result, the particle’s force is zero.
When 0< t< 4s occurs, the particle is travelling at a constant speed. As a result, there will be no force.
The particle remains at a fixed distance for t>4s. As a result, the particle’s force will be zero.
At t = 0, the impulse is zero.
u = 0 in this case.
0.75 m/s = v = 34
4 kg = M
mv – mu = m (v – u)
= 4 (0 – 0.75) = -3 kg m/s
Impulse at t= 4s
u = 0.75 m/s, v = 0
Impulse = m (v – u) = 4 (0 – 0.75) = -3 kg m/s
