The Durand Line was created during the time of the British Raj in 1893 and was established as an international border by Pakistan. Find out more about this division between Afghanistan and Pakistan and what it means for all around it.
What is the Durand Line
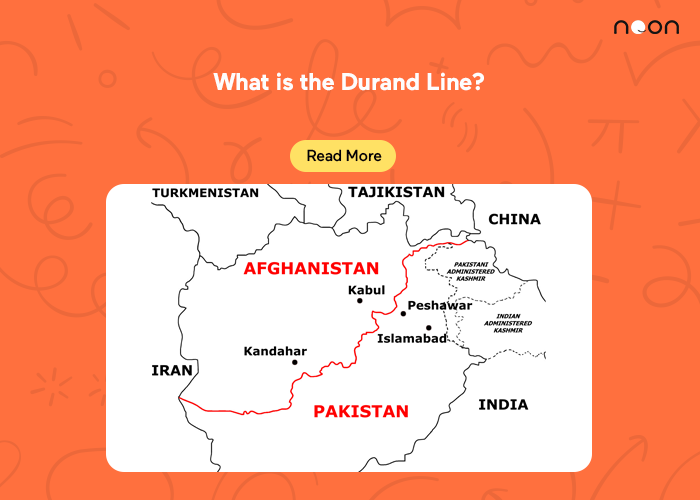
The Durand Line is the border between Afghanistan and Pakistan. It was drawn up in 1893 by British diplomat Sir Mortimer Durand as part of a Durand line agreement between the British Raj and Afghan Amir Abdur Rahman Khan to fix the limit of their respective spheres of influence in the region. The line is named after its creator and runs for nearly 2,640 km (1,645 mi) from the Hindu Kush in the west to the Pamir Mountains in the east.
The original intent of the Durand Line was to serve as a temporary demarcation until a more permanent solution could be reached between Afghanistan and British India. However, after the British withdrawal from Afghanistan in 1919 following the Third Anglo-Afghan War, the line became increasingly relevant as an international border. In 1947, when British India was partitioned into India and Pakistan, the Durand Line became the de facto border between the two newly independent states.
Despite its importance as an international boundary, the Durand Line has remained largely unrecognized by Afghan governments since independence. This is due in part to Afghan claims that Pakistan has illegally occupied Afghan territory on its side of the line, known as Pashtunistan. The issue remains a source of tension between Afghanistan and Pakistan today.
Durand Line Length in KM
The Durand Line is 2,430 kilometers long, running from the Afghan-Pakistan border in the north-west to the Wakhan Corridor in the north-east. The line was originally drawn by Sir Mortimer Durand, a British diplomat, as a temporary measure to delineate the territories of the British Raj and the Afghan Emirate.
The line has been largely respected by both countries, although there have been occasional disputes. In recent years, the Taliban have gained control of areas on both sides of the Durand Line, raising concerns about its continued viability as a boundary.
The Importance of the Durand Line
The Durand Line is a 2,640-kilometre (1,640 mi) international border between Pakistan and Afghanistan. It was established in 1893 by British diplomat Sir Mortimer Durand as part of the Anglo-Afghan Treaty of Kabul. The Durand Line runs northwest from the Afghan-Pakistan border along the Wakhan Corridor to the Khyber Pass area.
The importance of the Durand Line lies in its history and the geopolitics of South Asia. The line has been a source of conflict between Afghanistan and Pakistan since its creation, with both countries claiming ownership of the land on either side of it. The conflict flared up again in recent years, with Afghan President Hamid Karzai accusing Pakistan of harboring Taliban militants who cross the border to attack targets in Afghanistan.
The Durand Line is also significant because it is one of the few international borders that runs through mountainous terrain. This makes it difficult to police and easy for people and goods to cross illegally. As a result, the border region has become a haven for insurgents and smugglers.
The Future of the Durand Line
The future of the Durand Line is unclear. The line has been in place for over a century, and has been the source of much conflict between Pakistan and Afghanistan. There have been calls for the line to be redrawn, or for it to be abolished altogether. However, it is unlikely that any major changes will be made to the line in the near future.
Conclusion
The Durand Line is an internationally recognized boundary between Pakistan and Afghanistan. It was drawn up in 1893 by British diplomat Sir Mortimer Durand and Afghan ruler Amir Abdur Rahman Khan as part of the Treaty of Gandamak, and has been reaffirmed by both countries on numerous occasions since then. The line runs for nearly 2,500 kilometers (1,550 miles) from the northwest corner of Pakistan to the Khyber Pass in Afghanistan’s northeast, and has remained largely unchanged since it was first drawn.
Noon app is an online learning platform that helps teachers deliver high-quality lectures to their students. It offers a wide range of features that make online teaching easier and more engaging for both teachers and students. For example, Noon app provides teachers with tools for creating and managing online classroom courses, as well as delivering lectures through video streaming.
Additionally, the app also offers a library of over 10,000 high-quality video lectures on different subjects, which can be used by students to supplement their learning. So, what are you waiting for? Download the Noon app now and start learning!


