Solution:
Option (B) is correct.
One-One function
Suppose ![]() be two arbitrary elements in
be two arbitrary elements in ![]()
Therefore, ![]()
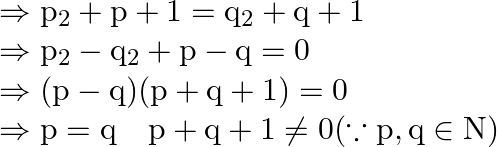
When ![]()
Therefore, ![]() is one-one function.
is one-one function.
Onto function
For ![]() assumes value 3 .
assumes value 3 .
Since, ![]() cannot assume value less than 3 , for
cannot assume value less than 3 , for ![]()
Hence, ![]() is not onto function. It is into function.
is not onto function. It is into function.
