Cathode ray tubes (CRTs) were once the mainstay of television sets and computer monitors. They have since been replaced by newer technologies such as LCDs and LEDs, but CRTs still have a place in modern technology.
This article will explain what a CRT is, how it works, and why it’s still used today. We’ll also look at its potential applications in the future and what alternatives are available to replace it.
So if you’re curious about this old-fashioned technology, read on!
What is Cathode ray tube?
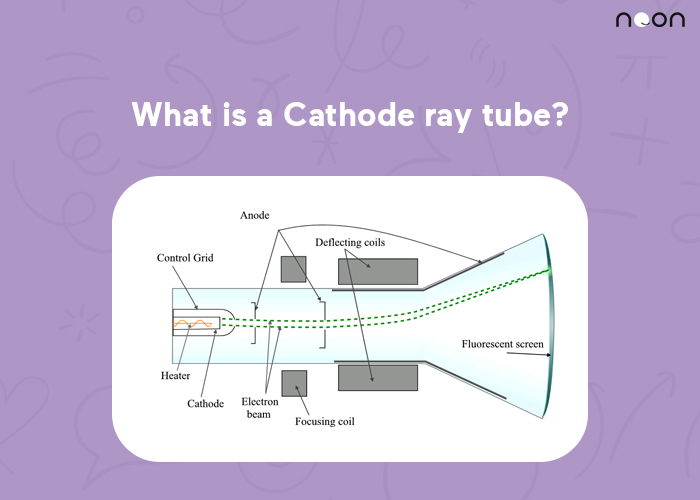
A cathode ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube that contains one or more electron guns and a phosphor-coated screen. The guns fire electrons at the screen, which lights up to produce images. CRTs were once widely used in televisions and computer monitors, but have largely been replaced by LCDs.
What is the principle behind Cathode ray Oscilloscope?
The principle behind CRT-based oscilloscopes is that the electron beam can be rapidly deflected from its path by an electric field, allowing it to trace out the shape of an electrical signal on the screen.
What are the benefits of using it?
There are many benefits to using a CRT.
- CRTs are highly efficient, provide excellent image quality, and are very versatile.
- CRTs are highly efficient because they use less power than other types of displays. This makes them ideal for use in portable devices such as laptops and handheld gaming consoles.
- CRTs also provide excellent image quality thanks to their high contrast ratios and wide viewing angles.
- Additionally, CRTs are very versatile and can be used for a variety of applications including computer monitors, television sets, and industrial equipment.
How long do cathode ray tubes last?
The lifespan of a CRT can depend on a number of factors, such as the manufacturing quality of the tube, the amount of use it gets, and whether or not it is properly maintained.
In general, though, most CRTs have a lifespan of around 10 to 15 years.
CRTs are used in a variety of electronic devices, including televisions, computer monitors, and microwave ovens.
They work by bombarding a target with electrons that generate a beam of light. This beam of light is then used to create an image on a screen.
While CRTs are generally very durable, they can be susceptible to damage if they are mishandled or not properly maintained.
For example, if a CRT is dropped or hit too hard, the glass inside the tube can break.
Additionally, if the seals on a CRT become damaged, air can leak into the tube and cause the electrons to lose their charge. This can result in distorted images or even a complete loss of pictures.
To help prolong the lifespan of your CRT, be sure to handle it carefully and keep it clean. If you notice any damage to the tube, have it repaired as soon as possible by a qualified technician.
Conclusion
The Cathode Ray Tube has been a mainstay of television and computer monitor technology for decades. Its unique design allowed for the creation of bright, clear images with excellent picture resolution and contrast that was unmatched by other displays of its time.
Despite the advent of newer technologies such as LCDs, LEDs, and OLEDs, CRTs remain an important part in many applications today.
With their reliability and affordability, they are still a great choice if you need to display detailed visuals or want to experience a classic piece of tech history.
The Noon app is the perfect app for students who want to learn more about other subjects and ace their next exam.
With over 10,000 lectures on different subjects available, students can learn from the best teachers from all around the globe.
Noon provides professional teachers with online teaching tools, including video streaming, high-quality videos, and interactive classrooms.
This makes it the ultimate teacher’s assistant tool for e-learning. Not only does it provide an easy way for teachers to deliver lectures online, but it also ensures that students have access to quality education resources.
So, what are you waiting for? Download the Noon app today!


