Solution:
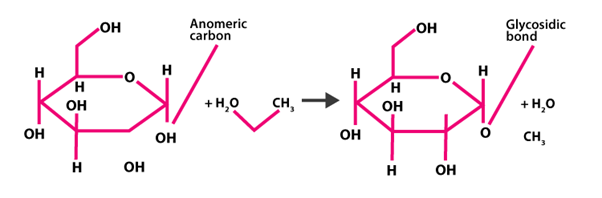
Glycosidic bond – A glycosidic linkage is the connection between separate monosaccharides. This bond is formed between two carbon atoms of two monosaccharide units that are nearby.
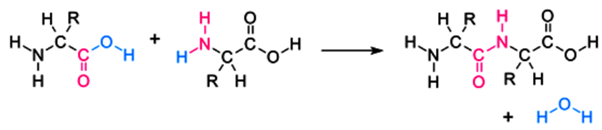
Peptide bond – It’s what’s known as a covalent bond. Proteins are held together by peptide bonds, which connect the amino acids. When the carboxyl group (-COOH) of one amino acid interacts with the amino group (-NH2 ) of the neighbouring amino acid when they are condensed, it is generated.
Formation of Peptide bond – Example
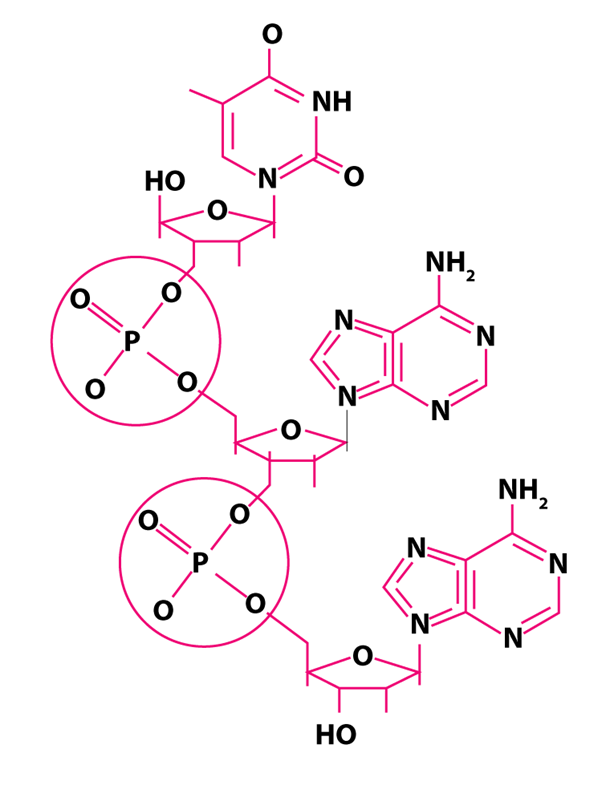
Phospho-diester bond – in a polynucleotide that connects successive sugar molecules A strong covalent connection between two adjacent sugar groups and phosphate is created. These are the bonds that make up the nucleic acid’s sugar-phosphate backbone.