The gravitational force between an H-atom and another particle of mass m will be given by Newton’s law:
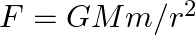
, where r is in km and
(a) M = mproton + m electron
(b) M = mproton
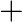
melectron
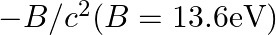
(c) M is not related to the mass of the hydrogen atom
(d) M = mproton +melectron
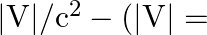
magnitude of the potential energy of electron in the
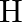
-atom)
![]() melectron
melectron ![]()
![]() melectron
melectron ![]()