Wavelength of the emitted radiation $=616 \mathrm{~nm}=616 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{~m}$ (Given) (a)Frequency of the emission $(\nu)$ $ \nu=\frac{c}{\lambda} $ Where, $c=$ speed of the radiation...
Glycogen is a branched-chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by the formation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to __________.
(i) Amylose
(ii) Amylopectin
(iii) Cellulose
(iv) Glucose
Option (ii) is the answer. Glycogen has a similar structure to amylopeptin. It's an a-D glucose unit branched chain polymer with C1-C4 glycosidic linkage for chain formation and C1-C6 glycosidic...
Which of the following polymer is stored in the liver of animals? (i) Amylose (ii) Cellulose (iii) Amylopectin (iv) Glycogen
Option (iv) is the answer. Glycogen is a type of sugar that is stored in the liver of mammals.
Sucrose (cane sugar) is a disaccharide. One molecule of sucrose on hydrolysis gives _________.
(i) 2 molecules of glucose
(ii) 2 molecules of glucose + 1 molecule of fructose
(iii) 1 molecule of glucose + 1 molecule of fructose
(iv) 2 molecules of fructose
Option (iii) is the answer. Cane sugar (sucrose) is a disaccharide. When sucrose is hydrolyzed, one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose are produced.
Which of the following pairs represents anomers?
Option (C) is the answer. Anomers are isomers that differ only in the conformation of the hydroxyl group at C—1 and are known as - and -fonns.
Proteins are found to have two different types of secondary structures viz. α-helix and β-pleated sheet structure. α-helix structure of the protein is stabilised by : (i) Peptide bonds (ii) van der Waals forces (iii) Hydrogen bonds (iv) Dipole-dipole interactions
Option ( iii) is the answer. Hydrogen bonding help to keep the -helix structure of proteins stable. By twisting into a right-handed helix and hydrogen bonding the -NH group of each amino acid...
In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e. aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars. Which of the following disaccharide is a non-reducing sugar?
Option (B) is the answer. This structure represents sucrose, in which the C1—C2 glycosidic bond connects -D glucose and -D-fructose. This is a non-reducing sugar since the reducing groups of glucose...
Which of the following acids is a vitamin? (i) Aspartic acid (ii) Ascorbic acid (iii) Adipic acid (iv) Saccharic acid
Option (ii) is the answer. Vitamin C is ascorbic acid. Amino acid aspartic acid is a kind of amino acid. Dicarboxylic acids include adipic acid and saccharic acid.
Dinucleotide is obtained by joining two nucleotides together by phosphodiester linkage. Between which carbon atoms of pentose sugars of nucleotides are Are these linkages present? (i) 5′ and 3′ (ii) 1′ and 5′ (iii) 5′ and 5′ (iv) 3′ and 3′
Option (i) is the answer. Between the pentose sugars of nucleotides, there are 5′ and 3′ connections.
Nucleic acids are the polymers of ______________. (i) Nucleosides (ii) Nucleotides (iii) Bases (iv) Sugars
Option (ii) is the answer. Nucleic acids are nucleotide polymers connected together by phosphodiester linkage.
Which of the following statements is not true about glucose?
(i) It is an aldohexose.
(ii) On heating with HI, it forms n-hexane.
(iii) It is present in furanose form.
(iv) It does not give 2,4-DNP test.
Option (iii) is the answer. It's found in the pyranose structure.
Each polypeptide is a protein has amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence. This sequence of amino acids is said to be ____________.
(i) primary structure of proteins.
(ii) secondary structure of proteins.
(iii) the tertiary structure of proteins.
(iv) quaternary structure of proteins.
Option (i) is the answer. The main structure of proteins is the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
DNA and RNA contain four bases each. Which of the following bases is not present in RNA? (i) Adenine (ii) Uracil (iii) Thymine (iv) Cytosine
Option (iii) is the answer. Adenine, guanine, thymine, and cytosine are the four bases found in DNA. Adenine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine are the four bases found in RNA. As a result, thymine is...
Which of the following B group vitamins can be stored in our body? (i) Vitamin B1 (ii) Vitamin B2 (iii) Vitamin B6 (iv) Vitamin B12
Option (iv) is the answer. Because vitamin B12 is water insoluble, it can be stored in the body.
Which of the following bases is not present in DNA? (i) Adenine (ii) Thymine (iii) Cytosine (iv) Uracil
Option (iv) is the answer. In DNA, uracil is absent; instead, thymine is present.
Three cyclic structures of monosaccharides are given below which of these are anomers.
(i) I and II
(ii) II and III
(iii) I and III
(iv) III is anomer of I and II
Option (i) is the answer. Anomers are cyclic configurations of monosaccharides that differ in structure at carbon-1. I and II are anomers in this case because they differ solely in carbon-1.
Which of the following reactions of glucose can be explained only by its cyclic structure?
(i) Glucose forms pentaacetate.
(ii) Glucose reacts with hydroxylamine to form an oxime.
(iii) Pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine.
(iv) Glucose is oxidised by nitric acid to gluconic acid
Option (iii) is the answer. The absence of a free -CHO group is indicated by the fact that glucose pentaacetate does not react with hydroxylamine. Only the cyclic nature of glucose may explain this...
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
(i) I, II, III
(ii) II, III
(iii) I, II
(iv) III
Option (i) is the answer. The -OH group is on the lowest asymmetric carbon on the right side of the I, II, and III structures, which is similar to (+) glyceraldehyde.
Structure of a disaccharide formed by glucose and fructose is given below. Identify anomeric carbon atoms in monosaccharide units.
(i) ‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘a’ carbon of fructose.
(ii) ‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘e’ carbon of fructose.
(iii) ‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘b’ carbon of fructose.
(iv) ‘f’ carbon of glucose and ‘f ’ carbon of fructose.
Option (iii) is the answer. Anomeric carbon is carbon that is next to an oxygen atom in the cyclic structure of glucose or fructose. 'a' and 'b' are next to the oxygen atom, as illustrated in the...
Three structures are given below in which two glucose units are linked. Which of these linkages between glucose, units are between C1 and C4 and which linkages are between C1 and C6?
(i) (A) is between C1 and C4, (B) and (C) is between C1 and C6
(ii) (A) and (B) are between C1 and C4, (C) is between C1 and C6
(iii) (A) and (C) is between C1 and C4, (B) is between C1 and C6
(iv) (A) and (C) is between C1 and C6, (B) is between C1 and C4
Option (iii) is the answer (A) and (C) are in the Cl-C4 range, while (B) is in the Cl-C6 range.
Carbohydrates are classified on the basis of their behaviour on hydrolysis and also as reducing or non-reducing sugar. Sucrose is a __________. (i) monosaccharide (ii) disaccharide (iii) reducing sugar (iv) non-reducing sugar
Option (ii) and (iv) are the answers. Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar and a disaccharide.
Proteins can be classified into two types on the basis of their molecular shape i.e., fibrous proteins and globular proteins. Examples of globular proteins are : (i) Insulin (ii) Keratin (iii) Albumin (iv) Myosin
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers Globulular protein is the structure that develops when a chain of polypeptides coils around to form a spherical shape. Insulin and albumin, for example, are...
Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose?
(i) Amylose
(ii) Amylopectin
(iii) Cellulose
(iv) Glycogen
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Amylopectin and glycogen are both glucose branching polymers.
Amino acids are classified as acidic, basic or neutral depending upon the relative number of amino and carboxyl groups in their molecule. Which of the following is acidic?
Option (ii) and (iv) are the answers. Acidic amino acids have more than one -COOH group one against the –NH2 group.
Lysine, is _______________.
(i) α-Amino acid
(ii) Basic amino acid
(iii) Amino acid synthesised in the body
(iv) β-Amino acid
Option (i), (ii) and (iii) are the answers. (a)Lysine is a kind of amino acid with the structural formula . (b) Because the number of NH2 groups (2) is more than the number of COOH groups, it is a...
Which of the following monosaccharides are present as five-membered cyclic structure (furanose structure)? (i) Ribose (ii) Glucose (iii) Fructose (iv) Galactose
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. The five-membered cyclic structure of ribose and fructose is shown (furanose structures). They have a five-membered ring, similar to the foran compound....
In fibrous proteins, polypeptide chains are held together by ___________.
(i) van der Waals forces
(ii) disulphide linkage
(iii) electrostatic forces of attraction
(iv) hydrogen bonds
Option (ii) and (iv) are the answers. Disulphide linkage and hydrogen bonding hold polypeptide chains together in fibrous proteins.
Which of the following are purine bases?
(i) Guanine
(ii) Adenine
(iii) Thymine
(iv) Uracil
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers. Purines are made up of a six-membered nitrogen-containing ring fused together with a five-membered nitrogen-containing ring. Purine bases guanine and adenine...
Which of the following terms are correct about enzyme?
(i) Proteins
(ii) Dinucleotides
(iii) Nucleic acids
(iv) Biocatalysts
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Enzymes are protein molecules that act as biocatalysts in the body's chemical reactions.
Name the sugar present in milk. How many monosaccharide units are present in it? What are such oligosaccharides called?
Lactose is the sugar found in milk. Glucose and galactose are two monosaccharides found in lactose. Disaccharides are oligosaccharides that include two monosaccharide units.
How do you explain the presence of all the six carbon atoms in glucose in a straight chain?
When glucose is heated with HI for a long time, n-hexane develops, implying that all six carbon atoms are connected in a straight chain.
In nucleoside, a base is attached at 1C position of the sugar moiety. A nucleotide is formed by linking the phosphoric acid unit to the sugar unit of a nucleoside. At which position of sugar unit is the phosphoric acid linked in a nucleoside to give a nucleotide?
When a nitrogenous base is connected to the 1' position of a five-carbon sugar, a nucleoside is produced. The 5' carbon of the sugar in a nucleoside molecule is bonded to the 5' carbon of the sugar...
Name the linkage connecting monosaccharide units in polysaccharides.
Glycosidic linkages connect the monosaccharide units of polysaccharides. When an oxide bond is created between two monosaccharide units with the loss of a water molecule, it is called a glycosidic...
Under what conditions glucose is converted to gluconic and saccharic acid?
When glucose is treated with a mild oxidising agent like Br2 water, it is transformed to gluconic acid, a six-carbon carboxylic acid. When glucose is treated with nitric acid, it is transformed to...
Monosaccharides contain carbonyl group hence are classified, as aldose or ketose. The number of carbon atoms present in the monosaccharide molecule is also considered for classification. In which class of monosaccharide will you place fructose?
Carbonyl groups can be found in monosaccharides. As a result, they're categorised as either aldose or ketose. Aldose refers to monosaccharides that contain an aldehyde group. Ketose refers to...
The letters ‘D’ or ‘L’ before the name of a stereoisomer of a compound indicates the correlation of configuration of that particular stereoisomer. This refers to their relationship with one of the isomers of glyceraldehyde. Predict whether the following compound has ‘D’ or ‘L’ configuration.
On the left side of the C5 carbon atom, the –OH group is connected. As a result, the provided compound is in the 'L' configuration.
Aldopentoses named as ribose and 2-deoxyribose are found in nucleic acids. What is their relative configuration?
D-configuration is the configuration of both aldopentoses. -D-ribose is ribose, while -D-2-deoxyribose is 2-deoxyribose.
Which sugar is called invert sugar? Why is it called so?
Invert sugar is another name for sucrose. It comes from sugarcane and sugarbeet and is a naturally occurring sugar. When sucrose is hydrolyzed, the sign of rotation changes from Dextro (+) to laevo...
Amino acids can be classified as α-, β-, -, δ- and so on depending upon the relative position of the amino group concerning the carboxyl group. Which type of amino acids forms polypeptide chain in proteins?
The sort of amino acids that make up a polypeptide chain are -amino acids and alpha-amino acids, where the amino acid is linked to the -carbon in the molecule.
α-Helix is a secondary structure of proteins formed by twisting of the polypeptide chain into right-handed screw-like structures. Which type of interactions is responsible for making the a-helix structure stable?
The –NH group of each amino acid residue hydrogen is bound to the –C=O of an adjacent turn of the helix, forming a right-handed screw helix shape.
Some enzymes are named after the reaction, where they are used. What name is given to the class of enzymes which catalyse the oxidation of one substrate with simultaneous reduction of another substrate?
Enzyme oxidoreductases is the name given to a group of enzymes that catalyse redox processes. Alcohol Dehydrogenase, for example, aids in the reduction of alcohol levels in the human body when...
During curdling of milk, what happens to sugar present in it?
The sugar found in milk, lactose, is transformed to lactic acid during curdling, which is produced by bacteria.
How do you explain the presence of five —OH groups in the glucose molecule?
When glucose is acetylated using acetic anhydride (CH3CO)2O in the presence of ZnCl2, glucose pentaacetate is formed, confirming the presence of five –OH groups.
Why does compound (A) give below not form an oxime?
The chemical in question is glucose pentaacetate. The presence of a free –C=O group in glucose indicates the presence of a free carbonyl group, as does the synthesis of oxime from glucose. Because...
Why must vitamin C be supplied regularly in diet?
Because vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin, any excess is eliminated from the body on a regular basis. Vitamin C cannot be stored in the body, thus it must be consumed on a regular basis.
Sucrose is dextrorotatory but the mixture obtained after hydrolysis is laevorotatory. Explain.
Sucrose's aqueous solution is dextrorotatory, rotating plane-polarized light entering the solution 66.5 degrees to the right. When sucrose is hydrolyzed with dilute acids or invertase enzyme, two...
Amino acids behave like salts rather than simple amines or carboxylic acids. Explain
An amino acid has both a –NH2 and a –COOH group. The –COOH group loses a proton [H]+ in aqueous solution of the amino acid, while the –NH2 acquires a proton to create a zwitterion, which is a...
Structures of glycine and alanine are given below. Show the peptide linkage in glycylalanine.
Glycylalanine is formed when the hydroxyl group of glycine is bonded to the amine group of alanine via a peptide (-CONH) linkage.
Protein found in a biological system with a unique three-dimensional structure and biological activity is called a native protein. When a protein in its native form, is subjected to a physical change like change in temperature or a chemical change like change in pH, denaturation of protein takes place. Explain the cause.
Hydrogen bonds and other intermolecular interactions connect the amino acid residues in proteins. The hydrogen bonds are disrupted when a physical or chemical change occurs, and the native protein...
The activation energy for the acid catalysed hydrolysis of sucrose is 6.22 kJ mol–1, while the activation energy is only 2.15 kJ mol–1 when hydrolysis is catalyzed by the enzyme sucrase. Explain.
Biocatalysts are enzymes. By providing an alternative approach, they lower the magnitude of activation energy. The enzyme sucrase lowers the activation energy of sucrose hydrolysis from 6.22 kJ...
How do you explain the presence of an aldehydic group in a glucose molecule?
Bromine water can be used to treat glucose, which results in the carboxylic acid gluconic acid, which verifies the presence of an aldehyde group.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain the assertion. (ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explain the assertion. (iii) Both assertion and reason are the wrong statements. (iv) The assertion is correct statement and reason is the wrong statement. (v) The assertion is the wrong statement and reason is the correct statement. Assertion: Polytetrafluoroethene is used in making non-stick cookware. Reason: Fluorine has the highest electronegativity
Option (i) is correct Teflon is a chemically inert and thermally stable material that is used to make nonstick cookware.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain the assertion. (ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explain the assertion. (iii) Both assertion and reason are the wrong statements. (iv) The assertion is correct statement and reason is the wrong statement. (v) The assertion is the wrong statement and reason is the correct statement.Assertion: Network polymers are thermosetting. Reason: Network polymers have high molecular mass.
Option (i) is correct During polymerisation, extensive cross linking results in the creation of a three-dimensional network that is rigid, insoluble, and infusible.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain the assertion. (ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explain the assertion. (iii) Both assertion and reason are the wrong statements. (iv) The assertion is correct statement and reason is the wrong statement. (v) The assertion is the wrong statement and reason is the correct statement. Assertion: For making rubber synthetically, isoprene molecules are polymerised. Reason: Neoprene (a polymer of chloroprene) is a synthetic rubber.
Option (v) is correct Natural rubber is made up of isoprene molecules, while neoprene, a synthetic rubber, is made up of chloroprene polymers.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain the assertion. (ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explain the assertion. (iii) Both assertion and reason are the wrong statements. (iv) The assertion is correct statement and reason is the wrong statement. (v) The assertion is the wrong statement and reason is the correct statement.Assertion: Polyamides are best used as fibres because of high tensile strength. Reason: Strong intermolecular forces (like hydrogen bonding within polyamides) lead to close packing of chains and increase the crystalline character, hence, provide high tensile strength to polymers.
Option (ii) is correct Polyamides, such as nylon, are the most often used fibres. Because of the strong intermolecular hydrogen connection, they have a high tensile strength.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain the assertion. (ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explain the assertion. (iii) Both assertion and reason are the wrong statements. (iv) The assertion is correct statement and reason is the wrong statement. (v) The assertion is the wrong statement and reason is the correct statement. Assertion: Olefinic monomers undergo addition polymerisation. Reason: Polymerisation of vinyl chloride is initiated by peroxides/ persulphates.
Option (i) is correct Polymerization of olefins like ethene results in polymers like polythene.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain the assertion. (ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explain the assertion. (iii) Both assertion and reason are the wrong statements. (iv) The assertion is correct statement and reason is the wrong statement. (v) The assertion is the wrong statement and reason is the correct statement.Assertion: Most of the Synthetic polymers are not biodegradable. Reason: Polymerisation process induces toxic character in organic molecules.
Option (iv) is correct Enzymatic hydrolysis and environmental oxidation do not destroy the majority of synthetic polymers. Toxic characteristics are not produced via polymerization.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain the assertion. (ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explain the assertion. (iii) Both assertion and reason are the wrong statements. (iv) The assertion is correct statement and reason is the wrong statement. (v) The assertion is the wrong statement and reason is the correct statement. . Assertion: Rayon is a semi-synthetic polymer and is taken as a better choice than cotton fabric. Reason: Mechanical and aesthetic properties of cellulose can be improved by acetylation.
Option (ii) is correct. Rayon is a semi-synthetic polymer that is a better alternative than cotton because acetylation improves the characteristics of cellulose after processing.
Match the polymers given in Column I with their repeating units given in Column II.
(i) is d (ii) is a (iii) is b (iv) is e (v) is c
Match materials are given in Column I with the polymers given in Column II.
(i) is f (ii) is e (iii) is a (iv) is c (v) is b (vi) is d
Match the polymers given in Column I with the type of linkage present in they have given in Column II.
(i) is b (ii) is d (iii) is a (iv) is d (v) is c
Match the polymers given in Column I with the preferred mode of polymerisation followed by their monomers.
(i) is d (ii) is a (iii) is b
Match the polymers given in Column I with their main applications given in Column II.
(i) is d (ii) is e (iii) is a (iv) is f (v) is b (vi) is c
Match the polymers given in Column I with their commercial names given in Column II.
(i) is b (ii) is c (iii) is a (iv) is e (v) is d
Match the polymers given in Column I with their chemical names given in Column II.
(i) is c (ii) is a (iii) is b (iv) is e (v) is d
Match the polymer of column I with a correct monomer of column II.
(i) is e (ii) is c (iii) is a (iv) is b (v) is d
Why should the monomers use also polymerisation through free radical pathway be very pure?
Pure monomers are employed instead of polymerization through the free radical pathway because even little impurities serve as inhibitors, causing the chain reaction to abruptly stop and short length...
Which type of biomolecules has some structural similarity with synthetic polyamides? What is this similarity?
Proteins and synthetic polyamides share certain structural similarities. Polyamides, such as Nylon, are made up of Glycine and aminocaproic acid molecules linked together by an amide bond. A similar...
Name the polymers used in laminated sheets and give the name of monomeric units involved in its formation.
In laminated sheets, urea-formaldehyde resin is utilised. The monomeric components used to make laminated sheets are urea and formaldehyde.
Which factor imparts crystalline nature to a polymer like nylon?
Intermolecular H –bonding exists between the two terminal groups –C=O and –NH, allowing one Nylon molecule to join another. Because intermolecular H –bonding is relatively strong, it can result in...
What is the role of benzoyl peroxide also polymerisation of alkenes? Explain its mode of action with the help of an example.
By providing chain initiation, benzoyl peroxide functions as an initiator in free radical addition polymerisation of alkenes. The generated radical reacts with the carbon-carbon double bond of an...
What is the structural difference between HDP and LDP? How does the structure account for different behaviour and nature, hence the use of a polymer?
HDP stands for high-density polymer with a linear structure, whereas LDP stands for low-density polymer with a branching structure. HDP has a greater melting point and is chemically inert, whereas...
Why does cis-polyisoprene possess elastic property?
The polymer may be stretched by applying force due to the presence of these weak forces. When the external force is released, the polymer recovers to its original condition, showing elastic...
To have practical applications why are cross-links required in rubber?
Cross-linking is used to increase these physical qualities by assisting in the binding of its planar polymer sheets, therefore improving elastomeric properties and thermal stability.
How is the following resin intermediate prepared and which polymer is formed by this monomer unit?
The two starting monomers for this Resin intermediate are melamine and formaldehyde. Melamine polymer is the result of their condensed polymerization.
Can nucleic acids, proteins and starch be considered as step growth polymers?
Proteins, nucleic acids, and starch are all examples of step-growth polymers. Condensation polymers are step growth polymers. The loss of a simple molecule allows monomers with bifunctional or...
Can the enzyme be called a polymer?
The enzyme functions as a catalyst, speeding up biological processes. Proteins make up their structure. Proteins are polymers made up of monomeric units called amino acids. As a result, enzymes are...
Why are rubbers called elastomers?
Rubber may be stretched by applying force and then returned to its original shape once the force is removed. As a result, they are referred to as elastomers.
Identify the polymer given below :
This is polyisoprene or natural rubber. This polymer's monomeric unit is 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene.
Identify the type of polymer given in the following figure.
This is a network or cross-linked polymer. Cross-linking connects two linear polymers.
Out of chain growth polymerisation and step-growth polymerisation, in which type will, you place the following.
In this illustration, a chain-growth polymerization process combines two monomers to produce a polymer. Only monomers react with each other to keep the chain expanding.
Identify the type of polymer. —A—B—B—A—A—A—B—A—
In this polymer chain, the monomers A' and 'B' are randomly linked. As an example, this is a copolymer. A When a mixture of two or more unsaturated monomers reacts, a copolymer is formed.
Identify the type of polymer. —A—A—A—A—A—A—
The monomer in this case is –A-. This polymer is a homopolymer since the same or same monomer is repeated to make it.
A natural linear polymer of 2-methyl-1, 3-butadiene becomes hard on treatment with sulphur between 373 to 415 K and —S—S— bonds are formed between chains. Write the structure of the product of this treatment?
The structure of 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene is Rubber vulcanization is the term for this procedure. Sulphur works as a crosslinking agent in this case, stiffening the rubber and giving it better...
Vulcanisation makes rubber ______________. (i) more elastic (ii) soluble in inorganic solvent (iii) crystalline (iv) more stiff
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Rubber becomes more elastic and rigid after vulcanization. Sulphur produces cross connections at the reactive locations of double bonds or at their reactive...
Which of the following polymers have vinylic monomer units? (i) Acrilan (ii) Polystyrene (iii) Nylon (iv) Teflon
Option (i), (ii) and (iv) are the answers. The vinylic monomer units of acrilan, polystyrene, and teflon are as follows:
Which of the following polymers can have strong intermolecular forces? (i) Nylon (ii) Polystyrene (iii) Rubber (iv) Polyesters
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Nylon and polyester are thread-forming fibres with a high melting point and tensile strength. Intermolecular forces such as hydrogen bonding are strong.
Which of the following is an example of a synthetic rubber? (i) Polychloroprene (ii) Polyacrylonitrile (iii) Buna-N (iv) cis-polyisoprene
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. Polychloroprene and Buna-N are examples of a synthetic rubber
Which of the following monomers form biodegradable polymers? (i) 3-hydroxybutyric acid + 3-hydroxypentanoic acid (ii) Glycine + aminocaproic acid (iii) Ethylene glycol + phthalic acid (iv) Caprolactam
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers. Biodegradable polymers are those that are quickly degraded and are not hazardous to the environment.
Which of the following polymers are condensation polymers? (i) Bakelite (ii) Teflon (iii) Butyl rubber (iv) Melamine formaldehyde resin
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Bakelite is a phenol and formaldehyde condensation polymer. Melamine formaldehyde resin is a melamine (2, 4, 6-triamino-1, 3, 5-triazine) and formaldehyde...
Which of the following are addition polymers? (i) Nylon (ii) Melamine formaldehyde resin (iii) Orlon (iv) Polystyrene
Option (iii) and (iv) are the answers. The addition polymers Orion and polystyrene are produced by polymerizing CH2 = CH – CN (acrylonitrile) and C6H5 – CH = CH2 styrene, respectively.
Which of the following polymers are used as fibre? (i) Polytetrafluoroethane (ii) Polychloroprene (iii) Nylon (iv) Terylene
Option (iii) and (iv) are the answers. Because of strong intermolecular interactions such as H-bonding, nylon and terylene are employed as fibres, resulting in tight chain packing and therefore...
Which of the following polymers are thermoplastic? (i) Teflon (ii) Natural rubber (iii) Neoprene (iv) Polystyrene
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Teflon and polystyrene are thermoplastics because they can be melted and moulded anew.
Which of the following are characteristics of thermosetting polymers? (i) Heavily branched cross-linked polymers. (ii) Linear slightly branched long-chain molecules. (iii) Become infusible on moulding so cannot be reused. (iv) Soften on heating and harden on cooling, can be reused.
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. Thermosetting polymers have a lot of branching cross links. They can't be used again since they don't melt when heated and can't be remoulded.
Which of the following polymers, need at least one diene monomer for their preparation? (i) Dacron (ii) Buna-S (iii) Neoprene (iv) Novolac
Option (ii) and (iii) are the answers. (b) (c)
Which of the following polymer can be formed by using the following monomer unit?
Option (iv) is the answer. Nylon -6 is a polymer made from caprolactam polymerization.
is a polymer having monomer units ____________.
Option (i) is the answer.
Which of the following statements is not true about low-density polythene? (i) Tough (ii) Hard (iii) Poor conductor of electricity (iv) Highly branched structure
Option (ii) is the answer. Low density polythene is a strong yet flexible (not too flexible) material with a weak electrical conductivity. Its structure is extremely branching.
In which of the following polymers ethylene glycol is one of the monomer units?
Option (i) is the answer. Condensation polymerization of ethylene glycol and phthalic acid with the removal of the water molecule yields the given polymer.
Which of the following polymer is biodegradable?
Option (C) is the answer. Biodegradable polymers are materials whose chemical and physical properties deteriorate and disintegrate entirely when exposed to microorganisms, aerobic, and anaerobic...
The commercial name of polyacrylonitrile is ______________. (i) Dacron (ii) Orlon (Acrilan) (iii) PVC (iv) Bakelite
Option (ii) is the answer.
Which of the following is not a semisynthetic polymer? (i) cis-polyisoprene (ii) Cellulose nitrate (iii) Cellulose acetate (iv) Vulcanised rubber
Option (i) is the answer M-polyisoprene is a polymer that comes from nature.
Which of the following polymers of glucose is stored by animals? (i) Cellulose (ii) Amylose (iii) Amylopectin (iv) Glycogen
Option (iv) is the answer. Glycogen is a glucose polymer present in animal livers, brains, and muscles. Amylase and amylopectin are structural components of starch, while cellulose is a polymer...
Find the area of the region bounded by the curve y^2 = 2x and x^2 + y^2 = 4x.
The equation of curves are y2 = 2x and x2 + y2 = 4x Solving the equations, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} {{x}^{2~}}-\text{ }4x\text{ }+\text{ }{{y}^{2~}}=\text{ }0 \\ {{x}^{2~}}-\text{ }4x\text{...
Find the area of the region enclosed by the parabola x^2 = y and the line y = x + 2
Given, equation of parabola x2 = y and line y = x + 2 Solving the above equations, we get \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} {{x}^{2}}~=\text{ }x\text{ }+\text{ }2 \\ {{x}^{2}}~-\text{ }x\text{ }-\text{...
Find the area of the region bounded by the parabola y^2 = 2px, x^2 = 2py.
equations of parabolas are \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} {{y}^{2}}~=\text{ }2px~\ldots .\text{ }\left( i \right) \\ ~{{x}^{2}}~=\text{ }2py~\ldots .\text{ }\left( ii \right) \\ \end{array}\] Now, from...
solve the following:
Solution:
Consider a ray of light incident from air onto a slab of glass (refractive index n) of width d, at an angle θ. The phase difference between the ray reflected by the top surface of the glass and the bottom surface is (a) 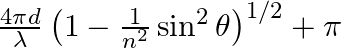 (b)
(b) 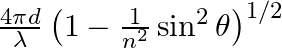 (c)
(c) 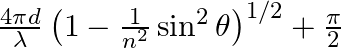 (d)
(d) 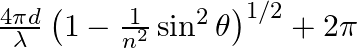
The correct answer is a) $ \frac{4 \pi d}{\lambda}\left(1-\frac{1}{n^{2}} \sin ^{2} \theta\right)^{1 / 2}+\pi $ Explanation: When a slab of glass is put in air, the wave reflected from the upper...
Can reflection result in plane-polarized light if the light is incident on the interface from the side with higher refractive index?
When the angle of incidence is equal to the Brewster's angle, polarised light is transmitted and plane-polarized light is reflected. The equation is as follows: $ \tan...
The figure shown a two-slit arrangement with a source which emits unpolarised light. P is a polariser with axis whose direction is not given. If I0 is the intensity of the principal maxima when no polarizer is present, calculate in the present case, the intensity of the principal maxima as well as of the first minima.
Given wave amplitude in perpendicular polarisation $ A_{\perp}=A_{\perp}^{0}(\sin (k x-\omega t)+\sin (k x-\omega t+\phi)) $ wave amplitude in parallel polarisation $ A_{\|}=A_{\|}^{0}(\sin (k...
AC = CO = D, S1 C = S2 C = d << D A small transparent slab containing material of µ =1.5 is placed along AS2. What will be the distance from O of the principal maxima and of the first minima on either side of the principal maxima obtained in the absence of the glass slab?
According to the question, $ \begin{array}{l} \Delta x=2 d \sin \theta+(\mu-1) L \\ \sin \theta 0=-1 / 16 \end{array} $ From central maxima, $O P=-D / 16$ $ \sin \theta_{1}=\frac{\pm \lambda / 2-d /...
An electron (mass m) with an initial velocity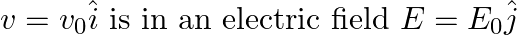 . If
. If  =
= 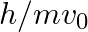 , it’s de Broglie wavelength at time t is given bya)
, it’s de Broglie wavelength at time t is given bya) 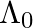 b)
b) 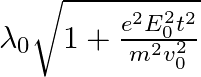 c)
c) 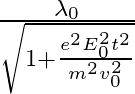 d )
d ) 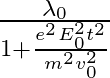
The correct answer is c)$ \frac{\lambda_{0}}{\sqrt{1+\frac{e^{2} E_{0}^{2} t^{2}}{m^{2} v_{0}^{2}}}} $ The de Broglie equation h=mv describes the relationship between a moving particle's momentum...
An electron (mass m ) with an initial velocity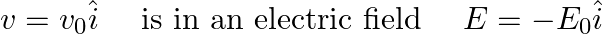 It’s de Broglie wavelength at time t is given bya)
It’s de Broglie wavelength at time t is given bya) 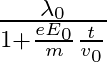 b)
b) 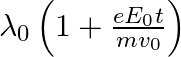 c)
c) 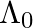 d)
d) 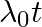
The correct answer is a) $\frac{\lambda_{0}}{1+\frac{e E_{0}}{m} \frac{t}{v_{0}}}$ The wave associated with moving particle is called matter wave or de-Broglie wave and it propagates in the form of...
A helicopter of mass 2000 kg rises with a vertical acceleration of 15 m/s2. The total mass of the crew and passengers is 500 kg. Give the magnitude and direction of the a) force on the floor of the helicopter by the crew and passengers b) action of the rotor of the helicopter on the surrounding air c) force on the helicopter due to the surrounding air
Given, M = 2000 kg helicopter mass m = 500 kg m = 500 kg m = 500 kg m = 500 kg m = 500 kg m = 500 kg Helicopter acceleration with crew and passengers = 15 m/s2 a) Force exerted by the crew and...
A rectangular box lies on a rough inclined surface. The coefficient of friction between the surface and the box is μ. Let the mass of the box be m. a) at what angle of inclination θ of the plane to the horizontal will the box just start to slide down the plane? b) what is the force acting on the box down the plane, if the angle of inclination of the plane is increased to a > θ c) what is the force needed to be applied upwards along the plane to make the box either remain stationary or just move up with uniform speed? d) what is the force needed to be applied upwards along the plane to make the box move up the plane with acceleration a.
a) As the box starts to slide down the plane, $\mu=\tan \theta$ $ \theta=\tan ^{-1}(\mu) $ b) If $a>\theta$, the angle of inclination will be the angle of repose and the net force acting will be...
There are four forces acting at a point P produced by strings as shown in the figure, which is at rest. Find the forces F1 and F2.
Because the point is at rest with a = 0, the resulting forces on the point are zero. As a result, the X and Y axis net components will be zero. It's difficult to resolve all of the forces along the...
A cricket bowler releases the ball in two different ways a) giving it only horizontal velocity and b) giving it horizontal velocity and a small downward velocity. The speed vs at the time of release is the same. Both are released at a height H from the ground. Which one will have greater speed when the ball hits the ground? Neglect air resistance.
a) $\frac{1}{2} v_{z}^{2}=g H \Rightarrow v_{z}=\sqrt{2 g H}$ Speed at ground is given as: $\sqrt{v_{s}^{2}+v_{z}^{2}}=\sqrt{v_{s}^{2}+2 g H}$ b)$\frac{1}{2} m v_{s}^{2}+m g H$ is the total energy...
The displacement vector of a particle of mass m is given by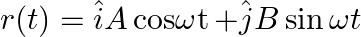 a) show that the trajectory is an ellipse b) show that
a) show that the trajectory is an ellipse b) show that 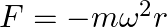
a) $ \begin{array}{l} r(t)=\hat{i} A \operatorname{coswt}+\hat{j} B \sin \omega t \\ x=A \cos \omega t \\ y=B \sin \omega t \\ x / A=\cos \omega t \\ y / B=\sin \omega t \end{array} $ Squaring both...
A racing car travels on a track ABCDEFA. ABC is a circular arc of radius 2 R. CD and FA are straight paths of length R and DEF is a circular arc of radius R = 100 m. The coefficient of friction on the road is μ = 0.1. The maximum speed of the car is 50 m/s. Find the minimum time for completing one round.
Time taken from $A$ to $B$ to $C$ $\mathrm{S} 1=$ length $\mathrm{pf}$ path $=3 / 42 \pi(2 \mathrm{R})=300 \pi \mathrm{m}$ $\mathrm{V} 1=$ speed(maximum) along the circular path of the car $...
Below figures show (vx, t) and (vy, t) diagrams for a body of unit mass. Find the force as a function of time.
For graph a) $ \begin{array}{l} v_{x}=2 t \text { for } 0<t<1 s \\ a_{x}=2 / 1 \text { for } 0<t<1 s \\ v_{x}=2(2-t) \text { for } 1<t<2 s \\ a_{x}=-2 / 1=-2 \text { for }...
When a body slides down from rest along a smooth inclined plane making an angle of 45 degree with the horizontal, it takes time T. When the same body slides down from rest along a rough inclined plane making the same angle and through the same distance, it is seen to take time pT, where p is some number greater than 1. Calculate the coefficient of friction between the body and the rough plane.
The inclined plane angle is $45^{\circ}$ such that $ \begin{array}{l} u=0 \\ s=s \\ t=T \\ a=g \sin 45^{\circ}=g / \sqrt{2} \\ s=u t+1 / 2 a t^{2} \\ s=g T^{2} / 2 \sqrt{2} \end{array} $ $...
There are three forces F1, F2, and F3 acting on a body, all acting on a point P on the body. The body is found to move with uniform speed. a) show that the forces are coplanar b) show that the torque acting on the body about any point due to these three forces is zero
a) The body's acceleration is zero because the resultant force of the three forces F1, F2, and F3 on a location on the body is zero. The directions of forces F1 and F2 are in the plane of the paper,...
A person in an elevator accelerating upwards with an acceleration of 2 m/s2, tosses a coin vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m/s. After how much time will the coin fall back into his hand?
a = 2 m/s2 is the rising acceleration of an elevator. Gravitational acceleration, g = 10 m/s2 As a result, the net effective acceleration, a' = (a + g) = 12 m/s2, is calculated. In light of the...
Figure shows (x,t) (y,t) diagram of a particle moving in 2-dimension. If the particle has a mass of 500 g, find the force acting on the particle.
For graph a) $ \begin{array}{l} v_{x}=d x / d t=2 / 2=1 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s} \\ a_{x}=d^{2} x / d t^{2}=d v_{x} / d t=0 \end{array} $ For graph b) $ \begin{array}{l} y=t^{2} \\ v_{y}=d y / d t=2...
A 100 kg gun fires a ball of 1 kg horizontally from a cliff of height 500 m. It falls on the ground at a distance of 400 m from the bottom of the cliff. Find the recoil velocity of the gun.
The ball's horizontal speed is = u m/s. The vertical component is equal to zero. Considering the ball's vertical downward motion $ \begin{array}{l} u=0 \\ s=h=500 \mathrm{~m} \\ g=10 \mathrm{~s} /...
A bock of mass M is held against a rough vertical wall by pressing it with a finger. If the coefficient of friction between the block and the wall is μ and the acceleration due to gravity is g, calculate the minimum force required to be applied by the ginger to hold the block against the wall?
F is the force exerted by the finger on a body of mass M that is resting on the wall. Using the balanced state as a starting point, $ \begin{array}{l} \mathrm{F}=\mathrm{N} \\ \mathrm{f}=\mathrm{Mg}...
Block A of weight 100N rests on a frictionless inclined plane of slope angle 30o. A flexible cord attached to A passes over a frictionless pulley and is connected to block B of weight W. Find the weight W for which the system is in equilibrium.
Equilibrium between $A$ or $B$, Then we know that, $\mathrm{mg} \sin 30^{\circ}=\mathrm{F}$ $ \begin{array}{l} 1 / 2 \mathrm{mg}=\mathrm{F} \\ \mathrm{F}=(1 / 2)(100)=50 \end{array} $ Therefore,...
Two masses of 5 kg and 3 kg are suspended with help of massless inextensible strings as shown in the figure. Calculate T1 and T2 when whole system is going upwards with acceleration = 2 m/s2.
The acceleration of the whole system is, $\mathrm{a}=2 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s} 2$ $ \begin{array}{l} \mathrm{m} 1=5 \mathrm{~kg} \\ \mathrm{~m} 2=3 \mathrm{~kg} \\ \mathrm{~g}=9.8 \mathrm{~m} /...
In the above-given problem if the lower thread is pulled with a jerk, what happens?
The thread CD breaks when the lower thread is jerked. The thread is inertia at rest, and the mass 2 kg above acts on it.
A mass of 2 kg is suspended with thread AB. Thread CD of the same type is attached to the other end of 2 kg mass. Lower thread is pulled gradually harder and harder in the downward direction so as to apply force on AB. Which of the threads will break and why?
As the mass 2 kg acts downward, the force acting on the thread AB is equal to the force F. As a result, the force exerted on the AB is 2 kg more than on the D, and the thread AB breaks.
Why are mountain roads generally made winding upwards rather than going straight up?
Because the force of friction is strong, which decreases the risks of sliding, mountain roads are typically built curving uphill rather than straight up. The value of frictional force increases when...
A woman throws an object of mass 500 g with a speed of 25 m/s. a) what is the impulse imparted to the object? b) if the object hits a wall and rebounds with half the original speed, what is the change in momentum of the object?
a) Mass of the object, $\mathrm{m}=500 \mathrm{~g}=0.5 \mathrm{~kg}$ $ u=0 $ $ \mathrm{v}=25 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s} $ Impulse is given as: $ \underset{F}{\vec{F}} \cdot d t=\frac{d \rightarrow}{d...
Why does a child feel more pain when falls down on a hard cement floor, than when she falls on the soft muddy ground in the garden?
When a kid falls on a hard cement floor, the child feels more pain than when the child falls on soft muddy ground in the yard, since the time it takes the child to stop on the cemented ground is...
Why are porcelain objects wrapped in paper or straw before packing for transportation?
Because porcelain artefacts are delicate, they are wrapped in paper or straw before being packed for shipment. When the acceleration (v – u)/t drops while carrying these items, the shift in velocity...
A block placed on a rough horizontal surface is pulled by a horizontal force F. Let f be the force applied by the rough surface on the block. Plot a graph of f versus F.
F1 is the force exerted on the heavy box, which is equal to F1 and is resisted by the lesser frictional force f1. F = Fs, which is the maximum static frictional force, is required for the box to...
The velocity of a body of mass 2 kg as a function of t is given by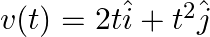 Find the momentum and the force acting on it at time t = 2 sec.
Find the momentum and the force acting on it at time t = 2 sec.
m=2kg $ \underset{v}{\rightarrow}(t)=2 t \hat{i}+t^{2} \hat{j} $ $ \vec{v} \text { at } 2 \mathrm{sec}, \underset{v}{\vec{v}}(2 t)=2(2 t) \hat{i} 2^{2} \hat{j}, v(2)=4 \hat{i}+4 \hat{j} $ $ \text {...
Compound ‘A’ with molecular formula C4H9Br is treated with aq. KOH solution. The rate of this reaction depends upon the concentration of the compound ‘A’ only. When another optically active isomer ‘B’ of this compound was treated with aq. KOH solution, the rate of reaction was found to be dependent on the concentration of compound and KOH both. (i) Write down the structural formula of both compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’. (ii) Out of these two compounds, which one will be converted to the product with an inverted configuration.
Because the rate of reaction of compound ‘A' (C4H9Br) with aqueous KOH is solely determined by the concentration of compound ‘A,' the reaction happens via the SN1 mechanism, and product ‘A' is...
Classify the following compounds as primary, secondary and tertiary halides. (i) 1-Bromobut-2-ene (ii) 4-Bromopent-2-ene (iii) 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane
(i)A main halide is 1-bromobut-2-ene. (ii) Bromine is linked to the secondary carbon atom in 4-Bromopent-2-ene, making it a secondary halide. (iii) Bromine is linked to the tertiary carbon atom in...
Draw other resonance structures related to the following structure and find out whether the functional group present in the molecule is ortho, para directing or meta directing.
Because electron density is higher at ortho and para locations, the functional groups contained in these compounds are ortho-para directed.
Why is the solubility of haloalkanes in water very low?
Because energy is required to overcome the attractions between the haloalkane molecules as well as to break the hydrogen bonds between water molecules, haloalkanes are only weakly soluble in water.
Which of the products will be a major product in the reaction given below? Explain. CH3CH=CH2 + HI → CH3CH2CH2I + CH3CHICH30 (A) (B)
The molecule (B) will be the reaction's main product. This addition reaction is carried out according to Markovnikoff's rule, in which the hydrogen from the hydrogen halide is added to the carbon...
Which of the following compounds (a) and (b) will not react with a mixture of NaBr and H2SO4. Explain why?
Br2 gas is produced when NaBr and H2SO4 are combined. Because of the stable molecule created as a result of resonance stabilisation, molecule (b) will not react with Br2 gas.
Discuss the role of Lewis acids in the preparation of aryl bromides and chlorides in the dark.
Electrophilic substitution can be used to make aryl bromides and chlorides from arenes. In the absence of light, this reaction is carried out by treating the arene with chlorine or bromine in the...
Haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes and haloalkenes. Explain.
This is due to the aryl ring's resonance stabilisation. There will be a conjugation of chlorine electrons with the electrons in the ring in the case of C6H5-Cl. The partial double bond nature of the...
Why iodoform has appreciable antiseptic property?
Iodoform has a significant antibacterial activity due to the release of free iodine.
Which of the compounds will react faster in SN1 reaction with the –OH ion? CH3— CH2— Cl or C6H5— CH2— Cl
In an SN1 reaction with the OH- ion, C6H5— CH2— Cl will react quicker. This is owing to the carbocation's stability in the compound. The C6H5 group is already stable owing to resonance, and the CH2...
Out of o-and p-bromobenzene which one has a higher melting point and why?
Because the symmetry of p-dibromobenzene allows the molecule to fit better in a crystal lattice, it has a higher melting point. As a result, breaking the bonds between the molecules needs a greater...
Aryl chlorides and bromides can be easily prepared by electrophilic substitution of arenes with chlorine and bromine respectively in the presence of Lewis acid catalysts. But why does the preparation of aryl iodides requires the presence of an oxidising agent?
Arenes' iodination can be reversed due to the production of HI. An oxidising agent, such as HNO3 or HIO4, oxidises HI to speed up the process and stabilise the result.
Alkyl fluorides are synthesised by heating an alkyl chloride/bromide in presence of ____________ or ____________. (i) Ca F2 (ii) CoF2 (iii) Hg2F2 (iv) NaF
Option (ii) and (iii) are the answers. Heating an alkyl chloride or bromide in the presence of a metallic fluoride such as AgF, FIg2F2, CoF2, or SbF3 results in the production of alkyl fluorides....
Alkyl halides are prepared from alcohols by treating with (i) HCl + ZnCl2 (ii) Red P + Br2 (iii) H2SO4+ KI (iv) All the above
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers (i) $R-\mathrm{OH} \stackrel{\mathrm{HCl}+\mathrm{ZnCl}}{\longrightarrow} R-\mathrm{Cl}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}$ (ii) $R-\mathrm{OH}...
Which of the following compounds can be classified as aryl halides? (i) p-ClC6H4CH2CH(CH3)2 (ii) p-CH3CHCl(C6H4)CH2CH3 (iii) o-BrH2C-C6H4CH(CH3)CH2CH3 (iv) C6H5-Cl
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Because the halogen atom is directly linked to the aromatic ring in compounds (i) and (iv), these compounds are classed as aryl halides.
Which of the following are secondary bromides? (i) (CH3)2 CHBr (ii) (CH3)3C CH2Br (iii) CH3CH(Br)CH2CH3 (iv) (CH3)2CBrCH2CH3
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. Secondary bromides are those in which the -carbone (bromine-bound carbon) is further attached to two alkyl groups. The -carbon in compounds (i) and (iii) is...
Which of the following compounds are gem-dihalides? (i) Ethylidene chloride (ii) Ethylene dichloride (iii) Methylene chloride (iv) Benzyl chloride
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. Dihalides with two halogen atoms linked to the same carbon atom are known as gem-dihalides. Gem-dihalides are formed when two halogen atoms are present on the...
Ethylene chloride and ethylidene chloride are isomers. Identify the correct statements. (i) Both the compounds form the same product on treatment with alcoholic KOH. (ii) Both the compounds form the same product on treatment with aq.NaOH. (iii) Both the compounds form the same product on reduction. (iv) Both the compounds are optically active.
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. They give ethyne on treatment with alcoholic $\mathrm{KOH}$. $ \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{CHCl}_{2} \underset{\mathrm{KOH}}{\stackrel{\text { alc....
Haloalkanes contain halogen atom (s) attached to the sp3 hybridised carbon atom of an alkyl group. Identify haloalkane from the following compounds. (i) 2-Bromopentane (ii) Vinyl chloride (chloroethene) (iii) 2-chloroacetophenone (iv) Trichloromethane
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Halogen atoms are linked to the sp3 hybridised carbon atom of the alkyl group in each of these molecules.
Which of the following statements are correct about the kinetics of this reaction? (i) The rate of reaction depends on the concentration of only (b). (ii) The rate of reaction depends on the concentration of both (a) and (b). (iii) Molecularity of reaction is one. (iv) Molecularity of reaction is two.
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. The SN1 mechanism is used in the given reaction. The production of carbocation is a gradual process in the SN1 mechanism. As a result, the pace of reaction is...
Which of the following statements are correct about the mechanism of this reaction? (i) A carbocation will be formed as an intermediate in the reaction. (ii) OH–will attach the substrate (b) from one side and Cl- will leave it simultaneously from the other side. (iii) An unstable intermediate will be formed in which OH– and Cl– will be attached by weak bonds. (iv) The reaction proceeds through an SN1 mechanism.
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Because it is a tertiary halide, it undergoes the SN1 process, resulting in the formation of a carbocation as an intermediate.
Which of the following statements are correct about the reaction intermediate? (i) Intermediate (c) is unstable because in this carbon is attached to 5 atoms. (ii) Intermediate (c) is unstable because carbon atom is sp2 hybridised. (iii) Intermediate (c) is stable because carbon atom is sp2 hybridised. (iv) Intermediate (c) is less stable than the reactant (b).
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Intermediate (iii) is unstable in the above reaction because the carbon atom is linked to 5 atoms and is less stable than reactant (ii).
Which of the following statements are correct about this reaction? (i) The given reaction follows the SN2 mechanism. (ii) (b) and (d) have the opposite configuration. (iii) (b) and (d) have the same configuration. (iv) The given reaction follows the SN1 mechanism.
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers. Alkyl halide is the main reactant in the given reaction. A transient condition is found here, in which one bond is broken and another is created synchronously,...
Which of the statements are correct about the above reaction? (i) (a) and (e) both are nucleophiles. (ii) In (c) carbon atom is sp3 hybridised. (iii) In (c) carbon atom is sp2 hybridised. (iv) (a) and (e) both are electrophiles.
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. Nucleophiles are HO and CF. The C atom is sp2 hybridised in (iii) due to the simultaneous creation of the C – OH bond and the breakdown of the C – Cl link. As a...
Which is the correct increasing order of boiling points of the following compounds? 1-Bromoethane, 1-Bromopropane, 1-Bromobutane, Bromobenzene (i) Bromobenzene < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromoethane (ii) Bromobenzene < 1-Bromoethane < 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromobutane (iii) 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Bromoethane < Bromobenzene (iv) 1-Bromoethane < 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromobutane < Bromobenzene
Option (iv) is the answer Reason: As the molecular mass of the alkyl halide grows, the boiling point rises.
Which is the correct increasing order of boiling points of the following compounds? 1-Iodobutane, 1-Bromobutane, 1-Chlorobutane, Butane (i) Butane < 1-Chlorobutane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Iodobutane (ii) 1-Iodobutane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Chlorobutane < Butane (iii) Butane < 1-Iodobutane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Chlorobutane (iv) Butane < 1-Chlorobutane < 1-Iodobutane < 1-BromobutaneSolution:
Option (i) is the answer. Explanation: The larger the surface area, the stronger the intermolecular forces of attraction and, as a result, the higher the boiling point. For comparable types of alkyl...
arrange the compounds in increasing order of the rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.(i) (a) < (b) < (c) (ii) (b) < (a) < (c) (iii) (c) < (b) < (a) (iv) (a) < (c) < (b)
Option (iii) is the answer. The amount of electron releasing groups increases the reactivity of aryl halides; the fewer the electron releasing groups, the slower the rate of nucleophilic...
arrange the compounds in increasing order of the rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.(i) (c) < (b) < (a) (ii) (b) < (c) < (a) (iii) (a) < (c) < (b) (iv) (a) < (b) < (c)
Option (iv) is the answer. Electron withdrawing groups boost aryl halide reactivity; the higher the number of electron withdrawing groups, the higher the rate of nucleophilic substitution.
arrange the compounds in increasing order of the rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.(i) (a) < (b) < (c) (ii) (a) < (c) < (b) (iii) (c) < (b) < (a) (iv) (b) < (c) < (a)
Option (iv) is the answer. The presence of an electron-releasing group in the ortho or para locations slows down nucleophilic substitution.
arrange the compounds in increasing order of the rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.(i) (a) < (b) < (c) (ii) (c) < (b) < (a) (iii) (a) < (c) < (b) (iv) (c) < (a) < (b)
Option (iii) is the answer. Nucleophilic substitution is facilitated by the presence of an electron withdrawing group (-NO2) in the ortho and para positions. At meta position, the presence of an...
Which of the following compounds will give racemic mixture on nucleophilic substitution by OH– ion?(i) (a) (ii) (a), (b), (c) (iii) (b), (c) (iv) (a), (c)
Option (i) is the answer. At least one chiral carbon must be present in the molecule to display racemic mixing. Chiral carbon is an asymmetric carbon that is linked to four distinct sorts of atoms...
Which of the carbon atoms present in the molecule given below are asymmetric?(i) a, b, c, d (ii) b, c (iii) a, d (iv) a b, c
Option (ii) is the answer. The chiral carbon, which is $sp_3$ hybridised carbon attached to four distinct substituents, is known as asymmetric carbon. Because (b) and (c) are $sp_3$ hybridised, they...
Reaction of C6H5CH2Br with aqueous sodium hydroxide follows ____________. (i) SN1 mechanism (ii) SN2 mechanism (iii) Any of the above two depending upon the temperature of the reaction (iv) Saytzeff rule
Option (i) is the answer. The $S_N$ 1 mechanism operates in watery media. As a result of this reaction, a stable carbocation forms as an intermediate.
Molecules whose mirror image is non-superimposable over them are known as chiral. Which of the following molecules is chiral? (i) 2-Bromobutane (ii) 1-Bromobutane (iii) 2-Bromopropane (iv) 2-Bromopropan-2-ol
Chiral molecules are those that lack a plane of symmetry as well as a centre of symmetry.. It is a chiral molecule because it lacks the plane of symmetry and the centre of symmetry. Option (i) is...
Chloromethane on treatment with an excess of ammonia yields mainly
Option (iii) is the answer. After reacting with $NH_3$ and chloromethane, methanamine is formed.
The reaction of toluene with chlorine in the presence of iron and the absence of light yields ____________.
Option (d) is the answer. In the presence of iron and in the absence of light, toluene reacts with chlorine to produce a mixture of 1-chloro-2-methylbenzene and 1-chloro-4-methylbenzene. The methyl...
What should be the correct IUPAC name for diethylbromomethane? (i) 1-Bromo-1,1-diethylmethane (ii) 3-Bromopentane (iii) 1-Bromo-1-ethylpropane (iv) 1-Bromopentane
Option (ii) is the answer. Diethylbromomethane's proper IUPAC designation is 3 - Bromopentane. $C_5H_{11}Br$ is the chemical formula for it.
Which is the correct IUPAC name for? (i) 1-Bromo-2-ethylpropane (ii) 1-Bromo-2-ethyl-2-methylethane (iii) 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane (iv) 2-Methyl-1-bromobutane
Option (iii) is the answer. correct IUPAC name for given compound is 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane
Which of the following alkyl halides will undergo SN1 reaction most readily? (i) (CH3)3C—F (ii) (CH3)3C—Cl (iii) (CH3)3C—Br (iv) (CH3)3C—I
Option (iv) is the answer. SN1 reactions occur mostly in polar protic solvents such as H2O and follow first-order kinetics. This indicates that the reaction rate is solely determined by one...
A primary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo _____________. (i) SN1 reaction (ii) SN2 reaction (iii) α–Elimination (iv) Racemisation
Option (ii) is the answer. Primary alkyl halides undergo SN2 mechanisms because 1∘ substrates have little steric hindrance to nucleophilic attack and 1∘ carbocations are relatively unstable....
What is ‘A’ in the following reaction?
The solution is option (iii). The addition of HCl across the double bond follows the Markovnikov rule in the aforementioned reaction. The negative portion of the addition molecule is linked to the...
Ethylidene chloride is a/an ______________. (i) vic-dihalide (ii) gem-dihalide (iii) allylic halide (iv) vinylic halide
Option (ii) is the answer. A gem-dihalide is ethylidene chloride. A compound with two halogen atoms on the same carbon atom is known as Gem Dihalide.
Chlorobenzene is formed by the reaction of chlorine with benzene in the presence of 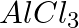 . Which of the following species attacks the benzene ring in this reaction? (i) Cl– (ii) Cl+ (iii)
. Which of the following species attacks the benzene ring in this reaction? (i) Cl– (ii) Cl+ (iii) 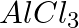 (iv) [AlCl4]–
(iv) [AlCl4]–
Option (ii) is the answer. Chlorobenzene is formed by the reaction of chlorine with benzene in the presence of AlCl3. Cl+ attacks the benzene ring in this reaction.
The position of –Br in the compound in CH3CH==CHC(Br)(CH3)2 can be classified as ____________. (i) Allyl (ii) Aryl (iii) Vinyl (iv) Secondary
Optuion (i) is the answer. A) Allyl : $\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CHC}(\mathrm{Br})\left(\mathrm{CH}_{3}\right)_{2}$ B) Aryl: $\mathrm{p}-\mathrm{ClC}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{4} \mathrm{CH}_{2}...
Which of the following is an example of vic-dihalide? (i) Dichloromethane (ii) 1,2-dichloroethane (iii) Ethylidene chloride (iv) Allyl chloride
Option (ii) is the answer. Vicinal dihalides are formed when a halogen reacts with an alkene to form compounds with halogen on neighbouring carbons. In terms of yearly output, 1, 2- dichloroethane...
Which of the following structures is enantiomeric with the molecule (A) given below :
Option (i) is the answer. Enantiomers are a pair of molecules that are mirror copies of one another.
In which of the following molecules carbon atom marked with an asterisk (*) is asymmetric?(i) (a), (b), (c), (d) (ii) (a), (b), (c) (iii) (b), (c), (d) (iv) (a), (c), (d)
Option (ii) is the answer. Asymmetric carbon atoms are those that have four distinct groups or atoms connected to them. The compounds a,b,c satisfy this criterion, thus B is the right answer.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points.(i) (b) < (a) < (c) (ii) (a) < (b) < (c) (iii) (c) < (a) < (b) (iv) (c) < (b) < (a)
Option (iii) is the answer. The boiling point of an alkyl halide falls as the branching rises. As a result, tert butyl bromide has the lowest boiling point while n butyl bromide has the greatest...
Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their densities.(i) (a) < (b) < (c) < (d) (ii) (a) < (c) < (d) < (b) (iii) (d) < (c) < (b) < (a) (iv) (b) < (d) < (c) < (a)
Option (i) is the answer. Reason:The density of a substance is exactly proportional to its molar mass at constant volume.
Which reagent will you use for the following reaction? CH3CH2CH2CH3 → CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl + CH3CH2CHClCH3 (i) Cl2/UV light (ii) NaCl + H2SO4 (iii) Cl2 gas in dark (iv) Cl2 gas in the presence of iron in dark
Option (i) is the answer. Mono-chlorinated isomeric products of Cl 2/UV light free radical substitution
Which of the following is the halogen exchange reaction?
Option (i) is the answer. Metal–halogen exchange is a basic reaction in organometallic chemistry that transforms an organic halide into an organometallic product. Electropositive metals (Li, Na, Mg)...
Toluene reacts with a halogen in the presence of iron (III) chloride giving ortho and para halo compounds. The reaction is (i) Electrophilic elimination reaction (ii) Electrophilic substitution reaction (iii) Free radical addition reaction (iv) Nucleophilic substitution reaction
Option (ii) is the answer. In the presence of Iron(III) chloride, toluene interacts with halogen to produce ortho and para halo compounds in an electrophilic substitution process. The Cl atom...
Identify the compound Y in the following reaction.
Option (i) is the answer.
Which of the following alcohols will yield the corresponding alkyl chloride on reaction with concentrated HCl at room temperature?
Option (iv) is the answer. If any alkyl halide forms a more stable carbocation at room temperature, the result is a more stable and efficient product. The formation of a $3^0$ carbocation as an...
The order of reactivity of following alcohols with halogen acids is ___________.(i) (A) > (B) > (C) (ii) (C) > (B) > (A) (iii) (B) > (A) > (C) (iv) (A) > (C) > (B)
Option (ii) is the answer. Alcohol reactivity towards halogen acids diminishes in the following order: (C) > (B) > (A) Because tertiary carbocation is the most stable of the three, it is...
Which of the following are benzylic alcohols?
Option (ii) and (iii) are the answers. Benzylic alcohols, as we all know, are molecules with an alcohol functional group on a carbon atom that is directly linked to the Benzene ring. Because the –OH...
Phenol can be distinguished from ethanol by the reactions with _________. (i) Br2/water (ii) Na (iii) Neutral FeCl3 (iv) All the above
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. Phenols react with FeCl3 to create a colourful Fe3+ ion complex. Depending on the structure of the phenol examined, the hue ranges from purple to orange....
Which of the following reagents can be used to oxidise primary alcohols to aldehydes? (i) CrO3 in an anhydrous medium. (ii) KMnO4 in acidic medium. (iii) Pyridinium chlorochromate. (iv) Heat in the presence of Cu at 573K
Option (i), (iii) and (iv) are the answers. Primary alcohols can be oxidised to aldehydes using CrO3 in an anhydrous media. CrO3 serves as an oxidizer in this situation. As a result, option I is the...
Which of the following reactions will yield phenol?
Option (A), (B) and (C) are correct Diazonium salt is produced when aniline is treated with NaNO2 + HCl. The Diazonium salts are then hydrolyzed to Phenols by heating them with water. As a result,...
Which of the following are used to convert RCHO into RCH2OH? (i) H2/Pd (ii) LiAlH4 (iii) NaBH4 (iv) Reaction with RMgX followed by hydrolysis
Option (i), (ii) and (iii) are the answers. In the presence of a catalyst such as Pd, Pt, or Ni, aldehydes can be transformed to their corresponding alcohols by hydrogen. Lithium aluminium hydride...
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of boiling point. Propan-1-ol, butan-1-ol, butan-2-ol, pentan-1-ol (i) Propan-1-ol, butan-2-ol, butan-1-ol, pentan-1-ol (ii) Propan-1-ol, butan-1-ol, butan-2-ol, pentan-1-ol (iii) Pentan-1-ol, butan-2-ol, butan-1-ol, propan-1-ol (iv) Pentan-1-ol, butan-1-ol, butan-2-ol, propan-1-ol
Option (i) is the answer As the moleculer mass of the alcohol grows, the boiling point rises. Furthermore, $1^0$ alcohols have greater boiling points than $2^0$ alcohols among isomeric alcohols.
Mark the correct increasing order of reactivity of the following compounds with HBr/HCl.(i) a < b < c (ii) b < a < c (iii) b < c < a (iv) c < b < a
Option (iii) is the answer. It's a nucleophilic substitution process that uses the $SN_1$ mechanism. The stability of the carbocation is required for the $SN_1$ mechanism to work. The presence of an...
Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.(i) e > d > b > a > c (ii) b > d > a > c > e (iii) d > e > c > b > a (iv) e > d > c > b > a
Option (ii) is the answer. The sequence of decreasing acid strength is b>d>a>c>e, with p-nitrophenol being the most acidic and p-methoxy phenol being the least acidic. The acidity is...
Which of the following is most acidic? (i) Benzyl alcohol (ii) Cyclohexanol (iii) Phenol (iv) m-Chlorophenol
Option (iv) is the answer. Alcohols have a lower acidity level than phenol. Furthermore, electron-withdrawing groups make phenols more acidic, therefore m-chlorophenol is the most acidic.
