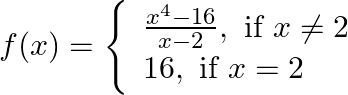(i)
A real function f is said to be continuous at x = c, where c is any point in the domain of f if

h is a very small positive number. i.e. left hand limit as x → c (LHL) = right hand limit as x → c (RHL) = value of function at x = c.
A function is continuous at x = c if

Function is defined for all real numbers so we need to comment about its continuity for all numbers in its domain (domain = set of numbers for which f is defined)
Function is changing its nature (or expression) at x = 1, so we need to check its continuity at x = 1.
=> f (1) = 4 [using equation 1]

∴ f (x) is discontinuous at x = 1.
Let c be any real number such that c ≠ 0

(ii)
A real function f is said to be continuous at x = c, where c is any point in the domain of f if

h is a very small positive number. i.e. left hand limit as x → c (LHL) = right hand limit as x → c (RHL) = value of function at x = c.
A function is continuous at x = c if

The function is defined for all real numbers, so we need to comment about its continuity for all numbers in its domain (domain = set of numbers for which f is defined)
Function is changing its nature (or expression) at x = 2, so we need to check its continuity at x = 2 first.
=> f (2) = 16 [from equation 1]

∴ f (x) is continuous at x = 2.
Let c be any real number such that c ≠ 0


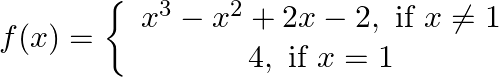 (ii)
(ii)