What Is Semantic Memory?
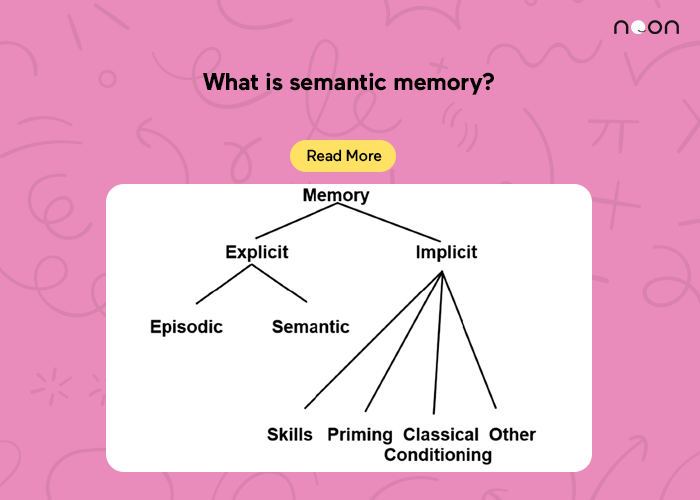
Semantic memory is a type of long-term memory that is responsible for storing and retrieving general knowledge and facts about the world. It is a form of declarative memory, which refers to memories that are consciously stored and retrieved, and it is distinct from episodic memory, which is responsible for storing and retrieving personal experiences and events.
Semantic memory is often referred to as “encyclopedic” memory because it stores and retrieves information about concepts, words, and language, as well as general knowledge about the world.
Example Of Semantic Memory
For example, semantic memory is what allows us to recognize and understand words and their meanings, to understand and use language, and to understand and remember general knowledge about things like historical events, scientific concepts, and mathematical principles.
Semantic memory is thought to be a central component of our long-term memory system, and it plays an important role in many cognitive processes, including language comprehension, problem-solving, and decision-making. It is also thought to be less affected by aging and brain damage than other types of memory, such as episodic memory.
Importance of Semantic Memory
Semantic memory is an important type of memory that plays a central role in many cognitive processes and is essential for our ability to understand and use language, learn and retain new information, and make decisions.
Some of the key ways in which semantic memory is important include:
- Semantic memory allows us to recognize and understand words and their meanings, which is essential for language comprehension and communication.
- Semantic memory allows us to understand and use language effectively, including learning new words and concepts.
- Semantic memory allows us to remember and retrieve general knowledge and facts about the world, which is important for problem-solving and decision-making.
- Semantic memory is less affected by aging and brain damage than other types of memory, such as episodic memory, which means that it can be a reliable source of information throughout a person’s life.
- Semantic memory is thought to be closely related to our ability to understand and use abstract concepts, which is important for many higher-level cognitive processes, such as reasoning and problem-solving.
Conclusion
Overall, semantic memory is an important aspect of our long-term memory system that plays a central role in many cognitive processes and is essential for our ability to understand and interact with the world around us.
Learn more with Noon App


