Option (ii) is the answer. Glycogen has a similar structure to amylopeptin. It's an a-D glucose unit branched chain polymer with C1-C4 glycosidic linkage for chain formation and C1-C6 glycosidic...
Glycogen is a branched-chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by the formation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to __________.
Which of the following polymer is stored in the liver of animals? (i) Amylose (ii) Cellulose (iii) Amylopectin (iv) Glycogen
Option (iv) is the answer. Glycogen is a type of sugar that is stored in the liver of mammals.
Sucrose (cane sugar) is a disaccharide. One molecule of sucrose on hydrolysis gives _________.
(i) 2 molecules of glucose
(ii) 2 molecules of glucose + 1 molecule of fructose
(iii) 1 molecule of glucose + 1 molecule of fructose
(iv) 2 molecules of fructose
Option (iii) is the answer. Cane sugar (sucrose) is a disaccharide. When sucrose is hydrolyzed, one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose are produced.
Which of the following pairs represents anomers?
Option (C) is the answer. Anomers are isomers that differ only in the conformation of the hydroxyl group at C—1 and are known as - and -fonns.
Proteins are found to have two different types of secondary structures viz. α-helix and β-pleated sheet structure. α-helix structure of the protein is stabilised by : (i) Peptide bonds (ii) van der Waals forces (iii) Hydrogen bonds (iv) Dipole-dipole interactions
Option ( iii) is the answer. Hydrogen bonding help to keep the -helix structure of proteins stable. By twisting into a right-handed helix and hydrogen bonding the -NH group of each amino acid...
In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e. aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars. Which of the following disaccharide is a non-reducing sugar?
Option (B) is the answer. This structure represents sucrose, in which the C1—C2 glycosidic bond connects -D glucose and -D-fructose. This is a non-reducing sugar since the reducing groups of glucose...
Which of the following acids is a vitamin? (i) Aspartic acid (ii) Ascorbic acid (iii) Adipic acid (iv) Saccharic acid
Option (ii) is the answer. Vitamin C is ascorbic acid. Amino acid aspartic acid is a kind of amino acid. Dicarboxylic acids include adipic acid and saccharic acid.
Which of the following statements is not true about glucose?
(i) It is an aldohexose.
(ii) On heating with HI, it forms n-hexane.
(iii) It is present in furanose form.
(iv) It does not give 2,4-DNP test.
Option (iii) is the answer. It's found in the pyranose structure.
Each polypeptide is a protein has amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence. This sequence of amino acids is said to be ____________.
(i) primary structure of proteins.
(ii) secondary structure of proteins.
(iii) the tertiary structure of proteins.
(iv) quaternary structure of proteins.
Option (i) is the answer. The main structure of proteins is the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
DNA and RNA contain four bases each. Which of the following bases is not present in RNA? (i) Adenine (ii) Uracil (iii) Thymine (iv) Cytosine
Option (iii) is the answer. Adenine, guanine, thymine, and cytosine are the four bases found in DNA. Adenine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine are the four bases found in RNA. As a result, thymine is...
Which of the following bases is not present in DNA? (i) Adenine (ii) Thymine (iii) Cytosine (iv) Uracil
Option (iv) is the answer. In DNA, uracil is absent; instead, thymine is present.
Three cyclic structures of monosaccharides are given below which of these are anomers.
(i) I and II
(ii) II and III
(iii) I and III
(iv) III is anomer of I and II
Option (i) is the answer. Anomers are cyclic configurations of monosaccharides that differ in structure at carbon-1. I and II are anomers in this case because they differ solely in carbon-1.
Which of the following reactions of glucose can be explained only by its cyclic structure?
(i) Glucose forms pentaacetate.
(ii) Glucose reacts with hydroxylamine to form an oxime.
(iii) Pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine.
(iv) Glucose is oxidised by nitric acid to gluconic acid
Option (iii) is the answer. The absence of a free -CHO group is indicated by the fact that glucose pentaacetate does not react with hydroxylamine. Only the cyclic nature of glucose may explain this...
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
(i) I, II, III
(ii) II, III
(iii) I, II
(iv) III
Option (i) is the answer. The -OH group is on the lowest asymmetric carbon on the right side of the I, II, and III structures, which is similar to (+) glyceraldehyde.
Structure of a disaccharide formed by glucose and fructose is given below. Identify anomeric carbon atoms in monosaccharide units.
(i) ‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘a’ carbon of fructose.
(ii) ‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘e’ carbon of fructose.
(iii) ‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘b’ carbon of fructose.
(iv) ‘f’ carbon of glucose and ‘f ’ carbon of fructose.
Option (iii) is the answer. Anomeric carbon is carbon that is next to an oxygen atom in the cyclic structure of glucose or fructose. 'a' and 'b' are next to the oxygen atom, as illustrated in the...
Three structures are given below in which two glucose units are linked. Which of these linkages between glucose, units are between C1 and C4 and which linkages are between C1 and C6?
(i) (A) is between C1 and C4, (B) and (C) is between C1 and C6
(ii) (A) and (B) are between C1 and C4, (C) is between C1 and C6
(iii) (A) and (C) is between C1 and C4, (B) is between C1 and C6
(iv) (A) and (C) is between C1 and C6, (B) is between C1 and C4
Option (iii) is the answer (A) and (C) are in the Cl-C4 range, while (B) is in the Cl-C6 range.
Proteins can be classified into two types on the basis of their molecular shape i.e., fibrous proteins and globular proteins. Examples of globular proteins are : (i) Insulin (ii) Keratin (iii) Albumin (iv) Myosin
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers Globulular protein is the structure that develops when a chain of polypeptides coils around to form a spherical shape. Insulin and albumin, for example, are...
Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose?
(i) Amylose
(ii) Amylopectin
(iii) Cellulose
(iv) Glycogen
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Amylopectin and glycogen are both glucose branching polymers.
Amino acids are classified as acidic, basic or neutral depending upon the relative number of amino and carboxyl groups in their molecule. Which of the following is acidic?
Option (ii) and (iv) are the answers. Acidic amino acids have more than one -COOH group one against the –NH2 group.
Lysine, is _______________.
(i) α-Amino acid
(ii) Basic amino acid
(iii) Amino acid synthesised in the body
(iv) β-Amino acid
Option (i), (ii) and (iii) are the answers. (a)Lysine is a kind of amino acid with the structural formula . (b) Because the number of NH2 groups (2) is more than the number of COOH groups, it is a...
Which of the following monosaccharides are present as five-membered cyclic structure (furanose structure)? (i) Ribose (ii) Glucose (iii) Fructose (iv) Galactose
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. The five-membered cyclic structure of ribose and fructose is shown (furanose structures). They have a five-membered ring, similar to the foran compound....
In fibrous proteins, polypeptide chains are held together by ___________.
(i) van der Waals forces
(ii) disulphide linkage
(iii) electrostatic forces of attraction
(iv) hydrogen bonds
Option (ii) and (iv) are the answers. Disulphide linkage and hydrogen bonding hold polypeptide chains together in fibrous proteins.
Which of the following are purine bases?
(i) Guanine
(ii) Adenine
(iii) Thymine
(iv) Uracil
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers. Purines are made up of a six-membered nitrogen-containing ring fused together with a five-membered nitrogen-containing ring. Purine bases guanine and adenine...
Which of the following terms are correct about enzyme?
(i) Proteins
(ii) Dinucleotides
(iii) Nucleic acids
(iv) Biocatalysts
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Enzymes are protein molecules that act as biocatalysts in the body's chemical reactions.
Name the sugar present in milk. How many monosaccharide units are present in it? What are such oligosaccharides called?
Lactose is the sugar found in milk. Glucose and galactose are two monosaccharides found in lactose. Disaccharides are oligosaccharides that include two monosaccharide units.
How do you explain the presence of all the six carbon atoms in glucose in a straight chain?
When glucose is heated with HI for a long time, n-hexane develops, implying that all six carbon atoms are connected in a straight chain.
In nucleoside, a base is attached at 1C position of the sugar moiety. A nucleotide is formed by linking the phosphoric acid unit to the sugar unit of a nucleoside. At which position of sugar unit is the phosphoric acid linked in a nucleoside to give a nucleotide?
When a nitrogenous base is connected to the 1' position of a five-carbon sugar, a nucleoside is produced. The 5' carbon of the sugar in a nucleoside molecule is bonded to the 5' carbon of the sugar...
Name the linkage connecting monosaccharide units in polysaccharides.
Glycosidic linkages connect the monosaccharide units of polysaccharides. When an oxide bond is created between two monosaccharide units with the loss of a water molecule, it is called a glycosidic...
Under what conditions glucose is converted to gluconic and saccharic acid?
When glucose is treated with a mild oxidising agent like Br2 water, it is transformed to gluconic acid, a six-carbon carboxylic acid. When glucose is treated with nitric acid, it is transformed to...
The letters ‘D’ or ‘L’ before the name of a stereoisomer of a compound indicates the correlation of configuration of that particular stereoisomer. This refers to their relationship with one of the isomers of glyceraldehyde. Predict whether the following compound has ‘D’ or ‘L’ configuration.
On the left side of the C5 carbon atom, the –OH group is connected. As a result, the provided compound is in the 'L' configuration.
Which sugar is called invert sugar? Why is it called so?
Invert sugar is another name for sucrose. It comes from sugarcane and sugarbeet and is a naturally occurring sugar. When sucrose is hydrolyzed, the sign of rotation changes from Dextro (+) to laevo...
Amino acids can be classified as α-, β-, -, δ- and so on depending upon the relative position of the amino group concerning the carboxyl group. Which type of amino acids forms polypeptide chain in proteins?
The sort of amino acids that make up a polypeptide chain are -amino acids and alpha-amino acids, where the amino acid is linked to the -carbon in the molecule.
α-Helix is a secondary structure of proteins formed by twisting of the polypeptide chain into right-handed screw-like structures. Which type of interactions is responsible for making the a-helix structure stable?
The –NH group of each amino acid residue hydrogen is bound to the –C=O of an adjacent turn of the helix, forming a right-handed screw helix shape.
Some enzymes are named after the reaction, where they are used. What name is given to the class of enzymes which catalyse the oxidation of one substrate with simultaneous reduction of another substrate?
Enzyme oxidoreductases is the name given to a group of enzymes that catalyse redox processes. Alcohol Dehydrogenase, for example, aids in the reduction of alcohol levels in the human body when...
During curdling of milk, what happens to sugar present in it?
The sugar found in milk, lactose, is transformed to lactic acid during curdling, which is produced by bacteria.
How do you explain the presence of five —OH groups in the glucose molecule?
When glucose is acetylated using acetic anhydride (CH3CO)2O in the presence of ZnCl2, glucose pentaacetate is formed, confirming the presence of five –OH groups.
Why does compound (A) give below not form an oxime?
The chemical in question is glucose pentaacetate. The presence of a free –C=O group in glucose indicates the presence of a free carbonyl group, as does the synthesis of oxime from glucose. Because...
Why must vitamin C be supplied regularly in diet?
Because vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin, any excess is eliminated from the body on a regular basis. Vitamin C cannot be stored in the body, thus it must be consumed on a regular basis.
Sucrose is dextrorotatory but the mixture obtained after hydrolysis is laevorotatory. Explain.
Sucrose's aqueous solution is dextrorotatory, rotating plane-polarized light entering the solution 66.5 degrees to the right. When sucrose is hydrolyzed with dilute acids or invertase enzyme, two...
Amino acids behave like salts rather than simple amines or carboxylic acids. Explain
An amino acid has both a –NH2 and a –COOH group. The –COOH group loses a proton [H]+ in aqueous solution of the amino acid, while the –NH2 acquires a proton to create a zwitterion, which is a...
Protein found in a biological system with a unique three-dimensional structure and biological activity is called a native protein. When a protein in its native form, is subjected to a physical change like change in temperature or a chemical change like change in pH, denaturation of protein takes place. Explain the cause.
Hydrogen bonds and other intermolecular interactions connect the amino acid residues in proteins. The hydrogen bonds are disrupted when a physical or chemical change occurs, and the native protein...
How do you explain the presence of an aldehydic group in a glucose molecule?
Bromine water can be used to treat glucose, which results in the carboxylic acid gluconic acid, which verifies the presence of an aldehyde group.
Assertion (A): (Fe(CN)6]3- ion shows magnetic moment corresponding to two unpaired electrons. Reason (R): Because it has d2sp3 type hybridisation.
(a) Assertion and Reason both are true, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (b) Assertion and Reason both are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (c) Assertion...
Assertion (A): Complexes of MX6 and MX5L type (X and L are unidentate) do not show geometrical isomerism. Reason (R): Geometrical isomerism is not shown by complexes of coordination number 6.
(a) Assertion and Reason both are true, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (b) Assertion and Reason both are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (c) Assertion...
Assertion (A): Linkage isomerism arises in coordination compounds containing ambidentate ligand. Reason (R): Ambidentate ligand has two different donor atoms.
(a) Assertion and Reason both are true, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (b) Assertion and Reason both are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (c) Assertion...
Assertion (A): [Cr(H2O)6]Cl2 and [Fe(H2O)6]Cl2 are reducing in nature. Reason (R): Unpaired electrons are present in their J-orbitals.
(a) Assertion and Reason both are true, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (b) Assertion and Reason both are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (c) Assertion...
Assertion (A): Toxic metal ions are removed by the chelating ligands. Reason (R): Chelate complexes tend to be more stable.
(a) Assertion and Reason both are true, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (b) Assertion and Reason both are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (c) Assertion...
Match the compounds given in Column I with the oxidation state of cobalt present in it (given in Column II) and assign the correct code. with the oxidation state of cobalt present in it (given in Column II) and assign the correct code.
Solution: \[\left( c \right)\text{ }\left( A\text{ }\to \text{ }5 \right),\text{ }\left( B\text{ }\to \text{ }1 \right),\text{ }\left( C\text{ }\to \text{ }4 \right),\text{ }\left( D\text{...
Match the complex species given in Column I with the possible isomerism given in Column II and assign the correct code:
Solution: \[\left( d \right)\text{ }\left( A\text{ }\to 4 \right),\text{ }\left( B\to \text{ }1 \right),\text{ }\left( C\text{ }\to 2 \right),\text{ }\left( D\text{ }\to 3 \right)\] Isomerism...
Match the complex ions given in Column I with the hybridisation and number of unpaired electrons given in Column II and assign the correct code :
Solution: \[\left( a \right)\text{ }\left( A\text{ }\to \text{ }3 \right),\text{ }\left( B\text{ }\to 1 \right),\text{ }\left( C\text{ }\to \text{ }5 \right),\text{ }\left( D\to \text{ }2...
Match the coordination compounds given in Column I with the central metal atoms given in Column II and assign the correct code : Code : (i) A (5) B (4) C (1) D (2) (ii) A (3) B (4) C (5) D (1) (iii) A (4) B (3) C (2) D (1) (iv) A (3) B (4) C (1) D (2)
Solution: \[\left( b \right)\text{ }\left( A\text{ }\to 5 \right),\text{ }\left( B\text{ }\to \text{ }4 \right),\text{ }\left( C\text{ }\to \text{ }1 \right),\text{ }\left( D~\to 2 \right)\] ...
Match the complex ions given in Column I with the colours given in Column II and assign the correct code :
Solution: \[\left( b \right)\text{ }\left( A\text{ }\to 4 \right),\text{ }\left( B\text{ }\to \text{ }3 \right),\text{ }\left( C\text{ }\to \text{ }2 \right),\text{ }\left( D\text{ }\to \text{ }1...
Name the type of isomerism when ambidentate ligands are attached to a central metal ion. Give two examples of ambidentate ligands.
Solution: Ambidendate ligands are those having diverse two restricting destinations. Example: Isothiocyanato Thiocyanato and Nitrite-N Nitrito-O The kind of isomerism when ambidentate ligands are...
CuSO4.5H2O is blue while CuSO4 is colourless. Why?
Solution: In CuSO4.5H2O, there are water particles that go about as ligands. The electrons will invigorate to higher d orbital and show tone. While, in CuSO4, there are no water particles to go...
Give the electronic configuration of the following complexes based on Crystal Field Splitting theory. [CoF6]3–, [Fe(CN)6]4– and [Cu(NH3)6]2+.
Solution: \[{{[CO{{F}_{\mathbf{6}}}]}^{\mathbf{3}-}}:\text{ }C{{o}^{\mathbf{3}+}}~({{d}^{\mathbf{6}}})\]
Which of the following complexes show linkage isomerism? (a) [CO(NH3)5(NO2)]2+ (b) [CO(H2O)5CO]3+ (c) [Cr(NH3)5SCN]2+ (d) [Fe(en)2Cl2]+
Solution: (a, c) NO2 and SCN are ambidentate ligands subsequently, show linkage isomerism.
Identify the correct statements for the behaviour of ethane-1, 2-diamine as a ligand. (a) It is a neutral ligand (b) It is a didentate ligand (c) It is a chelating ligand (d) It is a unidentate ligand
Solution: hence, option a, b and c are correct
Identify the optically active compounds from the following: (a) [Co(en)3]3+ (b) trans-[Co(en)2Cl2]+ (c) cis-[Co(en)2Cl2]+ (d) [Cr(NH3)5Cl]
Solution:
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain the assertion. (ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explain the assertion. (iii) Both assertion and reason are the wrong statements. (iv) The assertion is correct statement and reason is the wrong statement. (v) The assertion is the wrong statement and reason is the correct statement.Assertion: Network polymers are thermosetting. Reason: Network polymers have high molecular mass.
Option (i) is correct During polymerisation, extensive cross linking results in the creation of a three-dimensional network that is rigid, insoluble, and infusible.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain the assertion. (ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explain the assertion. (iii) Both assertion and reason are the wrong statements. (iv) The assertion is correct statement and reason is the wrong statement. (v) The assertion is the wrong statement and reason is the correct statement. Assertion: For making rubber synthetically, isoprene molecules are polymerised. Reason: Neoprene (a polymer of chloroprene) is a synthetic rubber.
Option (v) is correct Natural rubber is made up of isoprene molecules, while neoprene, a synthetic rubber, is made up of chloroprene polymers.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain the assertion. (ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explain the assertion. (iii) Both assertion and reason are the wrong statements. (iv) The assertion is correct statement and reason is the wrong statement. (v) The assertion is the wrong statement and reason is the correct statement.Assertion: Polyamides are best used as fibres because of high tensile strength. Reason: Strong intermolecular forces (like hydrogen bonding within polyamides) lead to close packing of chains and increase the crystalline character, hence, provide high tensile strength to polymers.
Option (ii) is correct Polyamides, such as nylon, are the most often used fibres. Because of the strong intermolecular hydrogen connection, they have a high tensile strength.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain the assertion. (ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explain the assertion. (iii) Both assertion and reason are the wrong statements. (iv) The assertion is correct statement and reason is the wrong statement. (v) The assertion is the wrong statement and reason is the correct statement.Assertion: Most of the Synthetic polymers are not biodegradable. Reason: Polymerisation process induces toxic character in organic molecules.
Option (iv) is correct Enzymatic hydrolysis and environmental oxidation do not destroy the majority of synthetic polymers. Toxic characteristics are not produced via polymerization.
Match the polymers given in Column I with their repeating units given in Column II.
(i) is d (ii) is a (iii) is b (iv) is e (v) is c
Match the polymers given in Column I with the preferred mode of polymerisation followed by their monomers.
(i) is d (ii) is a (iii) is b
Match the polymers given in Column I with their main applications given in Column II.
(i) is d (ii) is e (iii) is a (iv) is f (v) is b (vi) is c
Match the polymers given in Column I with their commercial names given in Column II.
(i) is b (ii) is c (iii) is a (iv) is e (v) is d
Match the polymers given in Column I with their chemical names given in Column II.
(i) is c (ii) is a (iii) is b (iv) is e (v) is d
Which factor imparts crystalline nature to a polymer like nylon?
Intermolecular H –bonding exists between the two terminal groups –C=O and –NH, allowing one Nylon molecule to join another. Because intermolecular H –bonding is relatively strong, it can result in...
What is the structural difference between HDP and LDP? How does the structure account for different behaviour and nature, hence the use of a polymer?
HDP stands for high-density polymer with a linear structure, whereas LDP stands for low-density polymer with a branching structure. HDP has a greater melting point and is chemically inert, whereas...
Why does cis-polyisoprene possess elastic property?
The polymer may be stretched by applying force due to the presence of these weak forces. When the external force is released, the polymer recovers to its original condition, showing elastic...
How is the following resin intermediate prepared and which polymer is formed by this monomer unit?
The two starting monomers for this Resin intermediate are melamine and formaldehyde. Melamine polymer is the result of their condensed polymerization.
Can the enzyme be called a polymer?
The enzyme functions as a catalyst, speeding up biological processes. Proteins make up their structure. Proteins are polymers made up of monomeric units called amino acids. As a result, enzymes are...
Why are rubbers called elastomers?
Rubber may be stretched by applying force and then returned to its original shape once the force is removed. As a result, they are referred to as elastomers.
Identify the type of polymer given in the following figure.
This is a network or cross-linked polymer. Cross-linking connects two linear polymers.
Out of chain growth polymerisation and step-growth polymerisation, in which type will, you place the following.
In this illustration, a chain-growth polymerization process combines two monomers to produce a polymer. Only monomers react with each other to keep the chain expanding.
Which of the following complexes are heteroleptic? (a) [Cr(NH3)6]3+ (b) [Fe(NH3)4 Cl2]+ (c) [Mn(CN)6]4– (d) [Co(NH3)4Cl2]
Solution: (b, d) In complexes, [Fe(NH3)4Cl2]+ and [CO(NH3)4Cl2], metal is bonded to more than one sort of ligands subsequently, they are heteroleptic.
Which of the following complexes is homoleptic? (a) [Co(NH3)6]3+ (b) [Co(NH3)4 Cl2]+ (c) [Ni(CN)4]2– (d) [Ni(NH3)4Cl2]
Solution: (a, c) In complexes [Co(NH3)6]3+ and [Ni(CN)4]2-, both Co and Ni are connected to one sort of ligands just subsequently, they are homoleptic. hence, option a and c are correct
An aqueous pink solution of cobalt(II) chloride changes to deep blue on the addition of an excess of HCl. This is because____________. (a) [Co(H2O)6]2+ is transformed into [CoCl6]4– (b) [Co(H2O)6]2+ is transformed into [CoCl4]2– (c) tetrahedral complexes have smaller crystal field splitting than octahedral complexes. (d) tetrahedral complexes have larger crystal field splitting than octahedral complex.
Solution: (b, c) Aqueous pink arrangement of cobalt (II) chloride is because of electronic progress of electron from t2g to eg energy level of [Co(H2O)6]2+ complex. At the point when overabundance...
Which of the following polymers can have strong intermolecular forces? (i) Nylon (ii) Polystyrene (iii) Rubber (iv) Polyesters
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Nylon and polyester are thread-forming fibres with a high melting point and tensile strength. Intermolecular forces such as hydrogen bonding are strong.
Which of the following options are correct for [Fe(CN)6]3- complex? (a) d2sp3 hybridisation (b) sp3d2 hybridisation (c) Paramagnetic (d) Diamagnetic
Solution: hence, option a and c are correct for [Fe(CN)6]3- complex
Atomic number of Mn, Fe, Co and Ni are 25, 26 27 and 28 respectively. Which of the following outer orbital octahedral complexes have same number of unpaired electrons? (a) [MnCl6]3- (b) [FeF6]3- (c) [CoF6]3- (d) [Ni(NH3)6]2+
Solution: so, option a and c are the correct answer
Which of the following is an example of a synthetic rubber? (i) Polychloroprene (ii) Polyacrylonitrile (iii) Buna-N (iv) cis-polyisoprene
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. Polychloroprene and Buna-N are examples of a synthetic rubber
The atomic number of Mn, Fe and Co are 25, 26 and 27 respectively. Which of the following inner orbital octahedral complexions are diamagnetic? (a) [Co(NH3)6]3+ (b) [Mn(CN)6]3– (c) [Fe(CN)6]4– (d) [Fe(CN)6]3–
Solution: hence , a and c are the correct answer
IUPAC name of [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)] is (a) platinum diaminechloronitrite (b) chloronitrito-N-ammineplatinum (II) (c) diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum (II) (d) diamminechloronitrito-N-platinate (II).
Solution: (c) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)] is diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum (II)
What kind of isomerism exists between [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 (violet) and [Cr(H2O)5Cl)Cl2.H2O (greyish- green)? (a) Linkage isomerism (b) Solvate isomerism (c) Ionisation isomerism (d) Coordination isomerism
Solution: (b) The given mixtures have diverse number of water atoms inside and outside the organize circle.
Which of the following polymers are used as fibre? (i) Polytetrafluoroethane (ii) Polychloroprene (iii) Nylon (iv) Terylene
Option (iii) and (iv) are the answers. Because of strong intermolecular interactions such as H-bonding, nylon and terylene are employed as fibres, resulting in tight chain packing and therefore...
Which of the following polymers are thermoplastic? (i) Teflon (ii) Natural rubber (iii) Neoprene (iv) Polystyrene
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Teflon and polystyrene are thermoplastics because they can be melted and moulded anew.
Which of the following are characteristics of thermosetting polymers? (i) Heavily branched cross-linked polymers. (ii) Linear slightly branched long-chain molecules. (iii) Become infusible on moulding so cannot be reused. (iv) Soften on heating and harden on cooling, can be reused.
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. Thermosetting polymers have a lot of branching cross links. They can't be used again since they don't melt when heated and can't be remoulded.
Which of the following species is not expected to be a ligand? (a) NO (b) NH4– (c) NH2CH2CH2NH2 (d) CO
Solution: (b) Ligand should give a pair of electrons or inexactly held electron pair to metal and shape a M – L bond,
A chelating agent has two or more than two donor atoms to bind to a single metal ion. Which of the following is not a chelating agent? (a) Thiosulphate (b) Oxalato (c) Glycinato (d) Ethane-1, 2-diamine
Solution: (a) Thiosulphate or S2O3–isn't a chelating specialist since it is a monodentate ligand.
The compounds [Co(SO4)(NH3)5]Br and [CO(SO4)(NH3)5]Cl represent (a) linkage isomerism (b) ionization isomerism (c) coordination isomerism (d) no isomerism.
Solution: (d) [Co(SO4)(NH3)5]Br and [CO(SO4)(NH3)5]Cl address no isomerism since they are different compounds.
Due to the presence of ambidentate ligands coordination compounds show isomerism. Palladium complexes of the type [Pd(C6H5)2(SCN)2] and [Pd(C6H5)2(NCS)2] are (a) linkage isomers (b) coordination isomers (c) ionisation isomers (d) geometrical isomers
Solution: (a) The ligands having two distinctive holding locales are known as ambident ligands e.g., NCS, NO2, and so forth Here, NCS has two restricting locales at N and S. Subsequently, NCS...
The CFSE for octahedral [CoCl6]4– is 18,000 cm–1. The CFSE for tetrahedral [CoCl4]2– will be (a) 18,000 cm–1 (b) 16,000 cm–1 (c) 8,000 cm–1 (d) 20,000 cm–1
Solution:
Indicate the complex ion which shows geometrical isomerism. (a) [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]+ (b) [Pt(NH3)3 Cl] (c) [Co(NH3)6]3+ (d) [Co(CN)5(NC)]3–
Solution:
The correct IUPAC name of [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] is (a) diamminedichloridoplatinum (II) (b) diamminedichloridoplatinum (IV) (c) diamminedichloridoplatinum (I) (d) dichloridodiammineplatinum (IV)
Solution: (a) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] is diamminedichloridoplatinum (II) .
When 1 mol CrCl3.6H2O is treated with an excess of AgNO3, 3 mol of AgCl are obtained. The formula of the complex is : (a) [CrCl3 (H2O)3].3H2O (b) [CrCl2(H2O)4]Cl.2H2O (c) [CrCl(H2O)5]Cl2.H2O (d) [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3
Solution: (d) 3 mol of AgCl implies 3Cl are given in the arrangement henceforth, the equation of the complex will be [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3.
When 0.1 mol COCl3(NH3)5 is treated with excess of AgNO3, 0.2 mol of AgCl are obtained. The conductivity of solution will correspond to (a) 1:3 electrolyte (b) 1:2 electrolyte (c) 1:1 electrolyte (d) 3:1 electrolyte
Solution: (b) One mole of AgNO3 accelerates one mole of chloride particle. In the above response, when 0.1 mole COCl3(NH3)5 is treated with abundance of AgNO3, 0.2 mole of AgCl are obtained hence,...
The colour of the coordination compounds depends on the crystal field splitting. What will be the correct order of absorption of wavelength of light in the visible region, for the complexes, [Co(NH3)6]3+, [Co(CN)6]3–, [Co(H2O)6]3+ (a) [Co(CN)6]3–> [Co(NH3)6]3+>[Co(H2O)6]3+ (b) [Co(NH3)6]3+> [Co(H2O)6]3+> [Co(CN)6]3– (c) [Co(H2O)6]3+> [Co(NH3)6]3+> [Co(CN)6]3– (d) [Co(CN)6]3–> [Co(NH3)6]3+> [Co(H2O)6]3+
Solution:
Which of the following complexes formed by Cu2+ ions is most stable?
Solution: (b) The greater the value of log K, the more prominent will be strength of complicated compound shaped. For response, For this response, log K has most elevated worth among the...
For what reason do compounds having comparable calculation have an alternate attractive second?
Solution: They vary in the quantity of combined and unpaired electrons. A solid field ligand will cause blending of electrons while a feeble field ligand won't cause matching. Blending or not...
Mastermind following complex particles in expanding request of precious stone field parting energy (DO) : [Cr(Cl)6]3–, [Cr(CN)6]3–, [Cr(NH3)6]3+.
Solution: The expanding request of gem field energy is [Cr(Cl)6]3–<[Cr(NH3)6]3+ <[Cr(CN)6]3– This is additionally the request for field strength of the ligands as indicated by the...
Clarify why [Fe(H2O)6]3+ has an attractive second worth of 5.92 BM while [Fe(CN)6]3–has a worth of just 1.74 BM.
Solution: For [Fe(H2O)6]3+, H2O is a powerless field ligand will not cause matching of electrons. Along these lines, the quantity of unpaired electrons will be 5. [Fe(CN)6]3–, Fe3+ has six unpaired...
Why are low twist tetrahedral edifices not framed?
Solution: For tetrahedral edifices, the gem field parting energy is excessively low. It is lower than blending energy in this way, the matching of electrons isn't supported and consequently the...
In view of gem field hypothesis clarify why Co(III) structures a paramagnetic octahedral complex with feeble field ligands though it frames a diamagnetic octahedral complex with solid field ligands.
Solution: The electronic design will be t42g e2g. It has 4 unpaired electron and paramagnetic. With weal ligand Δ0 < p. The design with solid field ligand will be t62g e0g. the Δ0 > p and...
The attractive snapshot of [MnCl4]2–is 5.92 BM. Clarify giving an explanation.
Solution: An attractive snapshot of 5.92 BM implies there are 5 unpaired electrons in light of the fact that \[Attractive\text{ }Moment\text{ }=\text{ }\surd \text{ }n\left( n+2 \right)\] The...
A complex of the kind [M(AA)2X2]n+is known to be optically dynamic. What does this demonstrate about the design of the complex? Give one illustration of such complicated.
Solution: The design must be cis-octahedral. Model for a particularly mind boggling is [Co(en)2Cl2]+ which is optically dynamic.
A coordination compound CrCl3.4H2O hastens silver chloride when treated with silver nitrate. The molar conductance of its answer relates to a sum of two particles. Compose the primary recipe of the compound and name it.
Solution: Assuming it structures silver chloride, there is without one chlorine iota outside the coordination circle. The primary recipe must be [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl. The name of this complex is...
Organize the accompanying buildings in the expanding request of conductivity of their answer: [Co(NH3)3Cl3], [Co(NH3)4Cl2] Cl, [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 , [Cr(NH3)5Cl]Cl2
Solution: The expanding request of conductivity is as per the following: [Co(NH3)3Cl3]<[Co(NH3)4Cl2]Cl< [Cr(NH3)5Cl]Cl2<[Co(NH3)6]Cl3
Reactivity of change components diminishes routinely from Sc to Cu. Clarify.
Solution: Viable atomic charge increments as we move along the period from left to right. Because of the explanation, the size likewise lessens. Subsequently the electrons will be held all the more...
While topping off of electrons in the nuclear orbitals, the 4s orbital is filled before the 3d orbital yet the opposite occurs during the ionization of the molecule. Clarify why?
Solution: Electrons are filled by the n+l rule. Assuming an orbital has lower n+l esteem, the electron will enter that orbital. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} For\text{ }3d,\text{ }n+l=\text{...
The halides of progress components become more covalent with expanding oxidation condition of the metal. Why?
Solution: Halides become more covalent with expanding oxidation state. As the oxidation state expands, the charge on the iota increments and the size of the particle of progress component...
E° of Cu is + 0.34V while that of Zn is – 0.76V. Clarify.
Solution: The decreased type of Cu2+ is more steady than the oxidized type of Cu. In this manner, the worth of E° is positive for Cu. Eliminating two electrons gives a steady setup [Ar]3d10 with...
An answer of KMnO4 on decrease yields either lackluster arrangement or an earthy colored encourage or a green arrangement relying upon the pH of the arrangement. What various phases of the decrease do these address and how are they completed?
Solution: In acidic medium, permanganate changes to manganous particle which is lackluster. \[MnO4-+8H+\text{ }+\text{ }5e-\to \text{ }Mn2+\text{ }+\text{ }4H2O\] (drab) In basic...
At the point when an orange arrangement containing Cr2O72–particle is treated with an antacid, a yellow arrangement is framed and when H+ particles are added to a yellow arrangement, an orange arrangement is acquired. Clarify for what reason does this occur?
Solution: At the point when Cr2O72–is treated with an antacid: \[\left( orange \right)\text{ }Cr2O72+\text{ }OH-\to \text{ }2CrO42-\left( yellow \right)\] At the point when the yellow...
Clarify why the shade of KMnO4 vanishes when oxalic corrosive is added to its answer in acidic medium.
Solution: This is a redox titration. The profound purple shade of KMnO4 vanishes because of the development of MnSO4. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} ~ \\ 5H2C2O4\text{ }+\text{ }2KMnO4\text{...
At the point when an earthy colored compound of manganese (A) is treated with HCl it gives a gas (B). The gas taken in abundance responds with NH3 to give an unstable compound (C). Distinguish intensifies A, B and C.
Solution: At the point when earthy colored co pound of manganese (A) is treated with HCl it gives chlorine gas. \[MnO2\text{ }+\text{ }4HCl\text{ }\to \text{ }MnCl2\text{ }+\text{ }Cl2\text{...
At the point when Cu2+ particle is treated with KI, a white hasten is shaped. Clarify the response with the assistance of the compound condition.
Solution: \[~2Cu2+\text{ }+\text{ }4I-\to \text{ }Cu2I2\text{ }+\text{ }I2\] Cu2+ gets decreased to Cu+, and I–gets oxidized to I2.
Why first ionization enthalpy of Cr is lower than that of Zn?
Solution: The electronic setup of chromium and zinc are separately: \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Cr\text{ }\left( 24 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\left[ Ar \right]\text{ }3d54s2 \\ ~Zn\text{ }\left(...
In spite of the fact that +3 is the trademark oxidation state for lanthanoids however cerium additionally shows +4 oxidation state in light of the fact that (a) it has variable ionization enthalpy (b) it tends to accomplish respectable gas design (c) it tends to accomplish f° arrangement (d) it looks like Pb4+
Solution: (b, c) Cerium shows +4 oxidation state likewise on the grounds that it tends to accomplish respectable gas setup and achieve f° design. Ce – 4f15d'6s2 (Ce4+–4f°)
Which of the accompanying won’t go about as oxidizing specialists? (a) CrO3 (b) MoO3(c) WO3 (d) CrO42-
Solution: (b, c) An animal types can go about as an oxidizing specialist just when metal is available in high oxidation state however lower oxidation state show strength. As higher oxidations...
Change components structure double mixtures with incandescent lamp. Which of the accompanying components will frame MF3 type compounds? (a) Cr (b) Co (c) Cu (d) Ni
Solution: (a, b) Cr and Co structure MF3 kind of mixtures. The capacity of fluorine to balance out the most elevated oxidation state is because of higher grid energy in CoF3 and higher bond enthalpy...
Which of the accompanying particles show higher twist just attractive second worth? (a) Ti3+ (b) Mn2+ (c) Fe2+ (d) Co3+
Solution: (b, c) Mn2+ (3d5) and Fe2+ (3d6) have 5 and 4 unpaired electrons thus higher upsides of twist just attractive second when contrasted with Ti3+ (3d1) and Co2+ (3d7).
Which of the accompanying lanthanoids show +2 oxidation state other than the trademark oxidation state +3 of lanthanoids? (a) Ce (b) Eu (c) Yb (d) Ho
Solution: (b, c)
General electronic arrangement of actinoids is (n – 2)f1-14 (n – 1 )d0-2 ns2. Which of the accompanying actinoids have one electron in 6d orbital? (a) U (Atomic no. 92) (b) Np (Atomic no. 93) (c) Pu (Atomic no. 94) (d) Am (Atomic no. 95)
Solution:
Which of the accompanying actinoids show oxidation states up to +7? (a) Am (b) Pu (c) U (d) Np
Solution: (b, d) Np and Pu show +7 oxidation state.
As dichromate, Cr (VI) is a solid oxidizing specialist in acidic medium however, Mo (VI) in MoO3 and W (VI) in WO3 are not on the grounds that (a) Cr (VI) is more steady than Mo(VI) and W(VI) (b) Mo(VI) and W(VI) are more steady than Cr(VI) (c) higher oxidation conditions of heavier individuals from bunch 6 of change series are more steady (d) lower oxidation conditions of heavier individuals from bunch 6 of change series are more steady
Solution: (b, c) In d-block components, for heavier components, the higher oxidation states are more steady. Thus, Mo(VI) and W(VI) are more steady than Cr (VI). That is the reason, Cr (VI) as...
Change components show attractive second because of twist and orbital movement of electrons. Which of the accompanying metallic particles have practically same twist just attractive second? (a) Co2+ (b) Cr2+ (c) Mn2+ (d) Cr3+
Solution: (a, d) Co2+ (3d7) and Cr3+ (3d3) have 3 unpaired electrons. Thus they have practically same twist just attractive second.
For the most part, progress components and their salts are shaded because of the presence of unpaired electrons in metal particles. Which of the accompanying mixtures are hued? (a) kMnO4 (b) Ce(SO4)2 (c) TiCl4 (d) Cu2Cl2
Solution: (a, b) KMnO4 and Ce(S04)2 are shaded because of charge move
For what reason is HCl not used to make the medium acidic in oxidation responses of KMnO4 in acidic medium? (a) Both HCl and KMn04 go about as oxidizing specialists. (b) KMnO4 oxidizes HCl into Cl2 which is likewise an oxidizing specialist. (c) KMnO4 is a more fragile oxidizing specialist than HCl. (d) KMnO4 goes about as a decreasing specialist within the sight of HCl.
Solution: (b) HCl isn't utilized to make the medium acidic in oxidation responses of KMnO4 in acidic medium. The explanation is that in case HCl is utilized, the oxygen delivered from KMnO4 + HCl is...
In spite of the fact that zirconium has a place with 4d change series and hafnium to 5d change series and still, after all that they show comparative physical and substance properties in light of the fact that (a) both have a place with d-block (b) both have same number of electrons (c) both have comparative nuclear span (d) both have a place with a similar gathering of the intermittent table
Solution: (c) Zirconium and hafnium have comparable nuclear range thus they show comparable physical and synthetic properties.
Most elevated oxidation condition of manganese in fluoride is +4 (MnF4) however most noteworthy oxidation state in oxides is +7 (Mn2O7) in light of the fact that (a) fluorine is more electronegative than oxygen (b) fluorine doesn’t have d-orbitals (c) fluorine settles lower oxidation state (d) in covalent mixtures fluorine can frame single bond just while oxygen shapes twofold bond
Solution: (d) The most noteworthy oxidation condition of manganese in fluoride is +4 (MnF4) yet in oxides it is +7 (Mn2O7) in light of the fact that in covalent mixtures fluorine can frame single...
When fermented K2Cr2O7 arrangement is added to Sn2+ salts, Sn2+ changes to (a) Sn (b) Sn3+ (c) Sn4+ (d) Sn+
Solution: (c) When fermented K2Cr2O7 arrangement is added to Sn2+ salt, Sn2+ changes to Sn4+. The response is given underneath:
Which of the accompanying assertion isn’t right? (a) Copper frees hydrogen from acids (b) In its higher oxidation states, manganese structures stable mixtures with oxygen and fluorine (c) Mn3+ and Co3+ are oxidizing specialists in watery arrangement (d) Ti2+ and Cr2+ are decreasing specialists in watery arrangement
Solution: (a) Copper doesn't free hydrogen from acids. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Cu\text{ }+\text{ }2H2S04\text{ }\text{ }>\text{ }CuSO4\text{ }+\text{ }S02\text{ }+\text{ }2H2O \\ ~ \\...
KMn04 goes about as an oxidizing specialist in soluble medium. When soluble KMnO4 is treated with KI, iodide particle is oxidized to (a) I2 (b)Io–(c) I03 (d) I04
Solution: \[\left( c \right)\text{ }2KMnO4\text{ }+\text{ }KI\text{ }+\text{ }H2O\text{ }\text{ }>\text{ }2K0H\text{ }+\text{ }2MnO2\text{ }+\text{ }KI03\]
The attractive second is related with its twist rakish energy and orbital precise force. Twist just attractive second worth of Cr3+ particle is (a) 2.87 B.M. (b) 3.87 B.M. (c) 3.47 B.M. (d) 3.57 B.M.
Solution: (b) The attractive second is related with its twist precise force and orbital rakish energy.
Interstitial mixtures are shaped when little particles are caught inside the gem cross section of metals. Which of coming up next isn’t the trademark property of interstitial mixtures? (a) They have high liquefying focuses in contrast with unadulterated metals (b) They are exceptionally hard (c) They hold metallic conductivity (d) They are synthetically extremely receptive.
Solution: (d) Interstitial mixtures are synthetically idle.
Gadolinium has a place with 4f series. Its nuclear number is 64. Which of the following is the right electronic arrangement of gadolinium? (I) [Xe] 4f 75d16s2 (ii) [Xe] 4f 65d26s2 (iii) [Xe] 4f 86d2 (iv) [Xe] 4f 95s1
Solution: (a) 64Gd: [Xe] 4f7 5d1 6s2
Which of coming up next is amphoteric oxide? Mn2O7, CrO3, Cr2O3, CrO, V2O5, V2O4 (a) V2O5, Cr2O3 (b)Mn2O7, CrO3 (c) CrO, V2O5 (d) V2O5, V2O4
Solution: (a) V2O5 and Cr2O3 are amphoteric oxides on the grounds that both respond with alkalies just as acids. Keep in mind: In lower oxides, the fundamental person is transcendent while in higher...
KMnO4 goes about as an oxidizing specialist in acidic medium. The quantity of moles of KMnO4 that will be expected to respond with one mole of sulfide particles in acidic arrangement is (I) 2/5 (ii) 3/5 (iii) 4/5 (iv) 1/5
Solution:
There are 14 components in actinoid series. Which of the accompanying component doesn’t have a place with this series? (a) U (b) Np (c) Tm (d) Fm
Solution: (c) Tm (Thulium) is a lanthanoid.
At the point when KMnO4 arrangement is added to oxalic corrosive arrangement, the decolourisation is delayed to start with yet becomes momentary after some time on the grounds that (a) CO2 is shaped as the item (b) Reaction is exothermic (c) Mn04 catalyzes the response (d) Mn2+ goes about as autocatalyst
Solution: (d) When KMnO4 arrangement is added to oxalic corrosive arrangement, the decolourisation is delayed first and foremost yet becomes immediate after some time in light of the fact that Mn2+...
Which of the accompanying responses are disproportionation responses?
Solution:
Which of the accompanying oxidation state is normal for all lanthanoids? (a) +2 (b) +3 (c) +4 (d) +5
Solution: (b) +3 oxidation state is generally normal for all lanthanoids.
The attractive idea of components rely upon the presence of unpaired electrons. Distinguish the arrangement of change component, which shows the most elevated attractive second. (a) 3d7 (b) 3d5 (c) 3d8 (d) 3d2
Solution: (b) The more noteworthy the quantity of unpaired electron, the higher will be its worth of attractive second. Since, 3d5 has 5 unpaired electrons subsequently most noteworthy attractive...
On expansion of modest quantity of KMnO4 to concentrated H2SO4, a green slick compound is acquired which is exceptionally touchy in nature. Distinguish the compound from the accompanying: (a) Mn2O7 (b) MnO2 (c) MnSO4 (d) Mn2O3
Solution: \[\left( a \right)\text{ }2KMnO4\text{ }+\text{ }2H2SO4\left( Conc\text{ } \right)\text{ }\text{ }>\text{ }Mn2O7\text{ }+\text{ }2KHSO4\text{ }+\text{ }H2O\]
By and large, progress components structure shaded salts because of the presence of unpaired electrons. Which of the accompanying compound will be shaded in strong state? (a) Ag2SO4 (b) CUF2 (c) ZnF2 (d) Cu2Cl2
Solution: (b) Cu2+ has 1 unpaired electron in CuF2, consequently, it is hued in strong state.
Metallic radii of some change components are given underneath. Which of these components will have most noteworthy thickness?
Solution: (d) On moving passed on to directly along period, metallic span diminishes while mass increments. Diminishes in metallic span combined with expansion in nuclear mass outcomes in...
The electronic setup of Cu(II) is 3d9 while that of Cu(I) is 3d10. Which of coming up next is right? (I) Cu(II) is more steady (ii) Cu(II) is less steady (iii) Cu(I) and Cu(II) are similarly steady (iv) Stability of Cu(I) and Cu(II) relies upon the idea of copper salts
Solution: (a) Cu(II) is more steady because of more noteworthy compelling atomic charge of Cu(II).
Electronic design of a change component X in +3 oxidation state is [Ar]3d5. What is its nuclear number? (I) 25 (ii) 26 (iii) 27 (iv) 24
Solution:
Why is the solubility of haloalkanes in water very low?
Because energy is required to overcome the attractions between the haloalkane molecules as well as to break the hydrogen bonds between water molecules, haloalkanes are only weakly soluble in water.
Discuss the role of Lewis acids in the preparation of aryl bromides and chlorides in the dark.
Electrophilic substitution can be used to make aryl bromides and chlorides from arenes. In the absence of light, this reaction is carried out by treating the arene with chlorine or bromine in the...
Haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes and haloalkenes. Explain.
This is due to the aryl ring's resonance stabilisation. There will be a conjugation of chlorine electrons with the electrons in the ring in the case of C6H5-Cl. The partial double bond nature of the...
Why iodoform has appreciable antiseptic property?
Iodoform has a significant antibacterial activity due to the release of free iodine.
Which of the compounds will react faster in SN1 reaction with the –OH ion? CH3— CH2— Cl or C6H5— CH2— Cl
In an SN1 reaction with the OH- ion, C6H5— CH2— Cl will react quicker. This is owing to the carbocation's stability in the compound. The C6H5 group is already stable owing to resonance, and the CH2...
Aryl chlorides and bromides can be easily prepared by electrophilic substitution of arenes with chlorine and bromine respectively in the presence of Lewis acid catalysts. But why does the preparation of aryl iodides requires the presence of an oxidising agent?
Arenes' iodination can be reversed due to the production of HI. An oxidising agent, such as HNO3 or HIO4, oxidises HI to speed up the process and stabilise the result.
Alkyl fluorides are synthesised by heating an alkyl chloride/bromide in presence of ____________ or ____________. (i) Ca F2 (ii) CoF2 (iii) Hg2F2 (iv) NaF
Option (ii) and (iii) are the answers. Heating an alkyl chloride or bromide in the presence of a metallic fluoride such as AgF, FIg2F2, CoF2, or SbF3 results in the production of alkyl fluorides....
Alkyl halides are prepared from alcohols by treating with (i) HCl + ZnCl2 (ii) Red P + Br2 (iii) H2SO4+ KI (iv) All the above
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers (i) $R-\mathrm{OH} \stackrel{\mathrm{HCl}+\mathrm{ZnCl}}{\longrightarrow} R-\mathrm{Cl}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}$ (ii) $R-\mathrm{OH}...
Which of the following are secondary bromides? (i) (CH3)2 CHBr (ii) (CH3)3C CH2Br (iii) CH3CH(Br)CH2CH3 (iv) (CH3)2CBrCH2CH3
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. Secondary bromides are those in which the -carbone (bromine-bound carbon) is further attached to two alkyl groups. The -carbon in compounds (i) and (iii) is...
Ethylene chloride and ethylidene chloride are isomers. Identify the correct statements. (i) Both the compounds form the same product on treatment with alcoholic KOH. (ii) Both the compounds form the same product on treatment with aq.NaOH. (iii) Both the compounds form the same product on reduction. (iv) Both the compounds are optically active.
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. They give ethyne on treatment with alcoholic $\mathrm{KOH}$. $ \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{CHCl}_{2} \underset{\mathrm{KOH}}{\stackrel{\text { alc....
Haloalkanes contain halogen atom (s) attached to the sp3 hybridised carbon atom of an alkyl group. Identify haloalkane from the following compounds. (i) 2-Bromopentane (ii) Vinyl chloride (chloroethene) (iii) 2-chloroacetophenone (iv) Trichloromethane
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Halogen atoms are linked to the sp3 hybridised carbon atom of the alkyl group in each of these molecules.
Which of the following statements are correct about the mechanism of this reaction? (i) A carbocation will be formed as an intermediate in the reaction. (ii) OH–will attach the substrate (b) from one side and Cl- will leave it simultaneously from the other side. (iii) An unstable intermediate will be formed in which OH– and Cl– will be attached by weak bonds. (iv) The reaction proceeds through an SN1 mechanism.
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Because it is a tertiary halide, it undergoes the SN1 process, resulting in the formation of a carbocation as an intermediate.
Which of the following statements are correct about the reaction intermediate? (i) Intermediate (c) is unstable because in this carbon is attached to 5 atoms. (ii) Intermediate (c) is unstable because carbon atom is sp2 hybridised. (iii) Intermediate (c) is stable because carbon atom is sp2 hybridised. (iv) Intermediate (c) is less stable than the reactant (b).
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Intermediate (iii) is unstable in the above reaction because the carbon atom is linked to 5 atoms and is less stable than reactant (ii).
Which of the following statements are correct about this reaction? (i) The given reaction follows the SN2 mechanism. (ii) (b) and (d) have the opposite configuration. (iii) (b) and (d) have the same configuration. (iv) The given reaction follows the SN1 mechanism.
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers. Alkyl halide is the main reactant in the given reaction. A transient condition is found here, in which one bond is broken and another is created synchronously,...
Which of the statements are correct about the above reaction? (i) (a) and (e) both are nucleophiles. (ii) In (c) carbon atom is sp3 hybridised. (iii) In (c) carbon atom is sp2 hybridised. (iv) (a) and (e) both are electrophiles.
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. Nucleophiles are HO and CF. The C atom is sp2 hybridised in (iii) due to the simultaneous creation of the C – OH bond and the breakdown of the C – Cl link. As a...
Which is the correct increasing order of boiling points of the following compounds? 1-Bromoethane, 1-Bromopropane, 1-Bromobutane, Bromobenzene (i) Bromobenzene < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromoethane (ii) Bromobenzene < 1-Bromoethane < 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromobutane (iii) 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Bromoethane < Bromobenzene (iv) 1-Bromoethane < 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromobutane < Bromobenzene
Option (iv) is the answer Reason: As the molecular mass of the alkyl halide grows, the boiling point rises.
Which is the correct increasing order of boiling points of the following compounds? 1-Iodobutane, 1-Bromobutane, 1-Chlorobutane, Butane (i) Butane < 1-Chlorobutane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Iodobutane (ii) 1-Iodobutane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Chlorobutane < Butane (iii) Butane < 1-Iodobutane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Chlorobutane (iv) Butane < 1-Chlorobutane < 1-Iodobutane < 1-BromobutaneSolution:
Option (i) is the answer. Explanation: The larger the surface area, the stronger the intermolecular forces of attraction and, as a result, the higher the boiling point. For comparable types of alkyl...
arrange the compounds in increasing order of the rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.(i) (c) < (b) < (a) (ii) (b) < (c) < (a) (iii) (a) < (c) < (b) (iv) (a) < (b) < (c)
Option (iv) is the answer. Electron withdrawing groups boost aryl halide reactivity; the higher the number of electron withdrawing groups, the higher the rate of nucleophilic substitution.
arrange the compounds in increasing order of the rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.(i) (a) < (b) < (c) (ii) (a) < (c) < (b) (iii) (c) < (b) < (a) (iv) (b) < (c) < (a)
Option (iv) is the answer. The presence of an electron-releasing group in the ortho or para locations slows down nucleophilic substitution.
arrange the compounds in increasing order of the rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.(i) (a) < (b) < (c) (ii) (c) < (b) < (a) (iii) (a) < (c) < (b) (iv) (c) < (a) < (b)
Option (iii) is the answer. Nucleophilic substitution is facilitated by the presence of an electron withdrawing group (-NO2) in the ortho and para positions. At meta position, the presence of an...
Which of the carbon atoms present in the molecule given below are asymmetric?(i) a, b, c, d (ii) b, c (iii) a, d (iv) a b, c
Option (ii) is the answer. The chiral carbon, which is $sp_3$ hybridised carbon attached to four distinct substituents, is known as asymmetric carbon. Because (b) and (c) are $sp_3$ hybridised, they...
Chloromethane on treatment with an excess of ammonia yields mainly
Option (iii) is the answer. After reacting with $NH_3$ and chloromethane, methanamine is formed.
The reaction of toluene with chlorine in the presence of iron and the absence of light yields ____________.
Option (d) is the answer. In the presence of iron and in the absence of light, toluene reacts with chlorine to produce a mixture of 1-chloro-2-methylbenzene and 1-chloro-4-methylbenzene. The methyl...
Which of the following alkyl halides will undergo SN1 reaction most readily? (i) (CH3)3C—F (ii) (CH3)3C—Cl (iii) (CH3)3C—Br (iv) (CH3)3C—I
Option (iv) is the answer. SN1 reactions occur mostly in polar protic solvents such as H2O and follow first-order kinetics. This indicates that the reaction rate is solely determined by one...
A primary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo _____________. (i) SN1 reaction (ii) SN2 reaction (iii) α–Elimination (iv) Racemisation
Option (ii) is the answer. Primary alkyl halides undergo SN2 mechanisms because 1∘ substrates have little steric hindrance to nucleophilic attack and 1∘ carbocations are relatively unstable....
What is ‘A’ in the following reaction?
The solution is option (iii). The addition of HCl across the double bond follows the Markovnikov rule in the aforementioned reaction. The negative portion of the addition molecule is linked to the...
Ethylidene chloride is a/an ______________. (i) vic-dihalide (ii) gem-dihalide (iii) allylic halide (iv) vinylic halide
Option (ii) is the answer. A gem-dihalide is ethylidene chloride. A compound with two halogen atoms on the same carbon atom is known as Gem Dihalide.
Chlorobenzene is formed by the reaction of chlorine with benzene in the presence of 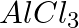 . Which of the following species attacks the benzene ring in this reaction? (i) Cl– (ii) Cl+ (iii)
. Which of the following species attacks the benzene ring in this reaction? (i) Cl– (ii) Cl+ (iii)  (iv) [AlCl4]–
(iv) [AlCl4]–
Option (ii) is the answer. Chlorobenzene is formed by the reaction of chlorine with benzene in the presence of AlCl3. Cl+ attacks the benzene ring in this reaction.
The position of –Br in the compound in CH3CH==CHC(Br)(CH3)2 can be classified as ____________. (i) Allyl (ii) Aryl (iii) Vinyl (iv) Secondary
Optuion (i) is the answer. A) Allyl : $\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CHC}(\mathrm{Br})\left(\mathrm{CH}_{3}\right)_{2}$ B) Aryl: $\mathrm{p}-\mathrm{ClC}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{4} \mathrm{CH}_{2}...
Which of the following is an example of vic-dihalide? (i) Dichloromethane (ii) 1,2-dichloroethane (iii) Ethylidene chloride (iv) Allyl chloride
Option (ii) is the answer. Vicinal dihalides are formed when a halogen reacts with an alkene to form compounds with halogen on neighbouring carbons. In terms of yearly output, 1, 2- dichloroethane...
Which of the following structures is enantiomeric with the molecule (A) given below :
Option (i) is the answer. Enantiomers are a pair of molecules that are mirror copies of one another.
In which of the following molecules carbon atom marked with an asterisk (*) is asymmetric?(i) (a), (b), (c), (d) (ii) (a), (b), (c) (iii) (b), (c), (d) (iv) (a), (c), (d)
Option (ii) is the answer. Asymmetric carbon atoms are those that have four distinct groups or atoms connected to them. The compounds a,b,c satisfy this criterion, thus B is the right answer.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points.(i) (b) < (a) < (c) (ii) (a) < (b) < (c) (iii) (c) < (a) < (b) (iv) (c) < (b) < (a)
Option (iii) is the answer. The boiling point of an alkyl halide falls as the branching rises. As a result, tert butyl bromide has the lowest boiling point while n butyl bromide has the greatest...
Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their densities.(i) (a) < (b) < (c) < (d) (ii) (a) < (c) < (d) < (b) (iii) (d) < (c) < (b) < (a) (iv) (b) < (d) < (c) < (a)
Option (i) is the answer. Reason:The density of a substance is exactly proportional to its molar mass at constant volume.
Which reagent will you use for the following reaction? CH3CH2CH2CH3 → CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl + CH3CH2CHClCH3 (i) Cl2/UV light (ii) NaCl + H2SO4 (iii) Cl2 gas in dark (iv) Cl2 gas in the presence of iron in dark
Option (i) is the answer. Mono-chlorinated isomeric products of Cl 2/UV light free radical substitution
Which of the following is the halogen exchange reaction?
Option (i) is the answer. Metal–halogen exchange is a basic reaction in organometallic chemistry that transforms an organic halide into an organometallic product. Electropositive metals (Li, Na, Mg)...
Toluene reacts with a halogen in the presence of iron (III) chloride giving ortho and para halo compounds. The reaction is (i) Electrophilic elimination reaction (ii) Electrophilic substitution reaction (iii) Free radical addition reaction (iv) Nucleophilic substitution reaction
Option (ii) is the answer. In the presence of Iron(III) chloride, toluene interacts with halogen to produce ortho and para halo compounds in an electrophilic substitution process. The Cl atom...
Identify the compound Y in the following reaction.
Option (i) is the answer.
Which of the following alcohols will yield the corresponding alkyl chloride on reaction with concentrated HCl at room temperature?
Option (iv) is the answer. If any alkyl halide forms a more stable carbocation at room temperature, the result is a more stable and efficient product. The formation of a $3^0$ carbocation as an...
Phenol can be distinguished from ethanol by the reactions with _________. (i) Br2/water (ii) Na (iii) Neutral FeCl3 (iv) All the above
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. Phenols react with FeCl3 to create a colourful Fe3+ ion complex. Depending on the structure of the phenol examined, the hue ranges from purple to orange....
Which of the following reagents can be used to oxidise primary alcohols to aldehydes? (i) CrO3 in an anhydrous medium. (ii) KMnO4 in acidic medium. (iii) Pyridinium chlorochromate. (iv) Heat in the presence of Cu at 573K
Option (i), (iii) and (iv) are the answers. Primary alcohols can be oxidised to aldehydes using CrO3 in an anhydrous media. CrO3 serves as an oxidizer in this situation. As a result, option I is the...
Which of the following reactions will yield phenol?
Option (A), (B) and (C) are correct Diazonium salt is produced when aniline is treated with NaNO2 + HCl. The Diazonium salts are then hydrolyzed to Phenols by heating them with water. As a result,...
Which of the following are used to convert RCHO into RCH2OH? (i) H2/Pd (ii) LiAlH4 (iii) NaBH4 (iv) Reaction with RMgX followed by hydrolysis
Option (i), (ii) and (iii) are the answers. In the presence of a catalyst such as Pd, Pt, or Ni, aldehydes can be transformed to their corresponding alcohols by hydrogen. Lithium aluminium hydride...
Mark the correct increasing order of reactivity of the following compounds with HBr/HCl.(i) a < b < c (ii) b < a < c (iii) b < c < a (iv) c < b < a
Option (iii) is the answer. It's a nucleophilic substitution process that uses the $SN_1$ mechanism. The stability of the carbocation is required for the $SN_1$ mechanism to work. The presence of an...
Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.(i) e > d > b > a > c (ii) b > d > a > c > e (iii) d > e > c > b > a (iv) e > d > c > b > a
Option (ii) is the answer. The sequence of decreasing acid strength is b>d>a>c>e, with p-nitrophenol being the most acidic and p-methoxy phenol being the least acidic. The acidity is...
Which of the following is most acidic? (i) Benzyl alcohol (ii) Cyclohexanol (iii) Phenol (iv) m-Chlorophenol
Option (iv) is the answer. Alcohols have a lower acidity level than phenol. Furthermore, electron-withdrawing groups make phenols more acidic, therefore m-chlorophenol is the most acidic.
Phenol is less acidic than ______________. (i) ethanol (ii) o-nitrophenol (iii) o-methyl phenol (iv) o-methoxy phenol
Option (ii) is the answer. Because electron withdrawing $-NO_2$ groups enhance the acidity of phenols, while electron donating groups ($-CH_3$,$-OCH_3$) lower the acidity of phenols, phenol is less...
Which of the following species can act as the strongest base?
Option (ii) is the answer. The conjugate base of the weakest acid is the strongest. Because R OH is the weakest acid, $RO^-$ is the most powerful base.
IUPAC name of the compound is ______________.(i) 1-methoxy-1-methylethane (ii) 2-methoxy-2-methylethane (iii) 2-methoxypropane (iv) isopropylmethyl ether
Option (iii) is the answer. 2methoxypropane is the IUPAC name for the compound.
IUPAC name of m-cresol is ___________. (i) 3-methylphenol (ii) 3-chlorophenol (iii) 3-methoxyphenol (iv) benzene-1,3-diol
Option (i) is the answer. Because OH has a greater priority, its position on the benzene ring is number one, and the methyl group with locant number three is meta to it. 3-Methylphenol will be its...
Give IUPAC name of the compound given below.(i) 2-Chloro-5-hydroxyhexane (ii) 2-Hydroxy-5-chlorohexane (iii) 5-Chlorohexan-2-ol (iv) 2-Chlorohexan-5-ol
Option (iii) is the answer. We begin by choosing the longest carbon chain in the supplied organic molecule, as defined by IUPAC nomenclature. We use hexane because the longest carbon chain has six...
