Solution:
Provided: Two sets each of 20 observations, have the same standard derivation 5 . The first set has a mean 17 and the second a mean ![]()
We now need to show that the standard deviation of the set obtained by combining the given two sets
As per the criteria given, for the first set
No. of observations, ![]()
Standard deviation, ![]()
And mean, ![]()
For the second set, no. of observations, ![]()
Standard deviation, ![]()
And mean, ![]()
It is known to us that the standard deviation for combined two series is
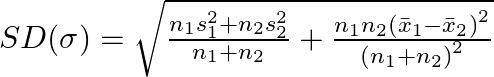
Substitute the corresponding values,
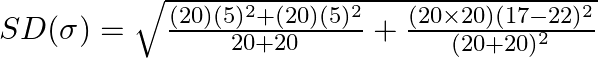
On simplifying we obtain
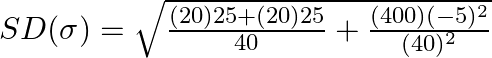
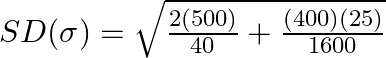
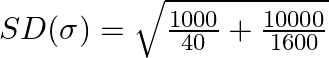
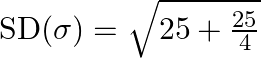
Take LCM and simplify,
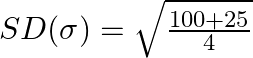
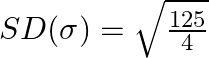
Or, ![]()
As a result, ![]() is the standard deviation of the set obtained by combining the given two sets.
is the standard deviation of the set obtained by combining the given two sets.
