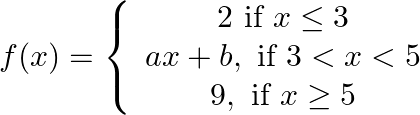(iii)
A real function f is said to be continuous at x = c, where c is any point in the domain of f if

h is a very small positive number. i.e. left hand limit as x → c (LHL) = right hand limit as x → c (RHL) = value of function at x = c.
A function is continuous at x = c if

To find the value of constants always try to check continuity at the values of x for which f(x) is changing its expression.
As most of the time discontinuities are here only, if we make the function continuous here, it will automatically become continuous everywhere
From equation 1, it is clear that f(x) is changing its expression at x = 0
Given, f (x) is continuous everywhere

since, above equality never holds true for any value of k
k = not defined
=> f (x) will always have a discontinuity at x = 0
(iv)
A real function f is said to be continuous at x = c, where c is any point in the domain of f if

h is a very small positive number. i.e. left hand limit as x → c (LHL) = right hand limit as x → c (RHL) = value of function at x = c.
A function is continuous at x = c if

From equation 1, f(x) is changing its expression at x = 3
Given, f(x) is continuous everywhere

∴ 3a + b = 2 ……………….Equation 2
f(x) is also changing its expression at x = 5
Given, f(x) is continuous everywhere


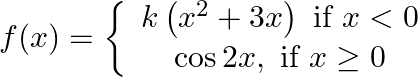 (i v)
(i v)