Cell theory was propounded by Schwann and Schleiden. Mathias Schleiden was a German botanist who concludes that cell arises from existing cells. Theodor Schwann was a zoologist and physiologist. The...
Comment on the cartwheel structure of centriole.
A centromere inside the nucleus is an organelle contains two cylindrical shaped structures which is called centrioles. A centrioles present in a centrosome which lie perpendicular to each other in...
How is the five-realm order worthwhile over the two realm arrangement?
solution: Two realm orders didn't recognize the prokaryotes and eukaryotes They didn't recognize unicellular and multicellular life forms They additionally didn't recognize...
Give a brief account of the counter current mechanism.
Solution: The counter-current system, which is active inside the kidney, is the most important adaptation for water conservation. There are two counter-current systems in the kidney: 1. The Henle...
Explain micturition.
Solution: The act of releasing urine is known as micturition. The micturition reflex is a neurological mechanism that causes micturition. The urine is briefly stored in the urinary bladder. When the...
Match the items of column I with those of column II:
Column I Column II (a) Ammonotelism (i) Birds (b) Bowman’s capsule (ii) Water reabsorption (c) Micturition (iii) Bony fish (d) Uricotelism (iv) Urinary bladder (d) ADH (v) Renal tubule Solution: (a)...
Draw a standard ECG and explain the different segments in it.
The electrocardiogram, or ECG, is a graphical representation of the heart cycle generated by the electrograph. A typical ECG is depicted in the diagram below: Each peak indicated by the letters ‘P'...
Define oxygen dissociation curve. Can you suggest any reason for its sigmoidal pattern?
Solution: The oxygen dissociation curve is a graph that shows the percentage of oxyhemoglobin saturation at different partial pressures of oxygen.The partial pressure of oxygen in the lungs is very...
What is the site of gaseous exchange in an insect?
Solution: The trachea is an insect's respiratory organ. Air enters the trachea through spiracles, which are small apertures. Spiracles can be seen on either side of the insect's abdomen. Each...
Explain the process of inspiration under normal conditions.
Solution: Inspiration is the process of allowing fresh air to enter the lungs. Inspiration occurs when the intrapulmonary pressure (pressure in the lungs) is lower than the atmospheric pressure. The...
Diffusion of gases occurs in the alveolar region only and not in the other parts of respiratory system. Why?
Solution: The alveoli present in the lungs are small air sacs that allow the fast exchange of gases. The alveolar membrane has a total thickness of less than a millimeter, and the outside surface of...
What are the major transport mechanisms for CO2? Explain.
Carbon dioxide is transported by plasma and red blood cells. This is due to their high water solubility.(1) Through plasma: 7% of $C{{O}_{2}}$ is transported in a dissolved state by the plasma....
What is the difference between cutaneous and pulmonary respiration?
Cutaneous respiration is an exchange of gases that is occurring from the skin while pulmonary respiration is the exchange of gases with the help of the lungs. We can see cutaneous respiration in...
Describe the internal structure of a dorsiventral leaf with the help of labelled diagram.
Solution: Dicots exhibit dorsiventral leaves. When examined, the vertical section of a dorsiventral leaf consists of three different parts, they are: Epidermis – It can be present on the adaxial...
What is periderm? How does periderm formation take place in the dicot stems?
Solution: Periderm:- A periderm is a group of cells through which the best of both kinds of tissues i.e., living and dead can be witnessed. They are the secondary...
How is the study of plant anatomy useful to us?
Solution: The anatomy of plants is beneficial to us in many ways- Plant anatomy helps us understand the concept behind the structure that is found in a plant. Under the anatomy, transverse...
Name the three basic tissue systems in the flowering plants. Give the tissue names under each system.
Solution: Following are the three basic tissue systems in the flowering plants. Epidermal tissue system Epidermis and epidermal appendages make up the epidermal tissue system. The epidermis is made...
What is stomatal apparatus? Explain the structure of stomata with a labelled diagram.
Solution: Stomata are the kidney/dumbell shaped cells present in the epidermal tissues. The tissues that get differentiated further, it is surrounding cells are called subsidiary cells. Stomata...
7. Why are xylem and phloem called complex tissues?
Solution: Complex tissues, such as xylem and phloem, are made up of multiple types of cells that work together to accomplish a specific job. Water is transported via xylem, whereas food is...
6. The transverse section of a plant material shows the following anatomical features – (a) the vascular bundles are conjoint, scattered and surrounded by a sclerenchymatous bundle sheaths. (b) phloem parenchyma is absent. What will you identify it as?
Solution: Monocot stem is used for the traversing section. Because the vascular bundles in monocot stems are distributed, this is the case. There is no phloem parenchyma to be identified.
Cut a transverse section of young stem of a plant from your school garden and observe it under the microscope. How would you ascertain whether it is a monocot stem or a dicot stem? Give reasons.
Solution: The following characteristics can be used to distinguish if it is a monocot or a dicot stem: Dicot stem Monocot stem Vascular bundles are arranged in a ring Vascular bundles are scattered...
Fill in the gaps:
(a) Ascending limb of Henle’s loop is ______ to water whereas the descending limb is _______ to it.
(b) Reabsorption of water from distal parts of the tubules is facilitated by hormone _______.
(c) Dialysis fluid contain all the constituents as in plasma except _______.
(d) A healthy adult human excretes (on an average) _______ gm of urea/day
Let's take a look at each assertion separately.(a) Water is impermeable to the ascending limb of Henle's loop but permeable to the descending limb.An ascending limb, a descending limb, and a hairpin...
4. Draw illustrations to bring out the anatomical difference between
(a) Monocot root and Dicot root (b) Monocot stem and Dicot stem. Solution: (a) Monocot root and Dicot rootMonocot root Dicot root (b) Monocot stem and Dicot stem Monocot stem Dicot...
3. Explain the process of secondary growth in the stems of woody angiosperms with the help of schematic diagrams. What is its significance?
Solution: In woody dicot roots, the primary xylem and phloem show the presence of an interfascicular cambium, which is created from the cells of the medullary rays linking the interfascicular...
2. Cork cambium forms tissues that form the cork. Do you agree with this statement? Explain.
Solution: Yes, the cork cambium produces tissues, which in turn produce cork. Another meristematic tissue known as phellogen or cork cambium grows in the cortical region of the stem as it grows in...
1. State the location and function of different types of meristems.
Solution: The location and function of different types of mersitems are as follows: MeristemLocationFunction1. Apical meristemRoot and shoot tipsForms primary tissue and increases the length of the...
Name the following:
(a) A chordate animal having flame cells as excretory structures
(b) Cortical portions projecting between the medullary pyramids in the human kidney
(c) A loop of capillary running parallel to the Henle’s loop.
Solution: The following are the one word answers- Amphioxus is a chordate animal with flame cells as excretory organs. Some animals have excretory structures called flame cells or...
What is the defining characteristic of a living organism
a. Growth b. Reproduction c. Response to external stimuli d. All the above Solution: Option (c) Response to external stimuli is the answer
What is the significance of the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) in kidney function?
Solution: The juxtaglomerular apparatus is a sensitive zone created by cellular changes in the distal convoluted tubule and the afferent arteriole at the point where they meet. The significance of...
15. Describe the arrangement of floral members in relation to their insertion on thalamus.
Solution: The arrangement of floral members in relation to their insertion on thalamus are of three types: The ovary is said to be superior in hypogynous flowers because the gynoecium is at the top...
14. Write the floral formula of a actinomorphic, bisexual, hypogynous flower with five united sepals, five free petals, five free stamens and two united carples with superior ovary and axile placentation.
Solution: The floral formula is as follows:
Define the term inflorescence. Explain the basis for the different types of inflorescence in flowering plants.
Solution: The arrangement of flowers on the floral axis is known as inflorescence. Depending on whether the apex is turned into a flower or continues to grow, there are two major forms of...
12. How do the various leaf modifications help plants?
Solution: Leaves fundamentally perform photosynthesis. But in some plants, leaves are modified to carry out different functionalities, mentioned as below: Tendrils: As with peas, tendrils aid in...
11. What is a flower? Describe the parts of a typical angiosperm flower
Solution: The flower is the reproductive component of an angiosperm. It's a modified shoot in which the apical meristem transforms into a floral meristem.On the swelling end of the pedicel or stalk...
10. Describe the various types of placentations found in flowering plants.
Solution: Various types of placentations found in flowering plants are as follows Marginal – The placenta forms a ridge that runs across the ovary's ventral suture, and ovules are carried on the...
Terrestrial animals are generally either ureotelic or uricotelic, not ammonotelic, why?
Solution: Ammonia is a highly poisonous nitrogenous waste. A substantial volume of water is required to minimize the toxicity of ammonia in the body. The bodies of terrestrial animals lack...
9. Take one flower each of the families Fabaceae and Solanaceae and write its semi-technical description. Also, draw their floral diagram after studying them.
Characters of Fabaceae • They are trees, shrubs, and herbs with nodules on their roots. • Erect or climber stems • Leaves are alternating, pinnately compound or simple, and pulvinate at the base;...
8. Describe modifications of stem with suitable examples
Solution: Modifications of stem: Food storage: Potato, ginger, and turmeric underground stems have been adapted to store food. They function as perennation organs, allowing them to survive in...
7. Draw the labelled diagram of the following: (i) gram seed (ii) V.S. of maize seed
Solution: (i) Gram seed (ii) V.S. of maize seed
What is meant by the term osmoregulation?
Solution: Osmoregulation is the process of checking the amount of water and salts in the body's cells to regulate the osmotic concentration.
6. Differentiate between
(a) Racemose and cymose inflorescence (b) Fibrous root and adventitious root (c) Apocarpous and syncarpous ovary Solution: The differences are as follows: (a) Racemose and cymose inflorescence...
5. Define the following terms:
(a) aestivation (b) placentation (c) actinomorphic (d) zygomorphic (e) superior ovary (f) perigynous flower (g) epipetalous stamen Solution: Aestivation is the arrangement of sepals or petals in a...
4. Explain with suitable examples the different types of phyllotaxy.
Solution: Phyllotaxy is the pattern of leaf arrangement on a stem or branch. A single leaf emerges at each node alternately in China rose, mustard, and sunflower plants, for example. Phyllotaxy is...
Describe the role of the liver, lungs, and skin in excretion.
Solution: The following is the role of the liver, lungs, and skin in the excretion process: Liver- The liver is the primary site for the elimination of inactive steroid hormones, cholesterol,...
3. How is a pinnately compound leaf different from a palmately compound leaf?
Solution: The differences are as follows: Pinnately compound leafPalmately compound leafOn a common axis, a large number of leaflets are found.Several leaflets are attached to a common...
2. Justify the following statements on the basis of external features:
(i) Underground parts of a plant are not always roots. (ii) The flower is a modified shoot. Solution: (i) Stems of a few plants, such as ginger, remain underground for vegetative reproduction and...
1. What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the:
(a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Solution: Roots change their architecture, which might include their size, shape, or even regular functioning, in order to perform secondary functions...
Indicate whether the following statements are true or false:
(a) Micturition is carried out by a reflex.
(b) ADH helps in water elimination, making the urine hypotonic.
(c) Protein-free fluid is filtered from blood plasma into the Bowman’s capsule.
(d) Henle’s loop plays an important role in concentrating the urine.
(e) Glucose is actively reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule.
Solution: The following statements are explained as- (a) Micturition is a reflex reaction of passing urine. The stretch receptors in the bladder wall are stimulated by distension, and reflex action...
Explain the autoregulatory mechanism of GFR.
Solution: The auto regulating mechanism in the kidneys regulates the glomerular filtration rate. It is mediated by the juxtaglomerular apparatus, a microscopic structure located between the...
Define Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR).
Solution: The glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is the quantity of filtrate produced every minute by both kidneys (nephrons). A healthy person's GFR is around 125 milliliters per minute. Water and...
Explain heart sounds.
Solution: Every cardiac cycle produces two sounds: lub and dub, which are produced by a heartbeat. The sound is produced in a specific order, in time with each heartbeat. The initial sound is a...
Define a cardiac cycle and the cardiac output.
Solution: Cardiac cycle: Blood circulates in the heart due to the alternate contraction and relaxation of the chambers of the heart.Diastole refers to the relaxation or expansion phase, whereas...
What is the significance of atrio-ventricular node and atrio-ventricular bundle in the functioning of the heart?
Solution: The atrioventricular bundle (AV) sends the cardiac impulse from the AV node to the ventricle walls, whereas the atrioventricular node (AVN) sends the impulse from the SA node. The action...
Sino-atrial node is called the pacemaker of our heart. Why?
Solution: The sinoatrial or sinus node (SAN) is a specialized bundle of neurons that generates action potentials and generates a cardiac impulse without any external stimulation, making it auto...
Why do we call our heart myogenic?
Solution: The terms ‘myo' and ‘genic' refer to muscle and genesis, respectively. The sino-atrial or sinus node (SA node) is capable of generating an impulse that extends across the heart wall,...
Describe the evolutionary change in the pattern of heart among the vertebrates.
Solution: Through rigorous investigation, an evolutionary alteration in the heart pattern among vertebrates have been discovered. Vertebrates have a chambered heart that is muscular. They've...
Write the differences between:
(a) Blood and Lymph
(b) Open and Closed system of circulation
(c) Systole and Diastole
(d) P-wave and T-wave
Solution: The differences are as follows: (a) Blood and Lymph LymphBloodIt's a type of white tissue fluid.It's a liquid connective tissue that's red in color.The lymph vessels carry lymph.Blood...
What is meant by double circulation? What is its significance?
Solution: The term "double circulation" refers to the fact that blood flows twice in the heart. The atrioventricular septum divides the heart into four chambers, the right and left halves, allowing...
What is the difference between lymph and blood?
Solution: Blood is a circulatory fluid that transports oxygen, nutrients, and metabolic wastes throughout the animal body. The lymphatic system, which consists of lymph nodes and lymph veins, is...
Why do we consider blood as a connective tissue?
Solution: Blood is a connective tissue that is generated from the mesoderm and contains plasma, an extracellular matrix. It is a plentiful and extensively dispersed tissue throughout the body....
Match Column I with Column II:
Column IColumn II(a) Eosinophils(i) Coagulation(b) RBC(ii) Universal Recipient(c) AB Group(iii) Resist Infections(d) Platelets(iv) Contraction of Heart(e) Systole(v) Gas transport Solution: The...
What is the importance of plasma proteins?
Solution: Plasma is responsible for blood's fluid-like consistency. It's the straw-colored liquid that aids in the transportation of food, waste, carbon dioxide, and other salts. Plasma makes up...
Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them.
Solution: The following are the components of blood's produced elements: • Erythrocytes, also known as red blood cells, are oxygen-carrying cells that also contain the pigment hemoglobin. Hemoglobin...
What is Tidal volume? Find out the Tidal volume (approximate value) for a healthy human in an hour.
Solution: The volume of air exhaled or inhaled during typical respiration is referred to as tidal volume (TV). For a healthy person, the tidal volume is roughly 500ml. A healthy person may exhale or...
Distinguish between
(a) IRV and ERV
(b) Inspiratory capacity and Expiratory capacity.
(c) Vital capacity and Total lung capacity.
Solution: The differences between all the following sets are as follows: (a) IRV and ERV IRV (Inspiratory reserve volume)ERV (Expiratory reserve volume)It's the amount of air that a person can...
Have you heard about hypoxia? Try to gather information about it, and discuss with your friends.
Solution: Hypoxia is a situation in which the supply of oxygen to the lungs is insufficient or reduced. Several external factors, such as a decrease in pO2, insufficient oxygen, and so on, induce...
What happens to the respiratory process in a man going up a hill?
Solution: The altitude rises as we go higher. The concentration of atmospheric oxygen is lower at this height, implying that the partial pressure of oxygen decreases. The lack of oxygen in this...
What is the effect of 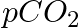 on oxygen transport?
on oxygen transport?
Solution: In the oxygen transport mechanism, $pC{{O}_{2}}$ plays a critical function. Oxyhaemoglobin is formed when low $pC{{O}_{2}}$ levels in the alveoli cause oxygen to bind to hemoglobin and...
What will be the pO2 and pCO2 in the atmospheric air compared to those in the alveolar air?
(i) pO2 lesser, pCO2 higher
(ii) pO2 higher, pCO2 lesser
(iii) pO2 higher, pCO2 higher
(iv) pO2 lesser, pCO2 lesser
Solution: When comparing the pO2 and pCO2 in atmospheric air to those in alveolar air, (ii) pO2 will be higher and pCO2 will be lower. Each gas in a combination exerts a pressure known as partial...
State the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal breathing.
Solution: The functional residual capacity can be used to express it (FRC). The volume of air that remains in the lungs following a normal expiration is referred to as the FRC. The expiratory...
Define vital capacity. What is its significance?
Solution: The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration is known as vital capacity. It is equal to the sum of inspiratory reserve volume (IRV), tidal volume (TV), and...
For taxonomic category of ‘family’ which of the following ‘suffixes’ used.
a. – Ae b. – Onae c. – Aceae d. – Ales Solution: Option (c) Aceae is the answer
Distinguish anaphase of mitosis from anaphase I of meiosis.
Solution: The differences are as follows: Anaphase of mitosis Anaphase I of meiosis The chromatids divide and the centromere separates. Sister chromatids remain connected at their centromeres...
Describe the following:
(a) synapsis (b) bivalent (c) chiasmata
Draw a diagram to illustrate your answer.
Solution: a) Synapsis — During Zygotene of prophase-I of meiosis, homologous chromosomes link together. Synapsis is the term for this couple. b) A bivalent or tetrad is a pair of synapsed homologous...
Explain pressure flow hypothesis of translocation of sugars in plants.
Solution: In plants, food is constantly prepared in the form of glucose in the mesophyll cells of the leaves. The prepared meal is transformed to sucrose, which is then transported to the phloem's...
(a) With the help of well-labelled diagrams, describe the process of plasmolysis in plants, giving appropriate examples.
(b) Explain what will happen to a plant cell if it is kept in a solution having higher water potential.
Solution: If a plant is kept in a solution having higher water potential, the following are the things that can happen- a) When water leaves a plant's cell and the cell membrane, the cell shrinks...
What are the steps involved in the formation of a root nodule?
Solution: The following steps are involved in the formation of nodules: • Rhizobia colonize roots and attach themselves to epidermal and root hair cells. • Bacteria infect the root hair, causing it...
What are the conditions necessary for the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen by Rhizobium? What is their role in N2 -fixation?
Solution: For Rhizobium to fix nitrogen, the following conditions must be met. The production of root nodules requires a symbiotic connection between Rhizobium and roots.The requirement for a...
Analyse the events during every stage of cell cycle and notice how the following two parameters change
(i) number of chromosomes (N) per cell
(ii) amount of DNA content (C) per cell
Solution: Yes, DNA replication can occur throughout the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Each chromosome is made up of one chromatid, and the number of chromosomes remains constant. The chromosome is...
Can there be DNA replication without cell division?
Solution: Yes, DNA replication can occur without the need for cell division. DNA replication is required to prepare cells for cell division. Cell division is the next logical stage after cell...
Can there be mitosis without DNA replication in ‘S’ phase?
Solution: DNA synthesis or replication occurs during the S phase. For cell division to take place, DNA replication is required. Cell division is impossible without DNA replication.
Discuss with your teacher about
(i) haploid insects and lower plants where cell-division occurs.
(ii) some haploid cells in higher plants where cell-division does not occur.
Solution: (i)Honey bee drones are haploid insects that undergo cell division, and lower plants include Spirogyra, Chlamydomonas, and Pteridophytes. They create haploid gametes by mitosis rather than...
What is the significance of meiosis?
Solution: Significances of Meiosis: • It maintains the number of chromosomes in each species over generations. • Increases the genetic variation of an organism's population from generation to...
List the main differences between mitosis and meiosis.
Solution: The differences are as follows: MitosisMeiosisOccurs in somatic cellsOccurs in germ cellsThe number of chromosomes in the daughter cell is the same as in the parent cell.In comparison to...
Find examples where the four daughter cells from meiosis are equal in size and where they are found unequal in size.
Solution: Four daughter cells are generated during meiosis during the generation of male gametes (sperms) in human beings. During meiosis, the female gamete (ovum) divides into four daughter cells,...
How does cytokinesis in plant cells differ from that in animal cells?
Solution: Plant cytokinesisAnimals cytokinesisCell plate development causes this to happen.It occurs as a result of cleavage known as cell furrowing.The cell plate moves to the centre and expands...
Name the stage of cell cycle at which one of the following events occur:
(i) Chromosomes are moved to spindle equator.
(ii) Centromere splits and chromatids separate.
(iii) Pairing between homologous chromosomes takes place.
(iv) Crossing over between homologous chromosomes takes place.
Solution: (i)In Metaphase, chromosomes are transported to the spindle equator. ii) In Anaphase, centrosomes split and chromatids separate. iii) In meiosis, the pairing of homologous chromosomes...
Why is mitosis called equational division?
Solution: Since the number of chromosomes in the parent and progeny cells is the same, mitosis is known as equational division.
What is Go (quiescent phase) of cell cycle?
Solution: In mature animals, certain cells will not divide, and many others will divide only when it is necessary to replace cells that have been lost due to injury or cell death. These cells depart...
Describe the events taking place during interphase.
Solution: The following are the events that occur during interphase: • G1 phase (Gap 1) - The cell is metabolically active at this time. It develops and prepares DNA for replication. • S phase...
Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
Solution: The difference between karyokinesis and cytokinesis is- CytokinesisKaryokinesisDuring the M phase of the cell cycle, the cytoplasm divides into two cells.The M phase of the cell cycle...
What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell?
Solution: A mammalian cell's average cell cycle lasts 24 hours.
What causes the opening and closing of guard cells of stomata during transpiration?
Solution: The change in the turgidity of the guard cells is one of the factors that causes the stomata to open and close. The stomatal hole opens when guard cells become turgid, causing their thin...
Explain why xylem transport is unidirectional and phloem transport bi-directional.
Solution: When water is absorbed by roots through the xylem, it only travels upward. As a result, water transport is one-way. The phloem tissue transports the food. Food is created in the leaves and...
Discuss the factors responsible for ascent of xylem sap in plants.
Solution: The following are the factors that cause xylem sap to rise in plants: Mutual attraction between water molecules is referred to as cohesion. Water molecules are drawn to the polar surface...
Describe transpiration pull model of water transport in plants. What are the factors influencing transpiration? How is it useful to plants?
Solution: The cohesion-tension model of water transport, which is formed by the loss of water or the process of transpiration from the pores of stomata of leaves, helps water rise in tall trees. The...
What role does root pressure play in water movement in plants?
Solution: Root pressure is developed in plant roots due to active nutrient absorption from the soil. Water (together with minerals) increases the pressure in the xylem when nutrients are actively...
How is the mycorrhizal association helpful in absorption of water and minerals in plants?
Solution: Mycorrhizal hyphae have a huge surface area, which aids in the absorption of water and minerals. As a result, plants' relationship with Mycorrhiza aids in the absorption of water and...
What happens when a pressure greater than the atmospheric pressure is applied to pure water or a solution?
Solution: When pure water or a solution is subjected to a pressure greater than atmospheric pressure, its water potential increases.
Briefly describe water potential. What are the factors affecting it?
Solution: The tendency of water to migrate from one location to another due to osmosis, gravity, and mechanical pressure is known as water potential. In other words, it is the difference between the...
Differentiate between the following:
(a) Diffusion and Osmosis
(b) Transpiration and Evaporation
(c) Osmotic Pressure and Osmotic Potential
(d) Imbibition and Diffusion
(e) Apoplast and Symplast pathways of movement of water in plants
(f) Guttation and Transpiration
Solution: The diffusion between all the following sets are- a) Diffusion and Osmosis DiffusionOsmosisIt is a form of passive transport in which a chemical moves from an area of higher concentration...
Explain why pure water has the maximum water potential.
Solution: Pure water has the greatest water potential since it has its own kinetic energy and is constantly in random motion. When solutes are added to pure water, the kinetic energy of the water...
Describe the role played by protein pumps during active transport in plants.
Solution: Protein pumps transport molecules through the cell membrane with the use of energy. These protein pumps transport the drug from a low-concentration area to a high-concentration area. They...
What are porins? What role do they play in diffusion?
Solution: Porins are proteins found in the outer membranes of plastids, mitochondria, and some bacteria that produce huge pores. Molecules as small as small proteins can pass through the huge holes....
What are the factors affecting the rate of diffusion?
Solution: Factors affecting the rate of diffusion are: Concentration gradient Permeability of the membrane separating them are all factors that influence the rate of diffusion. Temperature \s•...
Which of the following statements are true? If false, correct them:
(a) Boron deficiency leads to stout axis.
(b) Every mineral element that is present in a cell is needed by the cell.
(c) Nitrogen as a nutrient element is highly immobile in the plants.
(d) It is very easy to establish the essentiality of micronutrients because they are required only in trace quantities.
Solution: a) True b) False: Every mineral element found in a cell is not required by the cell. c) False- Nitrogen is a very mobile nutrient in plants. d) False- Since micronutrients are only...
Why is it that in certain plants deficiency symptoms appear first in younger parts of the plant while in others they do so in mature organs?
Solution: The emergence of symptoms is determined by the mobility of a missing element. Symptoms develop in juvenile portions of the plant if the deficient element is relatively stationary, while...
Name at least five different deficiency symptoms in plants. Describe them and correlate them with the concerned mineral deficiency.
Solution: Chlorosis is a loss of chlorophyll that causes the leaves to turn yellow. It is brought on by a lack of N, K, Mg, S, Fe, Mn, Zn, and Mo. Necrosis is the death of leaf tissue caused by a...
Explain with examples: macronutrients, micronutrients, beneficial nutrients, toxic elements and essential elements.
Solution: Macronutrients are nutrients found in plant tissues at concentrations of more than 10 mole kg-1 of dry matter. Plant growth necessitates a huge amount of them. Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen,...
Why is purification of water and nutrient salts so important in studies involving mineral nutrition using hydroponics?
Solution: Hydroponics is a way of growing plants without soil in a nutrient solution. Impure water has many contaminants in the form of soluble minerals that are dissolved in it. These contaminants...
‘All elements that are present in a plant need not be essential to its survival’. Comment
Solution: No, only around 17 of the 105 elements taken by plants are required for plant development and survival.
Organise a discussion in your class on the topic – Are viruses living or nonliving?
Solution: Characters who are non-living have the following features There isn't any cellular structure.Like crystals, they can be preserved in bottles.No energy storage or liberation systems...
Give a brief account of viruses with respect to their structure and nature of genetic material. Also, name four common viral diseases.
Solution: Viruses are infectious organisms that, when located outside the host cell, solidify in structure. The genetic material is either DNA or RNA (but never both), and it is found inside the...
What are the characteristic features of Euglenoids?
Solution: Eugenoids have the following characteristics: no cell wall.Their bodies are flexible due to a protein-rich coating known as a pellicle.There are two flagella of differing lengths. In...
Give a comparative account of the classes of Kingdom Fungi under the following:
(i) mode of nutrition (ii) mode of reproduction
Solution: Fungi are eukaryotic heterotrophic organisms. The kingdom fungus includes black dots on stale bread, yeast (which is used to make bread and beer), white spots on mustard leaves, and...
What do the terms phycobiont and mycobiont signify?
Solution: Fungi and algae form a symbiotic relationship in lichens. A phycobiont is a type of algae that is also seen in mycobiont fungi. Mycobiont provides structural protection for algae against...
Plants are autotrophic. Can you think of some plants that are partially heterotrophic?
Solution: These organisms are green and autotrophic, yet they hunt on and digest minute components for their nitrogen supply. Insectivores and carnivorous plants are somewhat heterotrophic....
State two economically important uses of:
(a) heterotrophic bacteria
(b) archaebacteria
Solution: The two economically important uses of- a) Vitamins, medicines, cheese, and curd are all made using heterotrophic bacteria. They aid in nitrogen fixation and the production of humus. b)...
Describe briefly the four major groups of Protozoa.
Solution: The following are the four primary groups of Protozoa: Protozoa of the amoeboid class: They live in aquatic habitats and use pseudopodia to move and catch their prey. Flagellated...
How are viroids different from viruses?
Solution: The difference between viroids from viruses- (i) Viroids have single-stranded RNA without a protein coat, whereas viruses contain single-stranded or double-stranded RNA associated with a...
Find out what do the terms ‘algal bloom’ and ‘red-tides’ signify.
Solution: In contaminated water, algal blooms can be discovered. Algae overgrowth, particularly blue-green algae, causes them (cyanobacteria). Their expansion pollutes the water supply. They breathe...
What is the nature of cell walls in diatoms?
Solution: Cell walls of diatoms are unbreakable and embedded with silica, which imparts distinctive patterns to the walls. These diatoms deposit a lot of cell wall deposits in their habitat, which...
Discuss how classification systems have undergone several changes over a period of time.
Solution: The scientific classification was initially introduced by Aristotle. He classified plants into trees, shrubs, and herbs based on simple physical characteristics. He separated the animals...
