i) Time taken by the ray to travel from S to P1 is = t1 = √u2 + b2/c Time taken by the ray to travel from P1 to O is = t2 = v/c (1+ ½ b2/v2) Time taken to travel through the lens is =...
(i) Consider a thin lens placed between a source (S) and an observer (O). Let the thickness of the lens vary as 2 0 () – α = b wb w, where b is the verticle distance from the pole. w0 is a constant. Using Fermat’s principle i.e. the time of transit for a ray between the source and observer is an extremum, find the condition that all paraxial rays starting from the source will converge at a point O on the axis. Find the focal length.
Show that for a material with refractive index µ ≥ 2 , light incident at any angle shall be guided along a length perpendicular to the incident face. Answer:
Let the refractive index of the rectangular slab be μ ≥ √2. μ = 1/sin ic sin ic > 1/ μ cos r ≥ 1/ μ sin i/sin r = μ From Snell’s law Sin I = μ sin r i = 90o 1 + 1 ≤ μ2 2 ≤ μ2 Taking the square...
A jar of height h is filled with a transparent liquid of refractive index µ. At the centre of the jar on the bottom surface is a dot. Find the minimum diameter of a disc, such that when placed on the top surface symmetrically about the centre, the dot is invisible.
tan ic d/2/h ic = d/2h d = 2h tan ic d = 2h ×1/√μ2 – 1
A short object of length L is placed along the principal axis of a concave mirror away from focus. The object distance is u. If the mirror has a focal length f, what will be the length of the image? You may take L << |v-f|
The mirror formula is 1/v + 1/u = 1/f u is the object distance v is the image distance du = |u1 – u2| = L Differentiating on the both sides we get, dv/v2 = -du/u2 v/u = f/u-f du = L, therefore,...
For a glass prism (µ = √3 ) the angle of minimum deviation is equal to the angle of the prism. Find the angle of the prism.
μ = sin[(A + δm)/2]/sin (A/2)
Three immiscible liquids of densities d1 > d2 > d3 and refractive indices µ1 > µ2 > µ3 are put in a beaker. The height of each liquid column is h/3. A dot is made at the bottom of the beaker. For near-normal vision, find the apparent depth of the dot. Answer:
An unsymmetrical double convex thin lens forms the image of a point object on its axis. Will the position of the image change if the lens is reversed?
The near vision of an average person is 25cm. To view an object with an angular magnification of 10, what should be the power of the microscope?
Will the focal length of a lens for red light be more, same or less than that for blue light?
An astronomical refractive telescope has an objective of focal length 20m and an eyepiece of focal length 2cm.(a) The length of the telescope tube is 20.02m. (b) The magnification is 1000. (c) The image formed is inverted. (d) An objective of a larger aperture will increase the brightness and reduce chromatic aberration of the image.
Answer: (a) The length of the telescope tube is 20.02m. (b) The magnification is 1000. (c) The image formed is inverted. ...
A magnifying glass is used, as the object to be viewed can be brought closer to the eye than the normal near point. This results in
(a) a larger angle to be subtended by the object at the eye and hence viewed in greater detail.
(b) the formation of a virtual erect image.
(c) increase in the field of view.
(d) infinite magnification at the near point.
Answer: (a) a larger angle to be subtended by the object at the eye and hence viewed in greater detail. (b) the formation of a virtual erect image. ...
Between the primary and secondary rainbows, there is a dark band known as Alexandar’s dark band. This is because
(a) light scattered into this region interfere destructively.
(b) there is no light scattered into this region
(c) light is absorbed in this region.
(d) angle made at the eye by the scattered rays with respect to the incident light of the sun lies between approximately 42° and 50°.
Answer: (a) light scattered into this region interfere destructively. (d) angle made at the eye by the scattered rays with respect to the incident light of the sun lies between approximately 42° and...
A rectangular block of glass ABCD has a refractive index 1.6. A pin is placed midway on the face AB. When observed from the face AD, the pin shall
(a) appear to be near A.
(b) appear to be near D.
(c) appear to be at the centre of AD.
(d) not be seen at all.
Answer: (a) appear to be near A. (d) not be seen at all. The pin will appear to be near A as long as the angle of incidence on AD of the ray emerging from the pin is smaller...
Consider an extended object immersed in water contained in a plane trough. When seen from close to the edge of the trough the object looks distorted because
(a) the apparent depth of the points close to the edge is nearer the surface of the water compared to the points away from the edge.
(b) the angle subtended by the image of the object at the eye is smaller than the actual angle subtended by the object in the air.
(c) some of the points of the object far away from the edge may not be visible because of total internal reflection.
(d) water in a trough acts as a lens and magnifies the object.
Answer: (a) the apparent depth of the points close to the edge is nearer the surface of the water compared to the points away from the edge. (b) the angle subtended by the image of the object at the...
A car is moving with at a constant speed of 60 km h–1 on a straight road. Looking at the rearview mirror, the driver finds that the car following him is at a distance of 100 m and is approaching with a speed of 5 km h –1. In order to keep track of the car in the rear, the driver begins to glance alternatively at the rear and side mirror of his car after every 2 still the other car overtakes. If the two cars were maintaining their speeds, which of the following statement (s) is/are correct?
(a) The speed of the car in the rear is 65 km h–1.
(b) In the side mirror, the car in the rear would appear to approach with a speed of 5 km h–1 to the driver of the leading car.
(c) In the rearview mirror the speed of the approaching car would appear to decrease as the distance between the cars decreases.
(d) In the side mirror, the speed of the approaching car would appear to increase as the distance between the cars decreases.
Answer: (d) In the side mirror, the speed of the approaching car would appear to increase as the distance between the cars decreases.
The optical density of turpentine is higher than that of water while its mass density is lower. The figure shows a layer of turpentine floating over water in a container. For which one of the four rays incident on turpentine in the figure, the path shown is correct?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Answer: b) 2 When light travels from (optically) rarer medium air to optically denser medium turpentine, it bends towards the normal, i.e., θ1 >...
The direction of a ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown by PQ while directions in which the ray would travel after reflection is shown by four rays marked 1, 2, 3, and 4. Which of the four rays correctly shows the direction of reflected ray?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Answer: b) 2 After reflection, the ray PQ of light that passes through focus F and strikes the concave mirror should become parallel to the primary...
The phenomena involved in the reflection of radiowaves by ionosphere is similar to
a) reflection of light by a plane mirror
b) total internal reflection of light in the air during a mirage
c) dispersion of light by water molecules during the formation of a rainbow
d) scattering of light by the particles of air
Answer: b) total internal reflection of light in the air during a mirage The ionosphere, a layer of the atmosphere, reflects radio waves, allowing them to reach far-flung portions of the globe....
The radius of curvature of the curved surface of a plano-convex lens is 20 cm. If the refractive index of the material of the lens be 1.5, it will
a) act as a convex lens only for the objects that lie on its curved side
b) act as a concave lens only for the objects that lie on its curved side
c) act as a convex lens irrespective of the side on which the object lies
d) act as a concave lens irrespective of the side on which the object lies
Answer: c) act as a convex lens irrespective of the side on which the object lies
A passenger in an aeroplane shall
a) never see a rainbow
b) may see a primary and a secondary rainbow as concentric circles
c) may see a primary and a secondary rainbow as concentric arcs
d) shall never see a secondary rainbow
Answer: b) may see a primary and a secondary rainbow as concentric circles As an aeroplane flies higher in the sky, passengers may notice a primary and secondary rainbow in the form of concentric...
An object approaches a convergent lens from the left of the lens with a uniform speed 5 m/s and stops at the focus. The image
a) moves away from the lens with a uniform speed 5 m/s
b) moves away from the lens with a uniform acceleration
c) moves away from the lens with a non-uniform acceleration
d) moves towards the lens with a non-uniform acceleration
Answer: c) moves away from the lens with a non-uniform acceleration In our case, the object approaches a convergent lens from the left at a uniform speed of 5 m/s, causing the image to travel away...
A short pulse of white light is incident from air to a glass slab at normal incidence. After travelling through the slab, the first colour to emerge is
a) blue
b) green
c) violet
d) red
Answer: d) Red The relation v = fλ describes the velocity of a wave. The frequency of light does not change when it travels from one medium to another. As a result, the bigger the wavelength, the...
Equipotential surfaces a) are closer in regions of large electric fields compared to regions of lower electric fields b) will be more crowded near sharp edges of a conductor c) will be more crowded near regions of large charge densities d) will always be equally spaced
The correct answer is a) are closer in regions of large electric fields compared to regions of lower electric fields b) will be more crowded near sharp edges of a conductor c) will be more crowded...
Consider a uniform electric field in the z direction. The potential is a constant a) in all space b) for any x for a given z c) for any y for a given z d) on the x-y plane for a given z
The correct answer is b) for any x for a given z c) for any y for a given z d) on the x-y plane for a given z
A parallel plate capacitor is made of two dielectric blocks in series. One of the blocks has thickness d1 and dielectric constant k1 and the other has thickness d2 and dielectric constant k2 as shown in the figure. This arrangement can be thought of as a dielectric slab of thickness d = d1 + d2 and effective dielectric constant k. The k is a) k1d1 + k2d2/d1+d2 b) k1d1 + k2d2/k1 + k2 c) k1k2 (d1 + d2)/(k1d1 + k2d2) d) 2k1k2/k1 + k2
The correct answer is c) k1k2 (d1 + d2)/(k1d1 + k2d2)
Equipotential at a great distance from a collection of charges whose total sum is not zero are approximately a) spheres b) planes c) paraboloids d) ellipsoids
The correct answer is a) spheres
The electrostatic potential on the surface of a charged conducting sphere is 100V. Two statements are made in this regard: S1: At any point inside the sphere, the electric intensity is zero S2: At any point inside the sphere, the electrostatic potential is 100V Which of the following is a correct statement? a) S1 is true but S2 is false b) Both S1 and S2 are false c) S1 is true, S2 is also true, and S1 is the cause of S2 d) S1 is true, S2 is also true but the statements are independent
The correct answer is c) S1 is true, S2 is also true, and S1 is the cause of S2
Figure shows some equipotential lines distributed in space. A charged object is moved from point A to point B. a) the work done in fig (i) is the greatest b) the work done in fig (ii) is least c) the work done is the same in fig (i), fig (ii), and fig (iii) d) the work done in fig (iii) is greater than fig (ii) but equal to that in fig (i)
The correct answer is c) the work done is the same in fig (i), fig (ii), and fig (iii)
A capacitor of 4μF is connected as shown in the circuit. The internal resistance of the battery is 0.5Ω. The amount of charge on the capacitor plates will be a) 0 b) 4μC c) 16μC d) 8μC
The correct answer is d) 8μC
A ball is dropped and its displacement vs time graph is as shown in the figure where displacement x is from the ground and all quantities are positive upwards. a) Plot qualitatively velocity vs time graph b) Plot qualitatively acceleration vs time graph
a) At t=0 and v=0 , v-t graph is: b) At x = 0, a-t graph is:
A positively charged particle is released from rest in a uniform electric field. The electric potential energy of the charge a) remains a constant because the electric field is uniform b) increases because the charge moves along the electric field c) decreases because the charge moves along the electric field d) decreases because the charge moves opposite to the electric field
The correct answer is c) decreases because the charge moves along the electric field
A certain mass of hydrogen is changed to Helium by the process of fusion. The mass defect in fusion reaction is 0.02866 u. The energy liberated per u is: (given 1u = 931 MeV)
Option A 13.35 MeV Option B 2.67 MeV Option C 26.7 MeV Option D 6.675 MeV Solution: The correct option is Option D The energy released per u is given by:
In a common emitter (CE) amplifier having a voltage gain G, transistor used has trans conductance 0.02 mho and current gain 20, the voltage gain will be
Option A 5/4 G Option B 2/3 G Option C 1.5 G Option D 1/3 G Solution: The correct answer is Option B 2/3G
In Young’s double slit experiment, the slits are 2mm apart and are illuminated by photons of two wavelength λ1 = 12000 Å and λ2 = 10000 Å. At what minimum distance from the common central bright fringe on the screen 2m from the slit will a bright fringe from one interference pattern coincide with a bright fringe from the other?
Option A 3 mm Option B 8 mm Option C 6 mm Option D 4 mm Solution: The correct option is Option C Explanation: According to question, we have n1λ1 = n2λ2 $ \frac{{{\lambda }_{1}}}{{{\lambda...
An audio signal is modulated by a carrier wave of 20MHz such that the bandwidth required for modulation is 3kHz. Could this wave be demodulated by a diode detector which has the values of R and C as
(i) R = 1 kΩ, C = 0.01µF (ii) R = 10 kΩ, C = 0.01µF (iii) R = 10 kΩ, C = 0.1µF Answer: Carrier wave frequency, fc – 20 MHz = 20 × 106 Hz Bandwidth = 2fm = 3 × 103 Hz fm = 1.5 × 103 Hz 1/fc = 0.5 ×...
(i) Draw the plot of amplitude versus ‘ω’ for an amplitude modulated wave whose carrier wave (ωc ) is carrying two modulating signals, ω1 and ω2 (ω2 > ω1). [Hint: Follow derivation from Eq 15.6 of NCERT Textbook of XII]
(ii) Is the plot symmetrical about ωc? Comment especially about plot in region ω < ωc (iii) Extrapolate and predict the problems one can expect if more waves are to be modulated (iv) Suggest...
An amplitude modulated wave is as shown in the figure. Calculate
(i) the percentage modulation (ii) peak carrier voltage and (iii) peak value of information voltage Answer; Maximum voltage is given by $ {{V}_{\max }}=\frac{100}{2}=50V $ Minimum voltage is given...
A 50 MHz sky wave takes 4.04 ms to reach a receiver via re-transmission from a satellite 600 km above earth’s surface. Assuming re-transmission time by satellite negligible, find the distance between source and receiver. If communication between the two was to be done by Line of Sight (LOS) method, what should size and placement of receiving and transmitting antenna be?
Answer: According to the question, the velocity of waves = 3 × 108 m/s The time to reach a receiver = 4.04 × 10-3 s we know that the height of satellite is: h = 600 km And the radius of earth = 6400...
(i) The intensity of a light pulse travelling along a communication
channel decreases exponentially with distance x according to the relation I = Ioe–αx, where I o is the intensity at x = 0 and α is the attenuation constant. Show that the intensity reduces by 75...
On radiating (sending out) an AM modulated signal, the total radiated power is due to energy carried by ωc, ωc – ωm & ωc + ωm. Suggest ways to minimise the cost of radiation without compromising on information
Answer: The total radiated power is due to ωc, (ωc – ωm) and (ωc + ωm) carrying energy. The carrier frequency is usually close to the sideband frequencies. In an amplitude modulated transmission,...
The maximum frequency for reflection of sky waves from a certain layer of the ionosphere is found to be f max = 9(Nmax) 1/2, where Nmax is the maximum electron density at that layer of the ionosphere. On a certain day, it is observed that signals of frequencies higher than 5MHz are not received by reflection from the F1 layer of the ionosphere while signals of frequencies higher than 8MHz are not received by reflection from the F2 layer of the ionosphere. Estimate the maximum electron densities of the F1 and F2 layers on that day.
Answer: Expression fpor the maximum frequency is: fmax = 9(Nmax)1/2 According to the question, for Layer F1, fmax = 5 MHz $ {{N}_{\max }}=\frac{F_{\max }^{2}}{9\times 9}=\frac{5\times...
If the whole earth is to be connected by LOS communication using space waves (no restriction of antenna size or tower height), what is the minimum number of antennas required? Calculate the tower height of these antennas in terms of earths radius?
Answer: We know that the distance or range of transmission tower is given by the expression: $dT=\sqrt{2{{h}_{T}}R}$ R represents the radius of the earth (approximately 6400 km). hT denotes the...
A TV transmission tower antenna is at a height of 20 m. How much service area can it cover if the receiving antenna is
(i) at ground level, (ii) at a height of 25 m? Calculate the percentage increase in area covered in case (ii) relative to case (i). Answer: We know that: $ {{R}_{e}}=6.4\times {{10}^{6}}m $ The...
Figure shows a communication system. What is the output power when the input signal is of 1.01mW? (gain in dB = 10 log10 (Po /Pi ).
Answer: It is given that there is a loss of signal 2dB per km. So total loss suffered in 5km = -2 x 5 = -10 dB. In both input and output amplifiers, the total gain of the signal is given by: =...
Why is an AM signal likely to be noisier than an FM signal upon transmission through a channel?
Answer: In an amplitude modulated wave, the carrier wave's instantaneous voltage varies. As a result, assuming noise as a part of the modulated signal, a noise signal can be added and received...
Compute the LC product of a tuned amplifier circuit required to generate a carrier wave of 1 MHz for amplitude modulation.
Answer: $ v=1MHz={{10}^{6}}Hz $ $ v=\frac{1}{2\pi \sqrt{LC}} $ $ Or,\sqrt{LC}=\frac{1}{2\pi v} $ $ LC=\frac{1}{{{(2\pi v)}^{2}}}=\frac{1}{4\times 3.14\times 3.14\times {{10}^{12}}} $ $...
The maximum amplitude of an A.M. wave is found to be 15 V while its minimum amplitude is found to be 3 V. What is the modulation index?
Answer: The modulation index is the ratio of the change in carrier wave amplitude to the original carrier wave amplitude. according to the question, the maximum amplitude of AM wave is Amax = Ac +...
Two waves A and B of frequencies 2 MHz and 3 MHz, respectively are beamed in the same direction for communication via skywave. Which one of these is likely to travel a longer distance in the ionosphere before suffering total internal reflection?
Answer: The refractive index rises as the frequency rises, implying that the angle of refraction is smaller for higher frequency waves. In other words, bending is less. As a result, after covering a...
Would sky waves be suitable for transmission of TV signals of 60 MHz frequency?
Answer; Skywaves will not be suitable for transmitting TV signals with a frequency of 60 MHz since the TV signals are higher than 60 MHz. It is necessary to use space wave transmission.
Which of the following would produce analogue signals and which would produce digital signals?
(i) A vibrating tuning fork (ii) Musical sound due to a vibrating sitar string (iii) Light pulse (iv) Output of NAND gate Answer: i) A vibrating tuning fork will produce an analog signal ii) musical...
In amplitude modulation, the modulation index m, is kept less than or equal to 1 because
(a) m > 1, will result in interference between the carrier frequency and message frequency, resulting in distortion (b) m > 1 will result in overlapping of both sidebands resulting into loss...
The frequency response curve in the figure for the filter circuit used for production of AM wave should be
(a) (i) followed by(ii) (b) (ii) followed by (i) (c) (iii) (d) (iv) Answer: The correct options are: (a) (i) followed by(ii) (b) (ii) followed by (i) (c) (iii) Explanation: The band pass filter...
A TV transmission tower has a height of 240 m. Signals broadcast from this tower will be received by LOS communication at a distance of (assume the radius of the earth to be 6.4 × 106 m)
(a) 100 km (b) 24 km (c) 55 km (d) 50 km Answer: The correct options are (b) 24 km (c) 55 km and (d) 50 km Explanation: $ {{h}_{T}}=240m $ $ R=6.4\times {{10}^{6}}m $ For, LOS communication we have:...
Audio sine waves of 3 kHz frequency are used to amplitude modulate a carrier signal of 1.5 MHz. Which of the following statements are true?
(a) The sideband frequencies are 1506 kHz and 1494 kHz (b) The bandwidth required for amplitude modulation is 6kHz (c) The bandwidth required for amplitude modulation is 3 MHz (d) The sideband...
An audio signal of 15kHz frequency cannot be transmitted over long distances without modulation because
(a) the size of the required antenna would be at least 5 km which is not convenient (b) the audio signal can not be transmitted through sky waves (c) the size of the required antenna would be at...
Identify the mathematical expression for amplitude modulated wave:
a) Ac sin [{ωc + k1vm(t)}t + φ ] (b) Ac sin {ωc t + φ + k2 vm(t)} (c) {Ac + k2 vm(t)} sin (ωc t + φ ) (d) Ac vm(t) sin (ωc t + φ ) Answer: The correct option is (c) {Ac + k2 vm(t)} sin (ωc t + φ )...
A basic communication system consists of
(A) transmitter (B) information source (C) user of information (D) channel (E) receiver Choose the correct sequence in which these are arranged in a basic communication system: (a) ABCDE (b) BADEC...
A male voice after modulation-transmission sounds like that of a female to the receiver. The problem is due to
a) poor selection of modulation index (selected 0 < m < 1) (b) poor bandwidth selection of amplifiers (c) poor selection of carrier frequency (d) loss of energy in transmission Answer: The...
I-V characteristics of four devices are shown in the figure.
Identify devices that can be used for modulation: (a) ‘i’ and ‘iii’ (b) only ‘iii’ (c) ‘ii’ and some regions of ‘iv’ (d) All the devices can be used. Answer: The correct option is (c) ‘ii’ and some...
A message signal of frequency ωm is superposed on a carrier wave of frequency ωc to get an amplitude modulated wave (AM). The frequency of the AM wave will be
(a) ωm (b) ωc (c) ωc + ωm/2 (d) ωc – ωm/2 Answer: The correct option is (b) ωc Explanation: Frequency of carrier wave = ωc Frequency of modulated wave = ωc
A speech signal of 3 kHz is used to modulate a carrier signal of frequency 1 MHz, using amplitude modulation. The frequencies of the sidebands will be
(a) 1.003 MHz and 0.997 MHz (b) 3001 kHz and 2997 kHz (c) 1003 kHz and 1000 kHz (d) 1 MHz and 0.997 MHz Answer: The correct option is (a) 1.003 MHz and 0.997 MHz Explanation: $ {{\omega...
A 1 KW signal is transmitted using a communication channel which provides attenuation at the rate of – 2dB per km. If the communication channel has a total length of 5 km, the power of the signal received is [gain in dB = 10 log P0/P1]
(a) 900 W (b) 100 W (c) 990 W (d) 1010 W Answer: The correct option is (b) 100 W Explanation: According to the question, Pi =1 kW = 1000W The rate of attenuation of the signal = -2dB/km Length of...
A 100m long antenna is mounted on a 500m tall building. The complex can become a transmission tower for waves with λ
(a) ~ 400 m (b) ~ 25 m (c) ~ 150 m (d) ~ 2400 m Answer: The correct option is (a) ~ 400 m Explanation: According to the question, the length of building ois l = 500m and Length of antenna is 100m...
Three waves A, B and C of frequencies 1600 kHz, 5 MHz and 60 MHz, respectively are to be transmitted from one place to another. Which of the following is the most appropriate mode of communication:
(a) A is transmitted via space wave while B and C are transmitted via skywave (b) A is transmitted via ground wave, B via skywave and C via space wave (c) B and C are transmitted via ground wave...
In the circuit, find the value of RC.
Answer: Ie = Ic + Ib IcRc + Vce + IeRe = Vcc Rib + Vbe + IeRe = Vcc Ib = 11.5/200 mA Rc + Re = 1.56 kilo ohm Rc = 560 Ohm
For the transistor circuit shown in Fig.14.19, evaluate VE, RB, RE given IC = 1 mA, VCE = 3V, VBE = 0.5 V and VCC = 12 V, β = 100.
Answer: $ {{I}_{C}}={{I}_{B}}+{{I}_{E}} $ $ {{I}_{B}}<<<{{I}_{C}} $ $ \therefore {{I}_{C}}={{I}_{E}} $ $ {{I}_{C}}=1mA(given) $ $ \therefore {{I}_{C}}={{I}_{E}}=1mA $ By Kirchhoff's loop...
Consider a box with three terminals on top of it:
Three components namely, two germanium diodes and one resistor are connected across these three terminals in some arrangement. A student performs an experiment in which any two of these three...
An X-OR gate has the following truth table:
A B Y 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 It is represented by the following logic relation Build this gate using AND, OR, and NOT gates. Answer: In given logic relation Y = AˉB + ABˉ =Y1Y2 Now, the logic...
Suppose a ‘n’-type wafer is created by doping Si crystal having 5 × 1028 atoms/m3 with 1ppm concentration of As. On the surface 200 ppm Boron is added to create the ‘P’ region in this wafer. Considering ni = 1.5 × 1016 m–3,
(i) Calculate the densities of the charge carriers in the n & p regions. (ii) Comment which charge carriers would contribute largely for the reverse saturation current when the diode is reverse...
An electron (mass m) with an initial velocity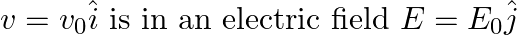 . If
. If 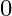 =
= 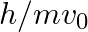 , it’s de Broglie wavelength at time t is given bya)
, it’s de Broglie wavelength at time t is given bya) 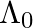 b)
b) 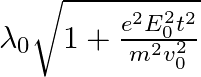 c)
c) 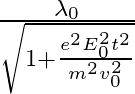 d )
d ) 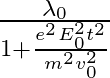
The correct answer is c)$ \frac{\lambda_{0}}{\sqrt{1+\frac{e^{2} E_{0}^{2} t^{2}}{m^{2} v_{0}^{2}}}} $ The de Broglie equation h=mv describes the relationship between a moving particle's momentum...
An electron (mass m ) with an initial velocity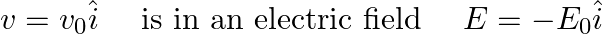 It’s de Broglie wavelength at time t is given bya)
It’s de Broglie wavelength at time t is given bya) 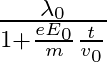 b)
b) 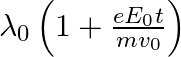 c)
c)  d)
d) 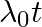
The correct answer is a) $\frac{\lambda_{0}}{1+\frac{e E_{0}}{m} \frac{t}{v_{0}}}$ The wave associated with moving particle is called matter wave or de-Broglie wave and it propagates in the form of...
Consider the circuit arrangement in which the input and output characteristics of NPN transistor in CE configuration
Select the values of RB and RC for a transistor whose VBE = 0.7 V, so that the transistor is operating at point Q as shown in the characteristics shown in the figure (b). Given that the input...
Assuming the ideal diode. Explain the waveform.
Answer: When signal 20sinωt provides an input voltage less than 5 volt (because after 5V, the diode will receive a positive voltage at its P-junction), the diode will be in reverse bias, and the...
Draw the output signals C1 and C2 in the given combination of gates in the figure.
In the circuit shown in the figure, when the input voltage of the base resistance is 10V, Vbe is zero and Vce is also zero. Find the values of Ib, Ic and β.
Answer: As $ {{V}_{BE}}=0 $, the potential drop across $ {{R}_{B}} $ is 10 Volts. $ {{I}_{B}}=\frac{10}{400\times {{10}^{3}}}=25\mu A $ Now, as $ {{V}_{CE}}=0 $, The potenial drop across $...
If each diode in the figure has a forward bias resistance of 25Ω and infinite resistance in reverse bias, what will be the values of the current I1, I2, I3 and I4?
Answer: Because the diode in that branch is reverse biased, I3 is zero. I3 = 0 We know that the resistance in AB = 150 ohms and the resistance in EF = 150 ohms and AB is parallel to EF Therefore,...
A Zener of power rating 1 W is to be used as a voltage regulator. If Zener has a breakdown of 5V and it has to regulate voltage which fluctuated between 3V and 7V, what should be the value of Rs for safe operation in the figure?
Answer: According to the question, Power = 1W and Zener breakdown voltage = 5V We are given that the minimum voltage = 3V and the maximum voltage = 7V $ {{I}_{\max }}=\frac{P}{{{V}_{z}}}=\frac{1}{5}...
Write the truth table for the circuit shown in the figure. Name the gate that the circuit resembles.
Answer: The given circuit is AND and the truth table is: A B X = A.B 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1
Explain why elemental semiconductor cannot be used to make visible LEDs.
Answer: The bandgap in an elemental conductor is such that the emissions are infrared rather than visible. Elemental semiconductors cannot be used to make visible LEDs. This is because the energy...
How would you set up a circuit to obtain NOT gate using a transistor?
Answer: a) There is only one input and only one output b) By making use of the Boolean expression c) Realization of NOT gate d) Making use of the truth table The NOT gate is a single-input,...
Two car garages have a common gate which needs to open automatically when a car enters either of the garages or cars enter both. Devise a circuit that resembles this situation using diodes for this situation.
Answer: When an automobile approaches the gate, one or both gates are open. As a result, the OR gate produces the required result. The following is a truth table for the same: A B Y = A + B 0 0 0 0...
If the resistance R1 is increased, how will the readings of the ammeter and voltmeter change?
Answer: From the circuit diagram, we have IbR1 + Vbe = Vbb Expression for the base current gives us Ib = Vbb – Vbe/R1 It can be seen that Ib is inversely proportional to R1 The reading of the...
Three photodiodes D1, D2 and D3 are made of semiconductors having band gaps of 2.5eV, 2eV and 3eV, respectively. Which ones will be able to detect light of wavelength 6000 Ao?
Answer: According to the question, the wavelength is: λ = 6000 Ao = 6000 × 10-10m Expression for the energy of the light photon is as follows: E = hc/ λ Upon substituting the values of h, c and...
(i) Name the type of a diode whose characteristics are shown in the figure (a) and in the figure (b)
(ii) What does the point P in the figure (a) represent? (iii) What does the points P and Q in the figure (b) represent? Answer: (i) Figure a) depicts the Zener diode's characteristics, whereas...
In a CE transistor amplifier there is a current and voltage gain associated with the circuit. In other words, there is a power gain. Considering power a measure of energy, does the circuit violate conservation of energy?
Answer: The DC supply is connected to the CE transistor amplifier to provide energy to the signal. As a result, the CE configuration amplifier has a significant power gain. The extra power necessary...
The amplifiers X, Y and Z are connected in series. If the voltage gains of X, Y and Z are 10, 20 and 30, respectively and the input signal is 1 mV peak value, then what is the output signal voltage (peak value)
(i) if dc supply voltage is 10V? (ii) if dc supply voltage is 5V? Answer: According to the question, we can write Voltage gain in X = vx = 10 Voltage gain in Y = vy = 20 Voltage gain in Z = vz = 30...
Draw the output waveform across the resistor in the figure.
The waveform formed across the resistance diode conducts when the diode is forward biassed in the given circuit, hence the output will be only when the input +1V is between t1 and t2. As a result,...
Can the potential barrier across a p-n junction be measured by simply connecting a voltmeter across the junction?
Answer: We can't use a voltmeter to detect the potential barrier across a p-n junction because the voltmeter's resistance must be very high relative to the junction resistance, which is almost...
Sn, C, and Si, Ge are all group XIV elements. Yet, Sn is a conductor, C is an insulator while Si and Ge are semiconductors. Why?
Answer: If there is no energy gap between the conduction and valence bands in an atom's energy band diagram, the material will conduct current. This energy gap narrows when the material transitions...
Why are elemental dopants for Silicon or Germanium usually chosen from group XIII or group XV?
Answer: Because the size of the dopant must be compatible with the semiconductor and they must form covalent bonds. The elemental dopants for silicon or germanium are usually chosen from groups XIII...
The breakdown in a reverse-biased p–n junction diode is more likely to occur due to
(a) large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is small (b) large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is large (c) strong electric...
To reduce the ripples in a rectifier circuit with capacitor filter
(a) RL should be increased (b) input frequency should be decreased (c) input frequency should be increased (d) capacitors with high capacitance should be used Answer: The correct options are: (a) RL...
What happens during regulation action of a Zener diode?
(a) The current in and voltage across the Zenor remains fixed (b) The current through the series Resistance (Rs ) changes (c) The Zener resistance is constant (d) The resistance offered by the Zener...
In the depletion region of a diode
(a) there are no mobile charges (b) equal number of holes and electrons exist, making the region neutral (c) recombination of holes and electrons has taken place (d) immobile charged ions exist...
In an NPN transistor circuit, the collector current is 10mA. If 95 per cent of the electrons emitted reaches the collector, which of the following statements are true?
(a) The emitter current will be 8 mA (b) The emitter current will be 10.53 mA (c) The base current will be 0.53 mA (d) The base current will be 2 mA Answer: The correct options are: (b) The emitter...
In the figure shows the transfer characteristics of a base biased CE transistor. Which of the following statements are true?
(a) At Vi = 0.4V, transistor is in active state (b) At Vi = 1V, it can be used as an amplifier (c) At Vi = 0. .5V, it can be used as a switch turned off (d) At Vi = 2.5V, it can be used as a switch...
Consider an NPN transistor with its base-emitter junction forward biased and collector-base junction reverse biased. Which of the following statements are true?
(a) Electrons crossover from emitter to collector (b) Holes move from base to collector (c) Electrons move from emitter to base (d) Electrons from emitter move out of base without going to the...
When an electric field is applied across a semiconductor
(a) electrons move from lower energy level to higher energy level in the conduction band (b) electrons move from higher energy level to lower energy level in the conduction band (c) holes in the...
Truth table for the given circuit in the figure is
(a) A B E 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 (b) A B E 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 (c) A B E 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 (d) A B E 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 Answer: The correct option is (c) A B E 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1...
In the circuit shown in the figure, if the diode forward voltage drop is 0.3 V, the voltage difference between A and B is
(a) 1.3 V (b) 2.3 V (c) 0 (d) 0.5 V Answer: The correct option is (b) 2.3 V Explanation: Let V represent the potential difference between A and B, then we can write: V - 0.3 = (5 +5) x 103 x (0.2 x...
The output of the given circuit in the figure
(a) would be zero at all times (b) would be like a half-wave rectifier with positive cycles in output (c) would be like a half-wave rectifier with negative cycles in output (d) would be like that of...
Hole is
(a) an anti-particle of the electron (b) a vacancy created when an electron leaves a covalent bond (c) absence of free electrons (d) an artificially created particle Answer: The correct option is...
A 220 V A.C. supply is connected between points A and B in the figure. What will be the potential difference V across the capacitor?
(a) 220V (b) 110V (c) 0V (d) 220 √2 V Answer: The correct option is (d) 220 √2 V Explanation: V(max) will be the potential difference across the capacitor. It is given by: ${{V}_{\max...
In the figure, assuming the diodes to be ideal,
(a) D1 is forward biased and D2 is reverse biased and hence current flows from A to B (b) D2 is forward biased and D1 is reverse biased and hence no current flows from B to A and vice versa (c) D1...
In the figure, Vo is the potential barrier across a p-n junction, when no battery is connected across the junction
(a) 1 and 3 both correspond to forward bias of junction (b) 3 corresponds to forward bias of junction and 1 corresponds to reverse bias of junction (c) 1 corresponds to forward bias and 3...
The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increase in temperature because
(a) number density of free current carriers increases (b) relaxation time increases (c) both number density of carriers and relaxation time increase (d) number density of current carriers...
If a proton had a radius R and the charge was uniformly distributed, calculate using Bohr theory, the ground state energy of a H-atom when
(i) R = 0.1Å,
and (ii) R = 10 Å.
(i) Consider the nucleus of a H atom as a point charge electron circling about it at a speed of $v$ and a radius of $r_A$ The Coulombian force acts as a centrifugal force, causing the nucleus to...
Would the Bohr formula for the H-atom remain unchanged if proton had a charge (+4/3)e and electron a charge 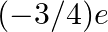 , where
, where  ? Give reasons for your answer.
? Give reasons for your answer.
The product of both charges will remain the same since the position of the proton and electron will not change.
When an electron falls from a higher energy to a lower energy level, the difference in the energies appears in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Why cannot it be emitted as other forms of energy?
Because the charged particle accelerates, the difference in energies shows in the form of electromagnetic radiation as an electron descends from a higher to a lower energy level.
Imagine removing one electron from 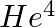 and
and 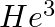 . Their energy levels, as worked out on the basis of Bohr model will be very close. Explain why.
. Their energy levels, as worked out on the basis of Bohr model will be very close. Explain why.
According to the Bohr model, the energies of $He^4$ and $He^3$ will be fairly near because each have one electron, much like the hydrogen atom, and the nucleus is four times heavier than the...
The simple Bohr model is not applicable to 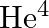 atom because
atom because
(a) 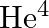 is an inert gas
is an inert gas
(b) 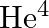 has neutrons in the nucleus
has neutrons in the nucleus
(c) 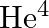 has one more electron
has one more electron
(d) electrons are not subject to central forces
The correct options are: (c) $\mathrm{He}^{4}$ has one more electron (d) electrons are not subject to central forces
The activity 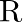 of an unknown radioactive nuclide is measured at hourly intervals. The results found are tabulated as follows:
of an unknown radioactive nuclide is measured at hourly intervals. The results found are tabulated as follows: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|l|l|l|} \hline$t(\mathrm{~h})$ & 0 & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 \\ \hline R(MBq) & 100 & $35.36$ & $12.51$ & $4.42$ & $1.56$ \\ \hline \end{tabular}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2cff4d33a1ea1a3274f405d5eee59de6_l3.png)
(i) Plot the graph of R versus 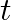 and calculate half-life from the graph.
and calculate half-life from the graph.
(ii) Plot the graph of 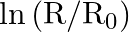 versus
versus 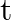 and obtain the value of half-life from the graph.
and obtain the value of half-life from the graph.
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|l|l|l|} \hline$t(\mathrm{~h})$ & 0 & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 \\ \hline R(MBq) & 100 & $35.36$ & $12.51$ & $4.42$ & $1.56$ \\ \hline \end{tabular}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2cff4d33a1ea1a3274f405d5eee59de6_l3.png)
(i) Graph between $\mathrm{R}$ versus $\mathrm{t}$ will be an exponential curve. From the graph at slightly more than $\mathrm{t}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{~h}$ the $\mathrm{R}$ should be $50 \%$ so at...
A nuclide 1 is said to be the mirror isobar of nuclide 2 if 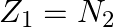 and
and 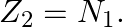
(a) What nuclide is a mirror isobar of 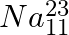 ?
?
(b) Which nuclide out of the two mirror isobars have greater binding energy and why?
a) We are given that a nuclide 1 is to be the mirror isobar of nuclide 2 if, $\mathrm Z_1=\mathrm N_2$ and $\mathrm Z_2=\mathrm N_1$ As a result, mirror isobar is $Z _2=12-N_ 1$ and $N_...
Why do stable nuclei never have more protons than neutrons?
Because protons are charged particles that resist one other, stable nuclei never have more protons than neutrons. Because of the strong repulsion, extra neutrons only produce attractive forces,...
Which one of the following cannot emit radiation and why? Excited nucleus, excited electron.
Because the energy of the electronic energy level is in the eV range rather than the MeV range, an excited electron cannot release radiation.
Draw a graph showing the variation of decay rate with number of active nuclei.
According to Rutherford and Soddy law, the radioactive decay is given as –dN/dt = λN.
The variation of the decay rate of two radioactive samples A and B with time is shown in the figure. Which of the following statements are true?
(a) The decay constant of A is greater than that of B, hence A always decays faster than B (b) The decay constant of B is greater than that of A but its decay rate is always smaller than that of A...
Fusion processes, like combining two deuterons to form a He nucleus are impossible at ordinary temperatures and pressure. The reasons for this can be traced to the fact:
(a) nuclear forces have short-range
(b) nuclei are positively charged
(c) the original nuclei must be completely ionized before fusion can take place
(d) the original nuclei must first break up before combining with each other
The correct options are: (a) nuclear forces have short-range (b) nuclei are positively charged
Heavy stable nuclei have more neutrons than protons. This is because of the fact that
(a) neutrons are heavier than protons
(b) electrostatic force between protons are repulsive
(c) neutrons decay into protons through beta decay
(d) nuclear forces between neutrons are weaker than that between protons
The correct option is: (b) electrostatic force between protons are repulsive
The gravitational force between an H-atom and another particle of mass m will be given by Newton’s law: 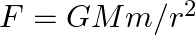 , where r is in km and
, where r is in km and
(a) M = mproton + m electron
(b) M = mproton  melectron
melectron 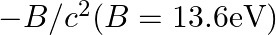
(c) M is not related to the mass of the hydrogen atom
(d) M = mproton +melectron 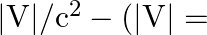 magnitude of the potential energy of electron in the
magnitude of the potential energy of electron in the  -atom)
-atom)
The correct option is: (b) M = mproton $+$ melectron $-B / c^{2}(B=13.6 \mathrm{eV})$
A plane EM wave travelling in vacuum along z-direction is given by 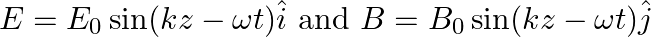
a) evaluate 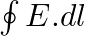 over the rectangular loop 1234 shown in the figure
over the rectangular loop 1234 shown in the figure
b) evaluate 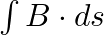 over the surface bounded by loop 1234
over the surface bounded by loop 1234
Solution: (a) $\oint_{\vec{E}} \cdot \overrightarrow{d l}=E_{0} h\left[\sin \left(k z_{2}-\omega t\right)-\sin \left(k z_{1}-\omega t\right)\right]$ (b) $\int \vec{B}.{\overrightarrow{d s}} =...
A long straight cable of length  is placed symmetrically along the z-axis and has radius
is placed symmetrically along the z-axis and has radius  . The cable consists of a thin wire and a co-axial conducting tube. An alternating current
. The cable consists of a thin wire and a co-axial conducting tube. An alternating current 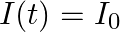 sin
sin 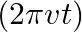 flows down the central thin wire and returns along the co-axial conducting tube. The induced electric field at a distance
flows down the central thin wire and returns along the co-axial conducting tube. The induced electric field at a distance 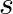 from the wire inside the cable is
from the wire inside the cable is 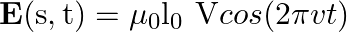 . In
. In 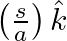 ,
,
a) calculate the displacement current density inside the cable
b) integrate the displacement current density across the cross-section of the cable to find the total displacement current I
a) The displacement current density is given as $\vec{J}_{d}=\frac{2 \pi I_{0}}{\lambda^{2}} \ln \frac{a}{s} \sin 2 \pi v t \hat{k}$ b) Total displacement current will be, $I^{d}=\int J_{d} 2 \pi s...
What happens to the intensity of light from a bulb if the distance from the bulb is doubled? As a laser beam travels across the length of a room, its intensity essentially remains constant. What geometrical characteristics of the LASER beam is responsible for the constant intensity which is missing in the case of light from the bulb?
When the distance between two points is doubled, the intensity of light is reduced by one-fourth. Geometrical characteristics of the LASER are: a) unidirectional b) monochromatic c) coherent...
Electromagnetic waves with wavelength
i) 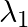 is used in satellite communication
is used in satellite communication
ii) 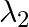 is used to kill germs in water purifies
is used to kill germs in water purifies
iii) 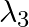 is used to detect leakage of oil in underground pipelines
is used to detect leakage of oil in underground pipelines
iv)  is used to improve visibility in runaways during fog and mist conditions
is used to improve visibility in runaways during fog and mist conditions
a) identify and name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which these radiations belong
b) arrange these wavelengths in ascending order of their magnitude
c) write one more application of each
a) i) $\lambda_{1}$ is a microwave, used in satellite communication. ii) $\lambda_{2}$ is UV rays, used in a water purifier for killing germs. iii) $\lambda_{3}$ is X-rays, used in improving the...
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in the figure.A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid (a) For a particular orientation, there shall be darkness as observed through the polaroid (b) The intensity of light as seen through the polaroid shall be independent of the rotation (c) The intensity of light as seen through the Polaroid shall go through a minimum but not zero for two orientations of the polaroid (d) The intensity of light as seen through the polaroid shall go through a minimum for four orientations of the polaroid
The correct answer is c) The intensity of light as seen through the Polaroid shall go through a minimum but not zero for two orientations of the polaroid
Consider sunlight incident on a slit of width 104 A. The image seen through the slit shall (a) be a fine sharp slit white in colour at the centre (b) a bright slit white at the centre diffusing to zero intensities at the edges (c) a bright slit white at the centre diffusing to regions of different colours (d) only be a diffused slit white in colour
The correct answer is (a) be a fine sharp slit white in colour at the centre
In a Young’s double-slit experiment, the source is white light. One of the holes is covered by a red filter and another by a blue filter. In this case (a) there shall be alternate interference patterns of red and blue (b) there shall be an interference pattern for red distinct from that for blue (c) there shall be no interference fringes (d) there shall be an interference pattern for red mixing with one for blue
The correct answer is c) there shall be no interference fringes
Two sources S1 and S2 of intensity I 1 and I 2 are placed in front of a screen in the figure (a). The pattern of intensity distribution seen in the central portion is given by the figure (b). In this case which of the following statements are true;(a) S1 and S2 have the same intensities (b) S1 and S2 have a constant phase difference (c) S1 and S2 have the same phase (d) S1 and S2 have the same wavelength.
The correct answer is a) S1 and S2 have the same intensities b) S1 and S2 have a constant phase difference c) S1 and S2 have the same phase
Consider sunlight incident on a pinhole of width 103A. The image of the pinhole seen on a screen shall be (a) a sharp white ring (b) different from a geometrical image (c) a diffused central spot, white in colour (d) diffused coloured region around a sharp central white spot
The correct answer is b) different from a geometrical image d) diffused coloured region around a sharp central white spot
Consider the diffraction pattern for a small pinhole. As the size of the hole is increased (a) the size decreases (b) the intensity increases (c) the size increases (d) the intensity decreases
The correct answer is a) the size decreases b) the intensity increases
For light diverging from a point source (a) the wavefront is spherical (b) the intensity decreases in proportion to the distance squared (c) the wavefront is parabolic (d) the intensity at the wavefront does not depend on the distance
The correct answer is a) the wavefront is spherical b) the intensity decreases in proportion to the distance squared
Is Huygen’s principle valid for longitudinal sound waves?
For longitudinal sound waves, Huygen's concept holds true.
Consider a point at the focal point of a convergent lens. Another convergent lens of short focal length is placed on the other side. What is the nature of the wavefronts emerging from the final image?
Wavefront and ray orientations are perpendicular to each other. L1 is the source of parallel rays that produce I2 at the focal length of the lens in the diagram above. The created picture serves as...
What is the shape of the wavefront on earth for sunlight?
The distance between the sun and the earth is known to be enormous. We also know that the sun is spherical and that it may be thought of as a point source of light that can be seen from a great...
Professor C.V.Raman surprised his students by suspending freely a ting light ball in a transparent vacuum chamber by shining a laser beam on it. Which property of EM waves was he exhibiting? Give one more example of this property.
Professor CV Raman demonstrated the radiation pressure property of EM waves.
The magnetic field of a beam emerging from a filter facing a floodlight is given by 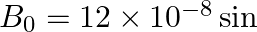
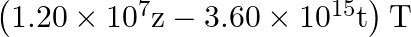 . What is the average intensity of the beam?
. What is the average intensity of the beam?
$\begin{array}{l} B_{0}=12 \times 10^{-8} \sin \left(1.20 \times 10^{7} z-3.60 \times 10^{15} \mathrm{t}\right) \mathrm{T} \\ \mathrm{B} 0=12 \times 10^{-8} \mathrm{~T} \\ \mathrm{lav}=1.71...
The source of electromagnetic waves can be a charge
a) moving with a constant velocity
b) moving in a circular orbit
c) at rest
d) falling in an electric field
The correct options are: b) moving in a circular orbit d) falling in an electric field
There are materials which absorb photons of shorter wavelength and emit photons of longer wavelength. Can there be stable substances which absorb photons of larger wavelength and emit light of shorter wavelength?
When the frequency of a photon drops, the wavelength of the photon rises. There are two alternative scenarios: case one, in which the photons have a shorter wavelength and the energy is consumed...
(i) In the explanation of the photoelectric effect, we assume one photon of frequency ν collides with an electron and transfers its energy. This leads to the equation for the maximum energy Emax of the emitted electron as Emax = hν – φ0 where φ0 is the work function of the metal. If an electron absorbs 2 photons (each of frequency ν ) what will be the maximum energy for the emitted electron? (ii) Why is this fact (two-photon absorption) not taken into consideration in our discussion of the stopping potential?
i)According to the question, the electron absorbs two protons with frequencies of v and v'= 2v, where v' is the frequency of the released electron. Emax = hv – ϕ0 ii) There is no emission since the...
Consider Fig. 11.7 in the NCERT textbook of physics for Class XII. Suppose the voltage applied to A is increased. The diffracted beam will have the maximum at a value of θ that (a) will be larger than the earlier value (b) will be the same as the earlier value (c) will be less than the earlier value (d) will depend on the target
The correct answer is c) will be less than the earlier value
Consider a beam of electrons (each electron with energy E0) incident on a metal surface kept in an evacuated chamber. Then (a) no electrons will be emitted as only photons can emit electrons (b) electrons can be emitted but all with an energy, E0 (c) electrons can be emitted with any energy, with a maximum of E0 – φ (φ is the work function) (d) electrons can be emitted with any energy, with a maximum of E0
The correct answer is d) electrons can be emitted with any energy, with a maximum of E0
The wavelength of a photon needed to remove a proton from a nucleus which is bound to the nucleus with 1 MeV energy is nearly (a) 1.2 nm (b) 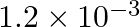 nm (c)
nm (c) 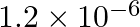 nm (d)
nm (d) nm
nm
The correct answer is b) 1.2 × 10–3 nm
An electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z-direction: 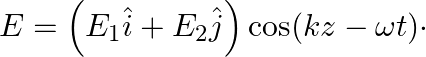 Choose the correct options from the following:
Choose the correct options from the following:
a) the associated magnetic field is given as 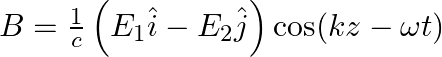
b) the associated magnetic field is given as 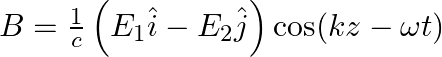
c) the given electromagnetic field is circularly polarised
d) the given electromagnetic waves is plane polarised
a) the associated magnetic field is given as $B=\frac{1}{c}\left(E_{1} \hat{i}-E_{2} \hat{j}\right) \cos (k z-\omega t)$ d) the given electromagnetic waves is plane polarised
An EM wave radiates outwards from a dipole antenna, with 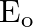 as the amplitude of its electric field vector. The electric field
as the amplitude of its electric field vector. The electric field 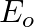 which transports significant energy from the source falls off as
which transports significant energy from the source falls off as
a) 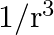
b) 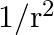
c) 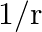
d) remains constant
c) $1 / \mathrm{r}$
The ratio of contributions made by the electric field and magnetic field components to the intensity of an EM wave is
a) 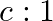
b) 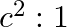
c) 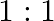
d) 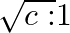
c) $1: 1$
If  and
and  represent electric and magnetic field vectors of the electromagnetic wave, the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic wave is along
represent electric and magnetic field vectors of the electromagnetic wave, the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic wave is along
a) 
b) 
c) 
d) 
d) $E \times B$
The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 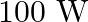 bulb at a
bulb at a 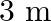 distance is E. The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from
distance is E. The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 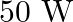 bulb at the same distance is
bulb at the same distance is
a) 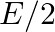
b) 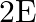
c) 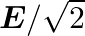
d) 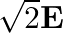
c) $\mathrm{E} / \sqrt{2}$
Light with an energy flux of 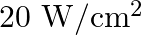 falls on a non-reflecting surface at normal incidence. If the surface has an area of
falls on a non-reflecting surface at normal incidence. If the surface has an area of 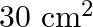 , the total momentum delivered during 30 minutes is
, the total momentum delivered during 30 minutes is
a) 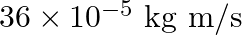
b) 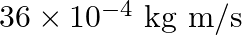
c) 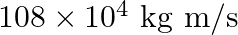
d) 
b) $36 \times 10^{-4} \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
A linearly polarized electromagnetic wave given as 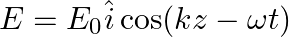 is incident normally on a perfectly reflecting infinite wall at
is incident normally on a perfectly reflecting infinite wall at  .
.
Assuming that the material of the wall is optically inactive, the reflected wave will be given as
a)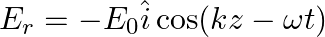
b)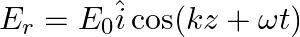
c)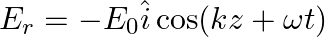
d)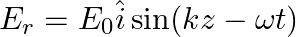
b)$E_{r}=E_{0} \hat{i} \cos (k z+\omega t)$
One requires 11eV of energy to dissociate a carbon monoxide molecule into carbon and oxygen atoms. The minimum frequency of the appropriate electromagnetic radiation to achieve the dissociation lies in
a) visible region
b) infrared region
c) ultraviolet region
d) microwave region
c) ultraviolet region
Both alternating current and direct current are measured in amperes. But how is the ampere defined for an alternating current?
The phenomenon called Joule's law of heating is used to determine the ampere for an alternating current. According to Joule's law of heating in a one-ohm resistance, AC is the current produced in a...
A multirange current meter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit shown in the figure. We want a current meter that can measure 10 mA, 100 mA, and 1 A using a galvanometer of resistance 10Ω and that produces maximum deflection for a current of 1 mA. Find S1, S2, and S3 that have to be used.
I1 is measured as = 10 mA = IGG = (I1 – IG)(S1 + S2 + S3) I2 is measured as = 100 mA = IG(G+S1)=(I2-IG)(S2-S3) I3 is measured as = 1 A = IG(G+S1+S2)=(I3-IG)(S3) S1 = 1 Ω S2 = 0.1 Ω S3 = 0.01...
Consider a circular current-carrying loop of radius R in the x-y plane with centre at the origin. Consider the line integral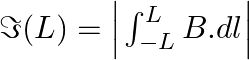 a) show that
a) show that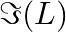 monotonically increases with L b) use an appropriate Amperian loop to that
monotonically increases with L b) use an appropriate Amperian loop to that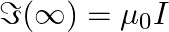 where I is the current in the wire c) verify directly the above result d) suppose we replace the circular coil by a square coil of sides R carrying the same current I. What can you say about
where I is the current in the wire c) verify directly the above result d) suppose we replace the circular coil by a square coil of sides R carrying the same current I. What can you say about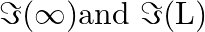
a) A circular current-carrying loop's magnetic field is given as \(\Im (L)=\int_{-L}^{+L}{Bdl}=2Bl\) It is a L function that increases monotonically. b) The Amperian loop is defined as follows:...
An electron enters with a velocity v = v0i into a cubical region in which there are uniform electric and magnetic fields. The orbit of the electron is found to spiral down inside the cube in the plane parallel to the x-y plane. Suggest a configuration of fields E and B that can lead to it.
The spiral route is formed by the fields E and B in their current configuration.
A current-carrying loop consists of 3 identical quarter circles of radius R, lying in the positive quadrants of the x-y, y-z, and z-x planes with their centres at the origin, joined together. Find the direction and magnitude of B at the origin.
The quarter's vector sum of the magnetic field at the origin is given as \({{\vec{B}}_{net}}=\frac{1}{4}\left( \frac{{{\mu }_{0}}I}{2R} \right)(\widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k})\)
Describe the motion of a charged particle in a cyclotron if the frequency of the radio frequency (rf) field were doubled.
The time period of the radio frequency is halved when the frequency is doubled, resulting in a half revolution of the charges.
Two identical current-carrying coaxial loops, carry current I in an opposite sense. A simple amperian loop passes through both of them once. Calling the loop as C, a)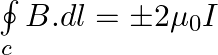 b) the value of
b) the value of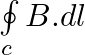 c) there may be a point on C where B and dl are perpendicular d) B vanishes everywhere on C
c) there may be a point on C where B and dl are perpendicular d) B vanishes everywhere on C
b) the value of \(\oint\limits_{c}{B.dl\) is independent of sense of C c) there may be a point on C where B and dl are perpendicular
The gyro-magnetic ratio of an electron in an H-atom, according to Bohr model is a) independent of which orbit it is in b) negative c) positive d) increases with the quantum number n
a) independent of which orbit it is in b) negative
In a cyclotron, a charged particle a) undergoes acceleration all the time b) speeds up between the dees because of the magnetic field c) speeds up in a dee d) slows down within a dee and speeds up between dees
a) undergoes acceleration all the time
An electron is projected with uniform velocity along the axis of a current-carrying long solenoid. Which of the following is true? a) the electron will be accelerated along the axis b) the electron path will be circular about the axis c) the electron will experience a force at 45o to the axis and hence execute a helical path d) the electron will continue to move with uniform velocity along the axis of the solenoid
d) the electron will continue to move with uniform velocity along the axis of the solenoid
A current circular loop of radius R is placed in the x-y plane with centre at the origin. Half of the lop with x > 0 is now bent so that it now lies in the y-z plane. a) the magnitude of magnetic moment now diminishes b) the magnetic moment does not change c) the magnitude of B at (0,0,z),z >> R increases d) the magnitude of B at (0,0,z),z >> R is unchanged
a) the magnitude of magnetic moment now diminishes
Two charged particles traverse identical helical paths in an opposite sense in a uniform magnetic field a) they have equal z-components of momenta b) they must have equal charges c) they necessarily represent a particle-antiparticle pair d) the charge to mass ratio satisfy: (e/m)1 + (e/m)2 = 0
d) the charge to mass ratio satisfy: (e/m)1 + (e/m)2 = 0
Three identical bar magnets are riveted together at the centre in the same plane as shown in the figure. This system is placed at rest in a slowly varying magnetic field. It is found that the system of magnets does not show any motion. The north-south poles of one magnet is shown in the figure. Determine the poles of the remaining two.
As the system is in equilibrium, the net torque and net force will be equal to zero.
A permanent magnet in the shape of a thin cylinder of length 10 cm has M = 106 A/m. Calculate the magnetisation current Im.
Intensity = 106 A/m l = 0.1 m M = IM/l IM = Ml = 105 A
The magnetic field of the earth can be modelled by that of a point dipole placed at the centre of the earth. The dipole axis makes an angle of 11.3o with the axis of the earth. At Mumbai, declination is nearly zero. Then, a) the declination varies between 11.3o W to 11.3o E b) the least declination is 0o c) the plane defined by dipole axis and the earth axis passes through Greenwich d) declination average over the earth must be always negative
a) The declination ranges from 11.3 degrees West to 11.3 degrees East.
A metallic ring of mass m and radius l (ring being horizontal) is falling under gravity in a region having a magnetic field. If z is the vertical direction, the z-component of the magnetic field is Bz = Bo (1+λ z). If R is the resistance of the ring and if the ring falls with a velocity v, find the energy lost in the resistance. If the ring has reached a constant velocity, use the conservation of energy to determine v in terms of m, B, λ and acceleration due to gravity g.
v = mgR/B02π2λ2l4
A circular coil expands radially in a region of the magnetic field and no electromotive force is produced in the coil. This can be because (a) the magnetic field is constant. (b) the magnetic field is in the same plane as the circular coil and it may or may not vary. (c) the magnetic field has a perpendicular (to the plane of the coil) component whose magnitude is decreasing suitably. (d) there is a constant magnetic field in the perpendicular (to the plane of the coil) direction.
(b) the magnetic field is in the same plane as the circular coil and it may or may not vary. (c) the magnetic field has a perpendicular (to the plane of the coil) component whose magnitude is...
There are two coils A and B. A current starts flowing in B as shown, when A is moved towards B and stops when A stops moving. The current in A is counterclockwise. B is kept stationary when A moves. We can infer that (a) there is a constant current in the clockwise direction in A. (b) there is a varying current in A. (c) there is no current in A. (d) there is a constant current in the counterclockwise direction in A.
(d) In A, there is a counterclockwise current that is constant.
A cylindrical bar magnet is rotated about its axis. A wire is connected from the axis and is made to touch the cylindrical surface through a contact. Then (a) a direct current flows in the ammeter A. (b) no current flows through the ammeter A. (c) an alternating sinusoidal current flows through the ammeter A with a time period T=2π/ω. (d) a time-varying non-sinusoidal current flows through the ammeter A.
(b) There is no current flowing through ammeter A.
