If you’re like me, you probably think of Xylem vessels as the things that help a plant move water from the roots to the leaves. And while that is their primary role, they actually play an even more important role in keeping plants healthy!
In this blog post, I will tell you about what Xylem vessels are and what they do for plants. Stay tuned!
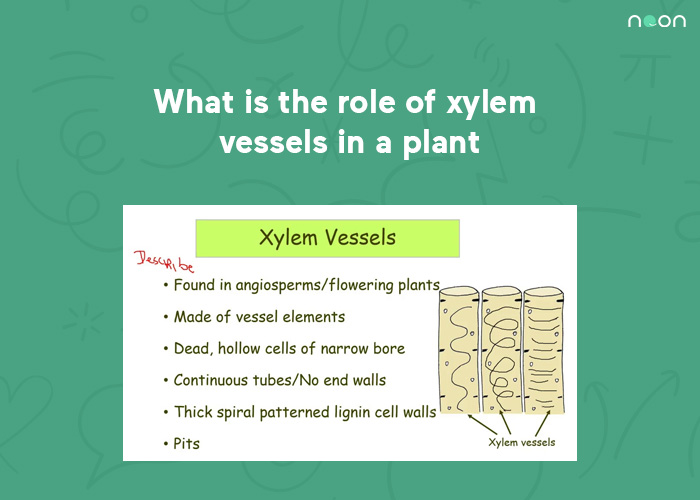
Xylem vessels

Xylem vessels are one of the main types of cells that make up the xylem tissue in plants. They are long, thin tubes that transport water and minerals from the roots to the leaves. Xylem vessels are lined with a layer of cells called the xylem parenchyma. These cells have large central vacuoles that help to keep the xylem vessels full of water.
Xylem vessels are often found in groups, known as bundles. Each bundle is surrounded by a layer of cells called the bundle sheath. The bundle sheath helps to protect the xylem vessels and keep them functioning properly. Together, the xylem vessels and the other cells of the xylem tissue make up the plant’s transport system, which is crucial for delivering water and minerals to all parts of the plant.
Xylem vessels function
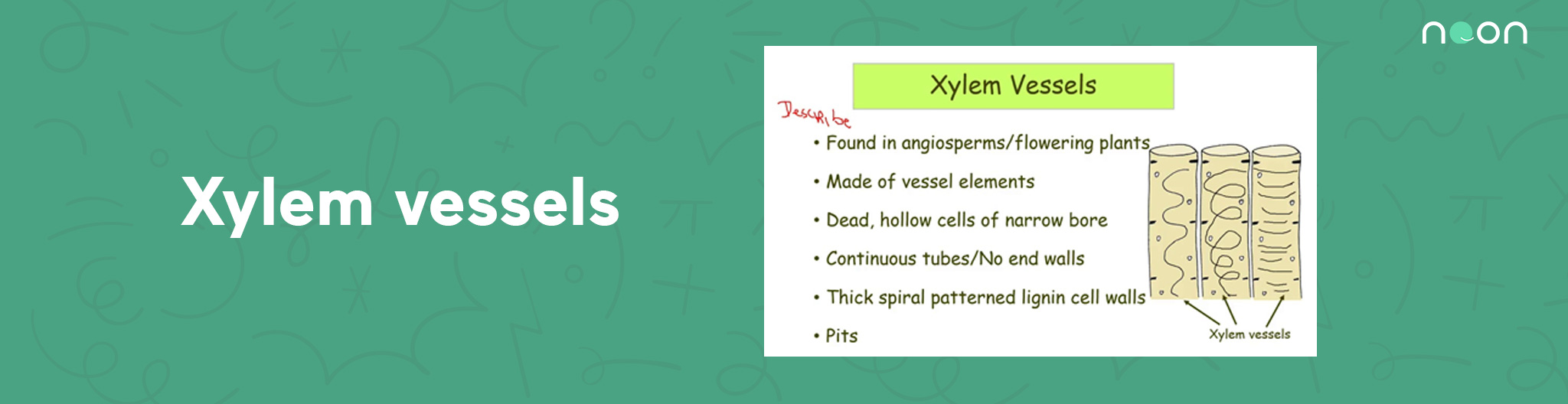
Xylem vessels are one of the main components of a plant’s vascular system. Their primary function is to transport water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves. Xylem vessels are long, thin tubes that are arranged in a series, with each tube connected to the next. The walls of xylem vessels are made of a special type of cell known as a vessel element.
Vessel elements are arranged end-to-end, with theirholes aligned, to form a continuous hollow tube. Water and minerals enter the xylem vessel at the root end, and are then transported up through the length of the tube to the leaves.
Xylem vessels are essential for a plant’s survival, as they provide the means by which water and nutrients can be transported from the roots to the leaves. without them, a plant would quickly dehydrate and die.
Xylem vessels structure
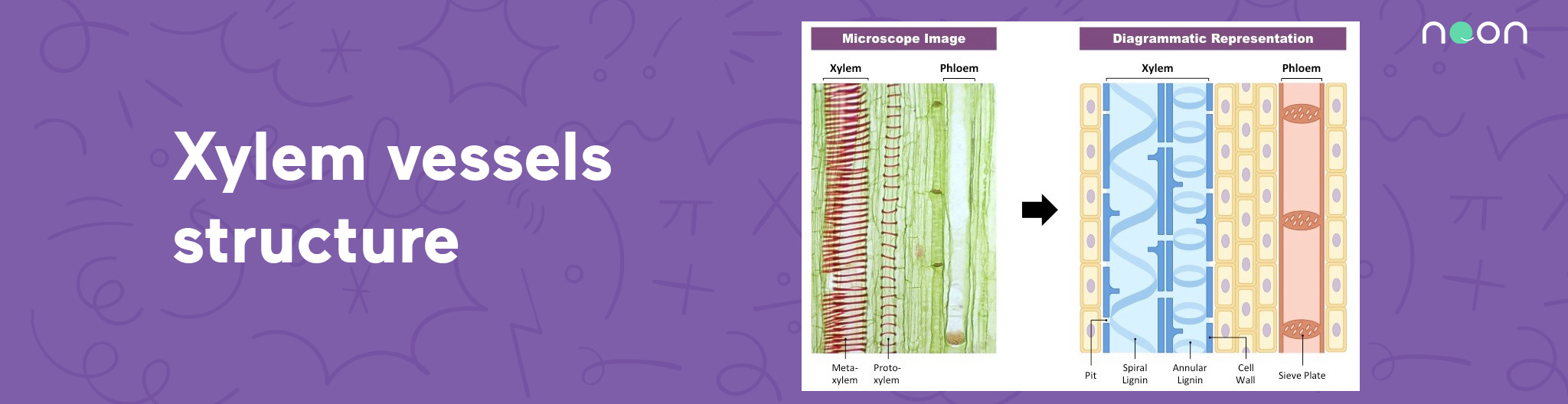
Xylem vessels are elongated cells that are arranged end-to-end to form long tubes. These tubes transport water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves. The walls of xylem vessels are made of cell membranes that are stacked on top of each other. The stacked membranes create pores that allow water and minerals to pass through.
Xylem vessels also have lignin, a tough polymer that gives them strength and rigidity. Lignin is also responsible for the dark color of xylem tissue. Xylem vessels are surrounded by a layer of supportive tissue called phloem. Phloem transports sugars and other organic molecules from the leaves to the rest of the plant. Together, xylem and phloem make up the vascular tissue of plants.
Conclusion
Though its role may seem small, the xylem vessel is an essential part of a plant. Without it, a plant would not be able to transport water and nutrients throughout its system, ultimately leading to its demise. The next time you see a plant, take a moment to appreciate the complex network of tissues and vessels that work together to keep it alive and thriving.
And if you’re looking for a great resource to help you learn more about plants (or anything else), be sure to check out Noon – we promise you won’t be disappointed!
To learn more about other subjects to ace your next exam, use the Noon app. It has over 10,000 lectures on different subjects. You can learn from the best teachers from across the globe. Download yours now!
Available on IOS and Android


