The mass of the particle executing simple harmonic motion is ![]() . The particle’s displacement at a given time
. The particle’s displacement at a given time ![]() is given by
is given by
![]()
Velocity of the particle is given as ![]()
Instantaneous Kinetic Energy can be calculated as,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Average value of kinetic energy over one complete cycle can be calculated as,
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \begin{aligned} &K_{a v}=\frac{1}{T} \int_{0}^{T} \frac{1}{2} m A^{2} \omega^{2} \cos ^{2} \omega t d t=\frac{m A^{2} \omega^{2}}{2 T} \int_{0}^{T} \cos ^{2} \omega t d t=\frac{m A^{2} \omega^{2}}{2 T} \int_{0}^{T} \frac{(1+\cos 2 \omega t)}{2} d t \\ &=\frac{m A^{2} \omega^{2}}{4 T}\left[t+\frac{\sin 2 \omega t}{2 \omega}\right]_{0}^{T} \\ &=\frac{m A^{2} \omega^{2}}{4 T}\left[(T-0)+\left(\frac{\sin 2 \omega t-\sin 0}{2 \omega}\right)\right] \\ &=\frac{1}{4} m A^{2} w^{2} \\ &\text { Average instantaneous potential energy, } U=(1 / 2) k x^{2}=(1 / 2) m \omega^{2} x^{2}=(1 / 2) m \omega^{2} A^{2} \sin ^{2} \omega t \end{aligned}](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a0bc1a460040fbd6c49223d5fea1732d_l3.png)
Average value of potential energy over one complete cycle can be calculated as
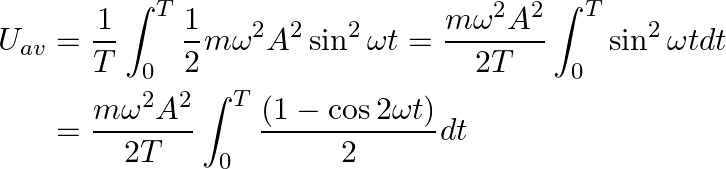
![]()
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \begin{aligned} &=\frac{m \omega^{2} A^{2}}{4 T}\left[(T-0)-\frac{(\sin 2 \omega t-\sin 0)}{2 \omega}\right] \\ &=\frac{1}{4} m \omega^{2} A^{2} \end{aligned}](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8e85d2caac3de468853791975cc05988_l3.png)
Kinetic energy ![]() Potential energy
Potential energy
