Volume of the room is given as ![]()
Temperature of the room is given as ![]()
Pressure in the room will be ![]()
The ideal gas equation can be written as:
![]()
Where,
![]() is Boltzmann constant having value
is Boltzmann constant having value
![]()
![]() is the number of air molecules in the room
is the number of air molecules in the room
Therefore,
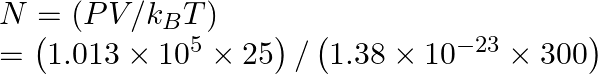
We get,
![]() molecules
molecules
As a result, ![]() is the total number of air molecules in the given room.
is the total number of air molecules in the given room.
