Solution:
Given that ![]() is differentiable at each
is differentiable at each ![]()
For ![]()
![]() i.e. a polynomial
i.e. a polynomial
for ![]()
![]() , which is also a polynomial
, which is also a polynomial
As, a polynomial function is everywhere differentiable. So, ![]() is differentiable for all
is differentiable for all ![]() and for all
and for all ![]()
![]() is continuous at
is continuous at ![]()
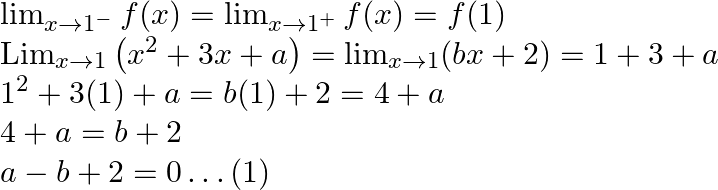
As function is differentiable, therefore, ![]()
![]() at
at ![]() :
:
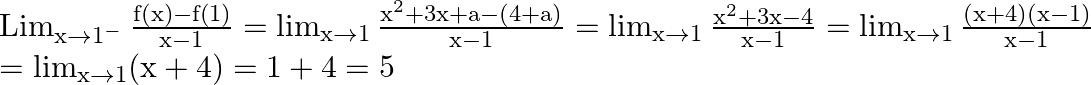
Right Hand Derivative at ![]()
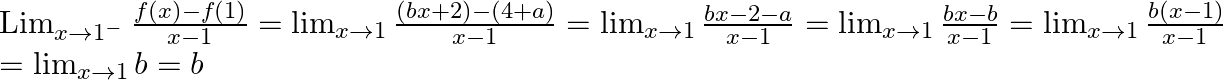
As, ![]()
Hence,
![]()
Putting ![]() in
in ![]() , we obtain,
, we obtain,
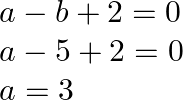
As a result,
![]()

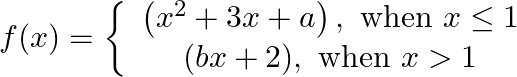 is differentiable at each
is differentiable at each