Solution:
Elements of group 14 (a) exhibit oxidation state of 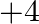 only (b) exhibit oxidation state of
only (b) exhibit oxidation state of 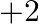 and
and 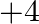 (c) form
(c) form 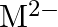 and
and 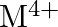 ion (d) form
ion (d) form 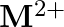 and
and 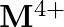 ions
ions
Solution: (b) Group 14 components have 4 valence electrons. Thus, bunch oxidation status is $+4$. In any case, the lower oxidation state turns out to be progressively steady because of the inactive...
An aqueous solution of borax is 

Solution: (b) Borax is a strong base salt (NaOH) and a feeble corrosive $\left(\mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{BO}_{3}\right)$. In this way, it is essential thing in nature.
Give one method for industrial preparation and one for laboratory preparation of CO and 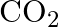 each.
each.
Solution: Carbon dioxide CO2 can be ready in the lab through the activity of weaken hydrochloric corrosive on calcium carbonate. Their response is as per the following: CO2 is industrially ready by...
Write balanced equations for: 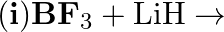 (ii)
(ii) 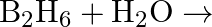 (iii)
(iii) 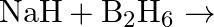 (iv)
(iv) 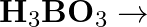 (v)
(v) 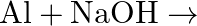 (vi)
(vi) 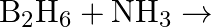
Solution: The balanced equations are as follow:
A certain salt  gives the following results. (i) Its aqueous solution is alkaline to litmus. (ii) It swells up to a glassy material
gives the following results. (i) Its aqueous solution is alkaline to litmus. (ii) It swells up to a glassy material 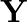 on strong heating. (iii) When conc.
on strong heating. (iii) When conc. 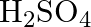 is added to a hot solution of
is added to a hot solution of 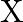 , a white crystal of an acid
, a white crystal of an acid 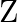 separates out Write equations for all the above reactions and identify X,
separates out Write equations for all the above reactions and identify X, 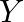 , and
, and 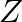 .
.
Solution: The salt given to litmus is antacid. $X$ is, subsequently, a salt with a solid base, and a feeble corrosive. When $X$ is warmed unnecessarily, it additionally enlarges to frame material...
When metal 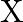 is treated with sodium hydroxide, a white precipitate (A) is obtained, which is soluble in excess of
is treated with sodium hydroxide, a white precipitate (A) is obtained, which is soluble in excess of 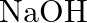 to give soluble complex (B). Compound (A) is soluble in dilute HCI to form compound (C). The compound (A) when heated strongly gives (D), which is used to extract the metal. Identify (X), (A), (B), (C) and (D). Write suitable equations to support their identities.
to give soluble complex (B). Compound (A) is soluble in dilute HCI to form compound (C). The compound (A) when heated strongly gives (D), which is used to extract the metal. Identify (X), (A), (B), (C) and (D). Write suitable equations to support their identities.
Solution: The given metal $X$ gives sodium hydroxide to a white accelerate, and the encourage breaks up surpassing sodium hydroxide. $X$ must, consequently, be made of aluminum. The acquired white...
(a) Classify the following oxides as neutral, acidic, basic or amphoteric. 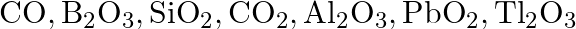 (B) Write suitable equations to show their nature.
(B) Write suitable equations to show their nature.
Solution: $\rightarrow$ CO $=$ Neutral $\rightarrow \mathrm{B}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}=$ Acidic Being acidic, it responds with bases to frame salts. It responds with $\mathrm{NaOH}$ to frame sodium...
What are allotropes? Sketch the structure of two allotropes of carbon namely diamond and graphite. What is the impact of structure on the physical properties of two allotropes?
Solution: Allotropy is the presence of a component in more than one structure, having diverse actual properties however similar substance properties. Diamond's solid 3-D construction makes it a...
How would you explain the lower atomic radius of Ga as compared to Al?
Solution: A tomic sweep (in pm) Aluminum Gallium In spite of the fact that Ga has more than one shell than Al, it is more modest in size than Al. This is on the grounds that the $3 \mathrm{~d}$...
Explain why is there a phenomenal decrease in ionization enthalpy from carbon to silicon?
Solution: Carbon ionizing enthalpy (the primary component in bunch 14 ) is exceptionally high $(1086 \mathrm{~kJ}/\mathrm{mol})$. That is normal on account of its little size. Nonetheless, there is...
Explain the following reactions (a) Silicon is heated with methyl chloride at high temperature in the presence of copper; (b) Silicon dioxide is treated with hydrogen fluoride; (c) CO is heated with ZnO; (d) Hydrated alumina is treated with aqueous 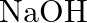 solution.
solution.
Solution: (a) Silicon is warmed with methyl chloride at high temperature within the sight of copper A class of organosilicon polymers called methyl-subbed chlorosilane $\mathrm{MeSiCl}_{3},...
What happens when (a) Borax is heated strongly (b) Boric acid is added to water (c) Aluminum is treated with dilute NaOH (d) 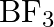 is reacted with ammonia?
is reacted with ammonia?
Solution: (a) Borax is warmed firmly Borax goes through different changes when warmed. It is losing atoms and expands of water right away. Then, at that point, it turns into a clear fluid, which...
Explain the structures of diborane and boric acid.
Solution: (a) Diborane $\mathrm{B}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{6}$ is a compound that does not have an electron. $\mathrm{B}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{6}$ just has 12 electrons $-6 \mathrm{e}^{-}$of $6 \mathrm{H}$...
Aluminium trifluoride is insoluble in anhydrous HF but dissolves when NaF is added. It precipitates out of the resulting solution when gaseous 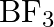 (boron trifluoride) is bubbled through. Give reasons.
(boron trifluoride) is bubbled through. Give reasons.
Solution: Hydrogen fluoride is a covalent compound with an exceptionally solid intermolecular clinging to hydrogen. Along these lines, it doesn't give particles and doesn't break up aluminum...
If B-CI bond has a dipole moment, explain why 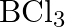 molecule has zero dipole moment.
molecule has zero dipole moment.
Solution: The $B-C l$ bond is normally polar as a result of the distinction in the electronegativities of $\mathrm{Cl}$ and $B$. However the particle of $\mathrm{BCl}_{3}$ is non-polar. That is on...
Suggest reasons why the B-F bond lengths in 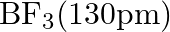 and
and 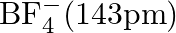 differ.
differ.
Solution; In $\mathrm{BF}_{3}$, the length of the $\mathrm{B}-\mathrm{F}$ bond is more limited than that of the $\mathrm{B}-\mathrm{F}$ bond in $\mathrm{BF}_{4}^{-} \cdot \mathrm{BF}_{3}$ is an...
Rationalize the given statements and give chemical reactions: – Lead (II) chloride reacts with 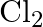 to give
to give 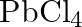 . – Lead (IV) chloride is highly unstable towards heat. – Lead is known not to form an iodide,
. – Lead (IV) chloride is highly unstable towards heat. – Lead is known not to form an iodide, 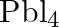 .
.
Solution: - Lead is an individual from bunch 14 of the occasional table. The two oxidation situations with bunch shows are $+2$ and $+4$. The $+2$ oxidation state turns out to be more steady when...
Explain the difference in properties of diamond and graphite on the basis of their structures.
Solution: Diamond: 1. It has a glasslike grid 2. In precious stone, every carbon molecule is sp3 hybridized and attached to four other carbon particles through a sigma bond. 3. It has an unbending...
What is the state of hybridisation of carbon in (a) 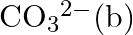 diamond (c) graphite?
diamond (c) graphite?
Solution: The condition of hybridization of carbon in: (a) $C O_{3}^{2-}$ c in $\mathrm{CO}_{3}^{2-}$ is sp $^{2}$ hybridized and is attached to 3 oxygen iotas. (b) Diamond Every precious stone...
Write the resonance structures of 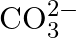 and
and 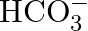 .
.
Solution: For $C O_{3}^{2-}$ There are just 2 resounding designs for the bicarbonate particle. For $\mathrm{HCO}_{3}^{-}$
Write reactions to justify amphoteric nature of aluminium
Solution: Amphoteric substances will be substances that display both acidic and essential characteristics. Since aluminum breaks up in the two acids and bases, it is said to have an amphoteric...
Describe the shapes of 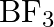 and
and 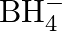 . Assign the hybridisation of boron in these species
. Assign the hybridisation of boron in these species
Solution: (I) $\mathbf{B} \boldsymbol{F}_{3}$ Boron will in general shape monomeric covalent halides in view of its little size and high electronegativity. These halides of boron generally have a...
Explain what happens when boric acid is heated .
Solution: After warming orthoboric corrosive at a temperature of $370 \mathrm{~K}$ or above, it is changed over into metaboric corrosive and, upon additional warming, yields boric oxide...
Is boric acid a protic acid? Explain.
Solution: Boric corrosive is a powerless monobasic corrosive which acts as a Lewis corrosive. In this way, it's anything but a protic corrosive. $\mathrm{B}(\mathrm{OH})_{3}+2 \mathrm{HOH}...
Consider the compounds, 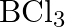 and
and 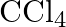 . How will they behave with water? Justify.
. How will they behave with water? Justify.
Solution: Since it is a Lewis corrosive, $\mathrm{BCl}_{3}$ promptly goes through hydrolysis to frame boric corrosive. $\mathrm{BCl}_{3}+3 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow 3...
Why does boron trifluoride behave as a Lewis acid?
Solution: The electronic arrangement of boron is $n s^{2} n p^{1}$. It contains 3 electrons in its valence shell. In this way, it can frame just 3 covalent bonds which imply that there are just 6...
How can you explain the higher stability of 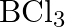 as compared to
as compared to 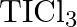 ?
?
Solution: Thallium and boron have a place with bunch 13 of the intermittent table and $+1$ oxidation state turns out to be more steady as we drop down the gathering. Boron is more steady than...
Discuss the pattern of variation in the oxidation states of (i) 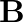 to
to 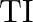 (ii)
(ii)  to
to 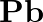
Solution: (I) $B$ to $\mathrm{TI}$ Gathering 13 components have their electronic design of $\mathrm{ns}^{2} \mathrm{np}^{1}$ and the oxidation state displayed by these components ought to be 3 ....
Depict the galvanic cell in which the reaction is:  Further show: (i) which of the electrode is negatively charged? (ii) the carriers of the current in the cell. (iii) individual reaction at each electrode.
Further show: (i) which of the electrode is negatively charged? (ii) the carriers of the current in the cell. (iii) individual reaction at each electrode.
Solution: The galvanic cell relating to the given redox response can be displayed as: $\mathrm{Zn}\left|Z n_{(a q)}^{2+} \| A g_{(a q)}^{+}\right| \mathrm{Ag}$ (I) Zn anode is contrarily charged on...
Given the standard electrode potentials, 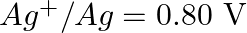
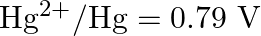
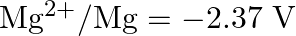
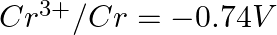 Arrange these metals in their increasing order of reducing power.
Arrange these metals in their increasing order of reducing power.
Solution: The diminishing specialist is more grounded as the terminal potential declines. Subsequently, the expanding request of the lessening force of the given metals is as given underneath: Ag...
Arrange the given metals in the order in which they displace each other from the solution of their salts. Al, Fe, Cu, Zn, Mg
Solution: A metal with more grounded diminishing force uproots one more metal with more vulnerable lessening power from its answer of salt. The request for the expanding diminishing force of the...
Predict the products of electrolysis in each of the following: (i) An aqueous solution of 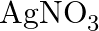 with silver electrodes (ii) An aqueous solution
with silver electrodes (ii) An aqueous solution 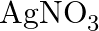 with platinum electrodes (iii) A dilute solution of
with platinum electrodes (iii) A dilute solution of 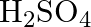 with platinum electrodes (iv) An aqueous solution of
with platinum electrodes (iv) An aqueous solution of 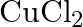 with platinum electrodes.
with platinum electrodes.
Solution: (I) In fluid arrangement, AgNO3 ionizes to give Ag+(aq) and NO3–(aq) particles. \[AgN03\left( aq \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }Ag+\left( aq \right)\text{ }+\text{ }NO3\left( aq...
Using the standard electrode potentials given in Table 8.1, predict if the reaction between the following is feasible: (a) 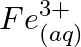 and
and 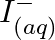 (b)
(b) 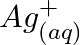 and
and 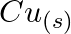 (c)
(c) 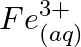 and
and 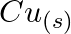 (d)
(d) 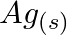 and
and 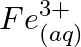 (e)
(e) 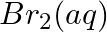 and
and 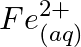
Solution: (a) $F e_{(a q)}^{3+}$ and $I_{(a q)}^{-}$ $2 F e_{(a q)}^{3+}+2 I_{(a q)}^{-} \rightarrow 2 F e_{(a q)}^{2+}+I_{2(s)}$ Oxidation half response: $2 I_{(a q)}^{-} \rightarrow I_{2}(s)+2...
In Ostwald’s process for the manufacture of nitric acid, the first step involves the oxidation of ammonia gas by oxygen gas to give nitric oxide gas and steam. What is the maximum weight of nitric oxide that can be obtained starting only with 10.00 g. of ammonia and 20.00 g of oxygen?
Solution: The reasonable response is as given underneath: $4 \mathrm{NH}_{3(g)}+5 \mathrm{O}_{2}(g) \rightarrow 4 \mathrm{NO}_{(g)}+6 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(g)}$ $4 N H_{3}=4 \times 17...
Refer to the periodic table given in your book and now answer the following questions: (a) Select the possible non – metals that can show disproportionation reaction? (b) Select three metals that show disproportionation reaction?
Solution: One of the responding components consistently has a component that can exist in somewhere around 3 oxidation numbers. (I) The non - metals which can show disproportionation responses are...
Chlorine is used to purify drinking water. Excess of chlorine is harmful. The excess of chlorine is removed by treating with sulphur dioxide. Present a balanced equation for this redox change taking place in water.
Solution: The redox response is as given beneath: Cl2(s)+SO2(aq)+H2O(l)→Cl(aq)-+SO4(aq)2- The oxidation half response: SO2(aq)→SO4(aq)2- Add 2 electrons to adjust the oxidation no. :...
The 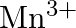 ion is unstable in solution and undergoes disproportionation to give
ion is unstable in solution and undergoes disproportionation to give 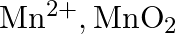 , and
, and 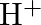 ion. Write a balanced ionic equation for the reaction.
ion. Write a balanced ionic equation for the reaction.
Solution: The response is as given beneath: $\mathrm{Mn}_{(a q)}^{3+} \rightarrow \mathrm{Mn}_{(a q)}^{2+}+\mathrm{MnO}_{2(s)}+\mathrm{H}_{(a q)}^{+}$ The oxidation half response: $\mathrm{Mn}_{(a...
What sorts of informations can you draw from the following reaction? 
Solution: The oxidation no. of $\mathrm{C}$ in $(C N)_{2}, C N^{-}$and $C N O^{-}$are $+3,+2$ and $+4$ separately. Let the oxidation no. of $\mathrm{C}$ be $\mathrm{y}$. $(C N)_{2}$ $2(y-3)=0$ Along...
Balance the following equations in basic medium by ion-electron method and oxidation number methods and identify the oxidising agent and the reducing agent. (a) 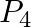 (s)
(s) 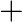
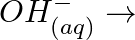
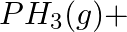
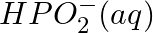 (b)
(b) 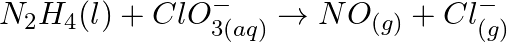 (c)
(c) 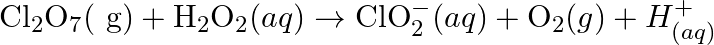
Solution:
Balance the following redox reactions by ion – electron method : (a) 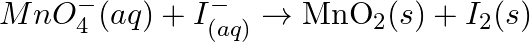 (Basic medium) (b)
(Basic medium) (b) 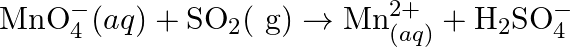 (Acidic medium) (c)
(Acidic medium) (c) 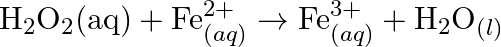 (Acidic medium) (d)
(Acidic medium) (d) 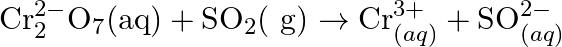 (Acidic medium)
(Acidic medium)
Solution: (a) $M n O_{4}^{-}(a q)+I_{(a q)}^{-} \rightarrow \operatorname{MnO}_{2}(s)+I_{2}(s)$ Stage 1 The two half responses are given beneath: Oxidation half response: $I_{(a q)} \rightarrow...
Consider the reactions: (a) 
 (b)
(b) 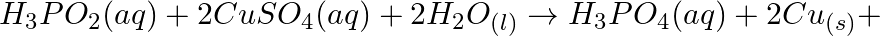
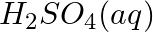 (c)
(c) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{CHO}_{(l)}+2\left[\mathrm{Ag}\left(\mathrm{NH}_{3}\right)_{2}\right]_{(a q)}^{+}+3 \mathrm{OH}_{(a q)}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{COO}_{(a q)}^{-}+2 \mathrm{Ag}_{(s)}+](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7aa1b43808014d89aabd5bf76808b357_l3.png)
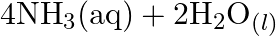 (d)
(d) 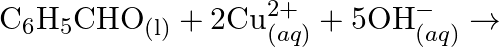 No change is observed What inference do you draw about the behavior of
No change is observed What inference do you draw about the behavior of 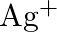 and
and 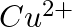 from these reactions?
from these reactions?
Solution: $\mathrm{Ag}^{+}$and $C u^{2+}$ acts as oxidizing specialist in responses (I) and (ii) individually. In response (iii), $\mathrm{Ag}^{+}$oxidizes $\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{5}...
Why does the following reaction occur?  What conclusion about the compound
What conclusion about the compound 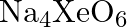 (of which
(of which 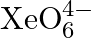 is a part) can be drawn from the reaction?
is a part) can be drawn from the reaction?
Solution: $X e O_{6(a q)}^{4-}+2 F_{(a q)}^{-}+6 H_{(a q)}^{+} \rightarrow X e O_{3(g)}+F_{2(g)}+3 H_{2} O_{(l)}$ The oxidation no. of Xe decreases from $+8$ in $\mathrm{XeO}_{6}^{4-}$ to $+6$ in...
Justify giving reactions that among halogens, fluorine is the best oxidant and among hydrohalic compounds, hydroiodic acid is the best reductant.
Solution: $F_{2}$ can oxidize $C l^{-}$to $C l_{2}, B r^{-}$to $B r_{2}$, and $I^{-}$to $I_{2}$ as: $F_{2(a q)}+2 C l_{(s)}^{-} \rightarrow 2 F_{(a q)}^{-}+C l_{2(g)}$ $F_{2}(a q)+2 B r_{(a q)}^{-}...
Consider the reactions : 
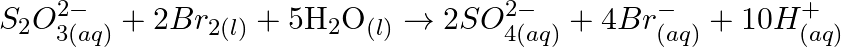 Why does the same reductant, thiosulphate react differently with iodine and bromine?
Why does the same reductant, thiosulphate react differently with iodine and bromine?
Solution: The normal oxidation no. of $\mathrm{S}$ in $\mathrm{S}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}^{2-}$ is $+2$. The normal oxidation no. of $\mathrm{S}$ in $S_{4} \mathrm{O}_{6}^{2-}$ is $+2.5$. The oxidation...
Identify the substance oxidised, reduced, oxidising agent and reducing agent for each of the following reactions: (a)  (b)
(b) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com H C H O_{(l)}+2\left[A g\left(N H_{3}\right)_{2}\right]_{(a q)}^{+}+3 O H_{(a q)}^{-} \rightarrow 2 A g_{(s)}+H C O O_{(a q)}^{-}+](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b8e4956dd6ca01b2ee5147606a038527_l3.png)
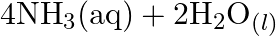 (c)
(c) 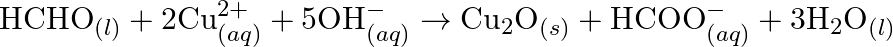 (d)
(d) 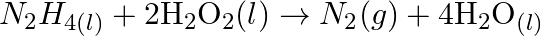 (e)
(e) 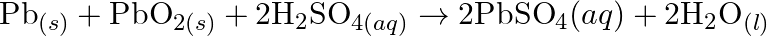
Solution: (a) $2 \mathrm{AgBr}_{(s)}+C_{6} H_{6} O_{2}(a q) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{Ag}_{(s)}+2 \mathrm{HBr}_{(a q)}+C_{6} \mathrm{H}_{4} O_{2}(a q)$ $\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{6}...
How do you count for the following observations? (a) Though alkaline potassium permanganate and acidic potassium permanganate both are used as oxidants, yet in the manufacture of benzoic acid from toluene we use alcoholic potassium permanganate as an oxidant. Why? Write a balanced redox equation for the reaction. (b) When concentrated sulphuric acid is added to an inorganic mixture containing chloride, we get colourless pungent smelling gas HCl, but if the mixture contains bromide then we get red vapour of bromine. Why?
Solution: (a) While producing benzoic corrosive from toluene, alcoholic potassium permanganate is utilized as an oxidant because of the given reasons. (I) In an impartial medium, $O H^{-}$ions are...
Whenever a reaction between an oxidisina adent and a reducina aqent is carried out, a compound of lower oxidation state is formed if the reducing agent is in excess and a compound of higher oxidation state is formed if the oxidising agent is in excess. J ustify this statement giving three illustrations. Justify the above statement with three examples.
Solution: When there is a response between lessening specialist and oxidizing specialist, a compound is framed which has lower oxidation number if the diminishing specialist is in abundance and a...
The compound 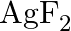 is unstable compound. However, if formed, the compound acts as a very strong oxidising agent. Why?
is unstable compound. However, if formed, the compound acts as a very strong oxidising agent. Why?
Solution: The oxidation no. of $A g$ in $A g F_{2}$ is $+2$. Be that as it may, $+2$ is entirely unsound oxidation no. of Ag. Consequently, when $A g F_{2}$ is framed, silver acknowledges an...
Consider the reactions: (a)  (b)
(b) 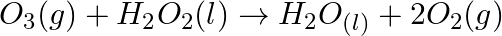 Why it is more appropriate to write these reactions as : (a)
Why it is more appropriate to write these reactions as : (a) 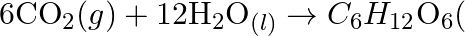 aq
aq 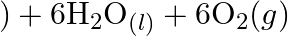 (b)
(b) 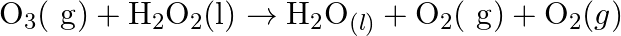 Also suggest a technique to investigate the path of the above (a) and (b) redox reactions
Also suggest a technique to investigate the path of the above (a) and (b) redox reactions
Solution: (a) Stage 1: $\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}$ breaks to give $\mathrm{H}_{2}$ and $\mathrm{O}_{2}$. $2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(\mathrm{l})} \rightarrow 2...
While sulphur dioxide and hydrogen peroxide can act as oxidising as well as reducing agents in their reactions, ozone and nitric acid act only as oxidants. Why?
Solution: In sulfur dioxide $\left(S O_{2}\right)$ the oxidation no. of $\mathrm{S}$ is $+4$ and the scope of oxidation no. of sulfur is from $+6$ to $-2$. Consequently, $S O_{2}$ can go about as a...
Suggest a list of substances where carbon can exhibit oxidation states from -4 to +4 and nitrogen from -3 to +5.
Solution: The compound where carbon has oxidation number from -4 to +4 are given below in the table:
Write formulas for the following compounds: (a) Mercury (II) chloride (b) Nickel (II) sulphate (c) Tin (IV) oxide (d) Thallium (I) sulphate (e) Iron (III) sulphate (f) Chromium (III) oxide
Solution: Formulas are: (a) Mercury (II) chloride $H g C l_{2}$ (b) Nickel (II) sulphate $\mathrm{NiSO}_{4}$ (c) Tin (IV) oxide $\mathrm{SnO}_{2}$ (d) Thallium (I) sulphate $\mathrm{Tl}_{2}...
Calculate the oxidation number of sulphur, chromium and nitrogen in H2SO5, Cr2O2 and NOT. Suggest structure of these compounds. Count for the fallacy. nitrogen in H2SO5, Cr2O2 and NOT. Suggest structure of these compounds. Count for the fallacy.
Solution: O.N. of S in H2SO5. By traditional strategy, the O.N. of S in H2SO5 is 2 (+1) + x + 5 (- 2) = 0 or x = +8 This is outlandish on the grounds that the most extreme O.N. of S can't be more...
Fluorine reacts with ice and results in the change:  Justify that this reaction is a redox reaction
Justify that this reaction is a redox reaction
Solution: $H_{2} O_{(s)}+F_{2}(g) \rightarrow H F_{(g)}+H O F_{(g)}$ In the above response, Oxidation no. of $\mathrm{H}$ and $\mathrm{O}$ in $\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}$ is $+1$ and $-2$...
Justify that the reactions is redox reactions: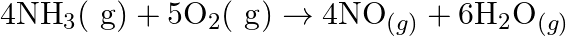
Solution: $4 \mathrm{NH}_{3(g)}+5 \mathrm{O}_{2}(g) \rightarrow 4 \mathrm{NO}_{(g)}+6 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(g)}$ In the above response, Oxidation no. of $\mathrm{N}$ and $\mathrm{H}$ in $N...
Justify that the reactions is redox reactions: 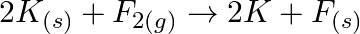
Solution: $2 K_{(s)}+F_{2(g)} \rightarrow 2 K+F_{(s)}$ In the above response, Oxidation no. of $\mathrm{K}$ is 0 . Oxidation no. of $F$ is 0 . Oxidation no. of $\mathrm{K}$ and $\mathrm{F}$ in...
Justify that the reactions is redox reactions: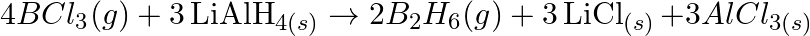
Solution: $4 \mathrm{BCl}_{3(g)}+3 \mathrm{LiAlH}_{4(s)} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{~B}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{6}(\mathrm{~g})+3 \mathrm{LiCl}_{(s)}+3 \mathrm{AlCl}_{3}(s)$ the above response, Oxidation no. of...
Justify that the reactions is redox reactions: 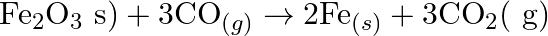
Solution: $\mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3(s)}+3 \mathrm{CO}_{(g)} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{Fe}_{(s)}+3 \mathrm{CO}_{2}(g)$ In the above response, Oxidation no. of Fe and $\mathrm{O}$ in $\mathrm{Fe}_{2}...
Justify that the reactions is redox reactions: 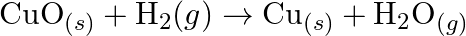
Solution: $\mathrm{CuO}_{(s)}+\mathrm{H}_{2}(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{Cu}_{(s)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(g)}$ Oxidation no. of $\mathrm{Cu}$ and $\mathrm{O}$ in $C u O$ is $+2$ and $-2$...
What are the oxidation number of the underlined elements and how do you rationalise your results?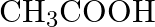
Solution: $\underline{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_{3} \underline{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{OOH}$ C2x+14O2 \mathrm{C}_{2}^{\mathrm{x}}+1_{4} \mathrm{O}_{2} Let $x$ be the oxidation no. of $C$. Oxidation...
What are the oxidation number of the underlined elements and how do you rationalise your results?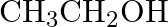
Solution: $\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{C} \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{OH}$ $$ $$ Let $x$ be the oxidation no. of $C$. Oxidation no. of $\mathrm{O}=-2$ Oxidation no. of $\mathrm{H}=+1$ Then, at that...
What are the oxidation number of the underlined elements and how do you rationalise your results?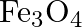
Solution: $\mathrm{Fe}_{3} \mathrm{O}_{4}$ Let $x$ be the oxidation no. of Fe. Oxidation no. of $0=-2$ Then, at that point, $3(x)+4(- 2)=0$ $3 x-8=0$ $x=\frac{8}{3}$ Oxidation no. can't be partial....
What are the oxidation number of the underlined element and how do you rationalise your results?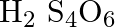
Solution: H2S4O6: Let x be the oxidation number of S. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Oxidation\text{ }no.\text{ }of\text{ }H\text{ }=\text{ }+1 \\ Oxidation\text{ }no.\text{ }of\text{ }O\text{ }=\text{...
What are the oxidation number of the underlined elements and how do you rationalise your results? 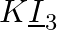
Solution: KI3: In KI3, the oxidation number (O.N.) of K is +1. Consequently, the normal oxidation number of I is Ncert Solutions Cbse Class 11-science Chemistry Chapter - Redox Reactions. In any...
Equivalent capacitance of A-D part So, the parallel combination gives us – 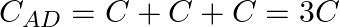
Equivalent capacitance of D-B part So, the parallel combination gives us – ${{C}_{DB}}=C+C+C=3C$
Why is Wurtz reaction not preferred for the preparation of alkanes containing odd number of carbon atoms? Illustrate your answer by taking one example
Solution: For the union of balanced alkanes (for example alkanes with a significantly number of carbon particles), the Wurtz response is restricted. Two comparative alkyl halides are taken as...
Out of benzene, m–dinitrobenzene and toluene, state the increasing order of nitration. Justify your answer?
Solution: The simplicity of nitration relies upon the presence of electron thickness on the compound to shape nitrates. Nitration responses are instances of electrophilic replacement responses where...
List the names of some Lewis acid which can be used during ethylation of benzene in a Friedel-Craft alkylation reaction.
Solution: The response of benzene to the presence of Lewis acids (AlCl3) with an acyl halide or corrosive anhydride yields acyl benzene (or benzene ring). A Friedel-Craft alkylation response is...
Arrange the following set of compounds in order of their increasing relative reactivity with an electrophile, E+ : p – H3C – C6H4 – NO2, Toluene, p-O2N – C6H4 – NO2.
Solution: Electrophiles are reagents that take part in a response by tolerating a couple of electrons to tie to nucleophiles. The higher the thickness of electrons on a benzene ring, the more...
Arrange the following set of compounds in order of their increasing relative reactivity with an electrophile, E+ p-nitrochlorobenzene, Chlorobenzene, 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene,
Solution: Electrophiles are reagents that take part in a response by tolerating a couple of electrons to tie to nucleophiles. The higher the thickness of electrons on a benzene ring, the more...
Write structures of all the alkenes which on hydrogenation give 2-methylbutane.
Solution: The fundamental design of 2-methylbutane is displayed beneath: Based on the above structure, different alkenes that will give 2-methylbutane on hydrogenation are displayed beneath: a) b)...
How would you convert the Hexane into benzene?
Solution: Hexane into benzene: When vapours of hexane are passed over heated catalyst consisting of Cr₂O3 MO₂O3, and V₂O5, at 773 K under 10-20 atm pressure, cyclization and aromatization occurs...
How would you convert the Ethene into benzene?
Solution: Ethene into benzene: Ethene is first converted inti Ethyne and then into benzene.
How would you convert Ethyne into benzene?
Solution: Ethyne into benzene:
What do you understand by the term : Fuel cell?
Solution: Fuel cell: Energy components are gadgets for creating power from fuel within the sight of an electrolyte. Dihydrogen can be utilized as a fuel in these cells. It is liked over different...
What do you understand by the term :Water-gas shift reaction
Solution: Water-gas shift response: It is a response of carbon monoxide of syngas blend with steam within the sight of an impetus as: $\mathrm{CO}_{(g)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(g)} \rightarrow...
What do you understand by the term :‘syngas’
Solution: 'syngas': Syngas is a combination of carbon monoxide and dihydrogen. Since the combination of the two gases is utilized for the blend of methanol, it is called syngas amalgamation gas, or...
What do you understand by the term :Hydrogenation
Solution: Hydrogenation: The method involved with adding dihydrogen to one more reactant is known as hydrogenation. It is utilized to decrease a compound within the sight of appropriate impetus. For...
What do you understand by the terms: Hydrogen economy ?
Solution: Hydrogen economy: Dihydrogen delivers more energy than petroleum and is more eco-accommodating. Subsequently, it tends to be utilized in energy units to create electric force. Hydrogen...
Do you expect different products in solution when aluminium (III) chloride and potassium chloride treated separately with (i) alkaline water (ii) acidified water, and (iii) normal water. Write equations wherever necessary.
Solution: Potassium chloride $(\mathrm{KCl})$ is the salt of a solid corrosive $(\mathrm{HCl})$ and solid base (KOH). Consequently, it is nonpartisan in nature and doesn't go through hydrolysis in...
What do you expect the nature of hydrides is, if formed by elements of atomic numbers 15,19, 23 and 44 with dihydrogen? Compare their behaviour with water.
Solution: The components of nuclear numbers 15 is phosphorus, 19 potassium, 23 is vanadium and 44 is ruthenium Hydride of Phosphorus Hydride of phosphorus $\left(\mathrm{PH}_{3}\right.$ ) is...
How can saline hydrides remove traces of water from organic compounds?
Solution: Normally, saline hydrides are ionic. Saline hydrides responds with water which brings about the arrangement of metal hydroxide alongside hydrogen gas freedom. It is addressed as, $A...
What is the difference between the terms ‘hydrolysis’ and ‘hydration’?
Solution: Hydration: The expansion of at least 1 atoms to a particle or particle which brings about arrangement of hydrated mixtures is known as hydration. For example $\mathrm{CuSO}_{4}+5...
Write chemical reactions to justify that hydrogen peroxide can function as an oxidising as well as reducing agent.
Solution: Hydrogen peroxide goes about as an oxidizing specialist just as diminishing specialist in both basic medium and acidic medium. The response which are associated with oxidizing activities...
Write chemical reactions to show the amphoteric nature of water
Solution: The amphoteric idea of water can be depicted based on the accompanying responses: 1) Reaction with $\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S}$ The response happens as: $\mathrm{H}_{2}...
Discuss the principle and method of softening of hard water by synthetic ionexchange resins.
Solution: The method involved with treating extremely durable hardness of water utilizing engineered saps commonly based or trade of anions and cations present in water by $\mathrm{OH}^{-}$and...
Complete the following chemical reactions. (i) 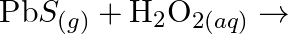 (ii)
(ii) 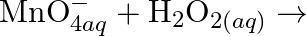 (iii)
(iii) 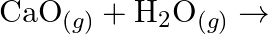 (iv)
(iv) 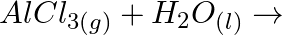 (v)
(v) 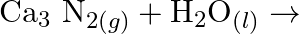 Classify the above into (a) Hydrolysis, (b) Redox and (c) Hydration reactions.
Classify the above into (a) Hydrolysis, (b) Redox and (c) Hydration reactions.
Solution: (I) $\mathrm{PbS}_{(g)}+4 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2(a q)} \rightarrow \mathrm{PbSO}_{4(s)}+4 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(l)}$ $\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2}$ is going about as an...
Consider the reaction of water with 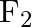 and suggest, in terms of oxidation and reduction, which species are oxidized/reduced.
and suggest, in terms of oxidation and reduction, which species are oxidized/reduced.
Solution: The response among water and fluorine can be addressed as: $2 F_{2(g)}+2 H_{2} O_{(l)} \rightarrow 4 H_{(a q)}^{+}+4 F_{(a q)}^{-}+O_{2(g)}$ This is an illustration of redox response $2...
What do you understand by the term ‘auto-protolysis’ of water? What is its significance?
Solution: Auto-protolysis (self-ionization) of water is a compound response wherein 2 water atoms respond to deliver a hydroxide particle $\left(\mathrm{OH}^{-}\right)$and a hydronium particle...
Saline hydrides are known to react with water violently producing fire. Can 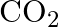 , a well known fire extinguisher, be used in this case? Explain.
, a well known fire extinguisher, be used in this case? Explain.
Solution: Saline hydrides [i.e.,LiH, NaH etc.] respond with water to shape hydrogen gas Furthermore, a base. The synthetic condition to address this response is $M H_{(g)}+H_{2} O_{(a q)}...
What characteristics do you expect from an electron-deficient hydride with respect to its structure and chemical reactions?
Solution: To shape an ordinary bond, an electron-lacking hydride doesn't have adequate electrons in which 2 electrons are shared by 2 particles. e.g., $B_{2} H_{6}$ $\mathrm{Al}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{6}$...
Complete the following reactions: (i) 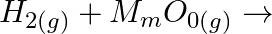 (ii)
(ii) 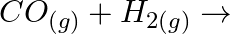 (iii)
(iii) 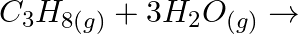 (iv)
(iv) 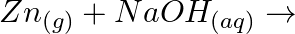
Solution: (i) $H_{2(g)}+M_{m} O_{0(g)} \rightarrow m M_{(s)}+H_{2} O_{(l)}$ (ii) $\mathrm{CO}_{(g)}+\mathrm{H}_{2(g)} \rightarrow \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{OH}_{(l)}$ (iii) $\mathrm{C}_{3}...
Describe the bulk preparation of dihydrogen by electrolytic method. What is the role of an electrolyte in this process?
Solution: The readiness of di hydrogen is by the electrolysis of fermented or soluble water utilizing platinum anodes Generally, $15-20 \%$ of a corrosive $\left(\mathrm{H}_{2}...
How can the production of dihydrogen, obtained from ‘coal gasification’, be increased?
Solution: By the course of coal gasification, dihydrogen is created as $C_{(g)}+H_{2} O_{(g)} \rightarrow C O_{(g)}+H_{2(g)}$ [C-Coal] Response with carbon monoxide with steam within the sight of an...
Write the names of isotopes of hydrogen. What is the mass ratio of these isotopes?
Solution: 3-isotopes are: (i) tritium ${ }_{1}^{3} H$ or $\mathrm{T}$ (ii) protium ${ }_{1}^{3} H$ (iii) deuterium ${ }_{1}^{2} H$ or $\mathrm{D}$ Mass Ratio: Tritium : Protium : deuterium $=1: 2:...
Explain the terms inductive and electromeric effects. Which electron displacement effect explain the following correct orders of acidity of the carboxylic acids? (a) Cl3CCOOH > Cl2CHCOOH > ClCH2 COOH (b) CH3CH2COOH > (CH3)2 CHCOOH > (CH3)3CCOOH
Solution: Inductive Effect: The inductive impact alludes to the extremity delivered in a particle because of higher electronegativity of one molecule contrasted with another.Atoms or gatherings...
For the following bond cleavage, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
Solution: The bond cleavage can be displayed as: It goes under heterolytic cleavage since the common remaining parts with one of the sections. A carbocation is framed as the response middle.
For the following bond cleavage, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
Solution: The bond cleavage can be displayed as: It goes under heterolytic cleavage since the common remaining parts with the bromine particle. A carbocation is framed as the response...
For the following bond cleavage, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
Solution: The bond cleavage can be displayed as: It goes under heterolytic cleavage since the common remaining parts with the carbon molecule of propanone. A carbanion is framed as the response...
For the following bond cleavage, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
Solution: The bond cleavage can be displayed as: It goes under homolytic cleavage since one of the common pair in a covalent bond goes with the reinforced molecule. A free revolutionary is framed as...
What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of structures? Are they structural or geometrical isomers or resonance contributors?
Solution: The given mixtures are a pair of contributing constructions or authoritative structures. They don't address any genuine particle and are absolutely speculative. They are additionally...
What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of structures? Are they structural or geometrical isomers or resonance contributors?
Solution: The given mixtures are a pair of mathematical isomers since they have a similar molecular formulas, succession of covalent bonds and a similar constitution yet vary in the general...
What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of structures? Are they structural or geometrical isomers or resonance contributors? following pairs of structures? Are they structural or geometrical isomers or resonance contributors?
Solution: The given mixtures are a pair of primary isomers since they have a similar molecular formula yet have various structures. These mixtures vary in the situation of the ketone bunch. For the...
Draw the resonance structures for ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{C}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{3}}}\mathbf{CH}=\mathbf{CHCH}2\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6637624364ee1ee04d838ff239050994_l3.png)
. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
Solution: \[\mathbf{C}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{3}}}\mathbf{CH}=\mathbf{CHCH}2\] Resonating structures:
Draw the resonance structure for the compound C6H5CH2. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
Solution: C6H5CH2 Resonating structures:
Draw the resonance structure for the compound C6H5—CHO. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
Solution: structure of C6H5CHO: Resonating structures:
Draw the resonance structure for the compound CH3CH=CHCHO. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
Solution: \[C{{H}_{3}}CH\text{ }=\text{ }CH\text{ }\text{ }CHO\] Resonating structures:
Draw the resonance structure for the compound C6H5N02. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
Solution: structure of C6H5NO2: Resonating structures:
Draw the resonance structure for the compound C6H5OH . Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
Solution: structure of C6H5OH : Resonating structures:
Explain why alkyl groups act as electron donors when attached to a π system.
Solution: Because of hyperconjugation, an alkyl bunch acts as an electron-benefactor bunch when joined to a π framework. For instance, take a gander at propene. The sigma electrons of the C-H bond...
Identify the functional groups in the compound:
Solution: Nitro (–NO2), C=C Ethylenic Alkene
Identify the functional groups in the compound:
Solution: \[~Ester\text{ }-\left( O\text{ }=\text{ }C\text{ }\text{ }O \right)-,\text{ }{{1}^{o}}Amino\text{ }\left( N{{H}_{2}} \right)\text{ }\left( aromatic \right),\text{ }Diethylamine\text{...
Identify the functional groups in the compound.
Solution: Hydroxyl (–OH), Aldehyde (–CHO), Methoxy (–OMe), C=C double bond
Give condensed and bond line structural formulas and identify the functional group(s) present, if any, for: Hexanedial.
Solution: Hexanedial Condensed Formula: \[\left( CHO \right){{\left( C{{H}_{2}} \right)}_{4}}\left( CHO \right)\] Bond line formula: Functional groups: Aldehyde (-CHO) group
Give condensed and bond line structural formulas and identify the functional group(s) present, if any, for: 2-Hydroxy-l, 2, 3-propanetricarboxylic acid
Solution: 2–hydroxy–1, 2, 3–propanetricarboxylic acid Condensed Formula: \[\left( COOH \right)C{{H}_{2}}C\left( OH \right)\text{ }\left( COOH \right)C{{H}_{2}}\left( COOH \right)\] Bond line...
Give condensed and bond line structural formulas and identify the functional group(s) present, if any, for : 2,2,4-Trimethylpentane
Solution: 2, 2, 4–trimethylpentane Condensed formula: \[{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}CHC{{H}_{2}}C\text{ }{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}\] Bond line formula : Functional group: no functional...
Give the IUPAC name of the compound :Cl2CHCH2OH
Solution: 2, 2–dichloroethanol
Give the IUPAC name of the compound :
Solution: 3–chloropropanal
Give the IUPAC name of the compound :
Solution: 3–bromo–3–chloroheptane
Give the IUPAC name of the compound :
Solution: 2, 5–dimethyl heptane
Give the IUPAC name of the compound :
Solution: 3–methylpentanenitrite
Give the IUPAC name of the compound:
Solution: Propylbenzene
Write bond line formula for : Heptan–4–one
Solution: Bond line formula for Heptan–4–one:
Write bond line formula for : 2, 3–dimethyl butanal
Solution: Bond line formula for 2, 3–dimethyl butanal :
Write bond line formula for :Isopropyl alcohol
Solution: Bond line formula for Isopropyl alcohol:
Indicate sigma (σ) and pi (Π) bonds in the molecule :HCONHCH3
Solution: HCONHCH3 There are four C–H sigma bonds, two C–N sigma bond, one N–H sigma bond, and one C=O pi bond in the given compound.
Indicate sigma (σ) and pi (Π) bonds in the molecule :CH3NO2
Solution: CH3NO2 There are three C–H sigma bonds, one C–N sigma bond, one N–O sigma bond, and one N=O pi bond in the given compound.
Indicate sigma (σ) and pi (Π) bonds in the molecule :CH2 = C = CH2
Solution: CH2 = C = CH2 There are two C–C sigma bonds, four C–H sigma bonds, and two C=C pi bonds in the given compound.
Indicate sigma (σ) and pi (Π) bonds in the molecule :CH2Cl2
Solution: CH2Cl2 There are two C – Cl sigma bonds and two C–H sigma bonds in the given compound.
Indicate the σ and π bonds in the molecule:C6H12
Solution: C6H12 There are six C – C sigma bonds and twelve C–H sigma bonds in the given compound.
Indicate the σ and π bonds in the following molecules:C6H6
Solution: C6H6 There are six C – C sigma bonds, six C–H sigma bonds, and three C=C pi resonating bonds in the given compound.
Assertion (A): (Fe(CN)6]3- ion shows magnetic moment corresponding to two unpaired electrons. Reason (R): Because it has d2sp3 type hybridisation.
(a) Assertion and Reason both are true, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (b) Assertion and Reason both are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (c) Assertion...
Assertion (A): Complexes of MX6 and MX5L type (X and L are unidentate) do not show geometrical isomerism. Reason (R): Geometrical isomerism is not shown by complexes of coordination number 6.
(a) Assertion and Reason both are true, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (b) Assertion and Reason both are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (c) Assertion...
Assertion (A): Linkage isomerism arises in coordination compounds containing ambidentate ligand. Reason (R): Ambidentate ligand has two different donor atoms.
(a) Assertion and Reason both are true, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (b) Assertion and Reason both are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (c) Assertion...
Assertion (A): [Cr(H2O)6]Cl2 and [Fe(H2O)6]Cl2 are reducing in nature. Reason (R): Unpaired electrons are present in their J-orbitals.
(a) Assertion and Reason both are true, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (b) Assertion and Reason both are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (c) Assertion...
Assertion (A): Toxic metal ions are removed by the chelating ligands. Reason (R): Chelate complexes tend to be more stable.
(a) Assertion and Reason both are true, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (b) Assertion and Reason both are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (c) Assertion...
Match the compounds given in Column I with the oxidation state of cobalt present in it (given in Column II) and assign the correct code. with the oxidation state of cobalt present in it (given in Column II) and assign the correct code.
Solution: \[\left( c \right)\text{ }\left( A\text{ }\to \text{ }5 \right),\text{ }\left( B\text{ }\to \text{ }1 \right),\text{ }\left( C\text{ }\to \text{ }4 \right),\text{ }\left( D\text{...
Match the complex species given in Column I with the possible isomerism given in Column II and assign the correct code:
Solution: \[\left( d \right)\text{ }\left( A\text{ }\to 4 \right),\text{ }\left( B\to \text{ }1 \right),\text{ }\left( C\text{ }\to 2 \right),\text{ }\left( D\text{ }\to 3 \right)\] Isomerism...
Match the complex ions given in Column I with the hybridisation and number of unpaired electrons given in Column II and assign the correct code :
Solution: \[\left( a \right)\text{ }\left( A\text{ }\to \text{ }3 \right),\text{ }\left( B\text{ }\to 1 \right),\text{ }\left( C\text{ }\to \text{ }5 \right),\text{ }\left( D\to \text{ }2...
Match the coordination compounds given in Column I with the central metal atoms given in Column II and assign the correct code : Code : (i) A (5) B (4) C (1) D (2) (ii) A (3) B (4) C (5) D (1) (iii) A (4) B (3) C (2) D (1) (iv) A (3) B (4) C (1) D (2)
Solution: \[\left( b \right)\text{ }\left( A\text{ }\to 5 \right),\text{ }\left( B\text{ }\to \text{ }4 \right),\text{ }\left( C\text{ }\to \text{ }1 \right),\text{ }\left( D~\to 2 \right)\] ...
Match the complex ions given in Column I with the colours given in Column II and assign the correct code :
Solution: \[\left( b \right)\text{ }\left( A\text{ }\to 4 \right),\text{ }\left( B\text{ }\to \text{ }3 \right),\text{ }\left( C\text{ }\to \text{ }2 \right),\text{ }\left( D\text{ }\to \text{ }1...
Name the type of isomerism when ambidentate ligands are attached to a central metal ion. Give two examples of ambidentate ligands.
Solution: Ambidendate ligands are those having diverse two restricting destinations. Example: Isothiocyanato Thiocyanato and Nitrite-N Nitrito-O The kind of isomerism when ambidentate ligands are...
CuSO4.5H2O is blue while CuSO4 is colourless. Why?
Solution: In CuSO4.5H2O, there are water particles that go about as ligands. The electrons will invigorate to higher d orbital and show tone. While, in CuSO4, there are no water particles to go...
Give the electronic configuration of the following complexes based on Crystal Field Splitting theory. [CoF6]3–, [Fe(CN)6]4– and [Cu(NH3)6]2+.
Solution: \[{{[CO{{F}_{\mathbf{6}}}]}^{\mathbf{3}-}}:\text{ }C{{o}^{\mathbf{3}+}}~({{d}^{\mathbf{6}}})\]
Which of the following complexes show linkage isomerism? (a) [CO(NH3)5(NO2)]2+ (b) [CO(H2O)5CO]3+ (c) [Cr(NH3)5SCN]2+ (d) [Fe(en)2Cl2]+
Solution: (a, c) NO2 and SCN are ambidentate ligands subsequently, show linkage isomerism.
Identify the correct statements for the behaviour of ethane-1, 2-diamine as a ligand. (a) It is a neutral ligand (b) It is a didentate ligand (c) It is a chelating ligand (d) It is a unidentate ligand
Solution: hence, option a, b and c are correct
Identify the optically active compounds from the following: (a) [Co(en)3]3+ (b) trans-[Co(en)2Cl2]+ (c) cis-[Co(en)2Cl2]+ (d) [Cr(NH3)5Cl]
Solution:
Which of the following complexes are heteroleptic? (a) [Cr(NH3)6]3+ (b) [Fe(NH3)4 Cl2]+ (c) [Mn(CN)6]4– (d) [Co(NH3)4Cl2]
Solution: (b, d) In complexes, [Fe(NH3)4Cl2]+ and [CO(NH3)4Cl2], metal is bonded to more than one sort of ligands subsequently, they are heteroleptic.
Which of the following complexes is homoleptic? (a) [Co(NH3)6]3+ (b) [Co(NH3)4 Cl2]+ (c) [Ni(CN)4]2– (d) [Ni(NH3)4Cl2]
Solution: (a, c) In complexes [Co(NH3)6]3+ and [Ni(CN)4]2-, both Co and Ni are connected to one sort of ligands just subsequently, they are homoleptic. hence, option a and c are correct
An aqueous pink solution of cobalt(II) chloride changes to deep blue on the addition of an excess of HCl. This is because____________. (a) [Co(H2O)6]2+ is transformed into [CoCl6]4– (b) [Co(H2O)6]2+ is transformed into [CoCl4]2– (c) tetrahedral complexes have smaller crystal field splitting than octahedral complexes. (d) tetrahedral complexes have larger crystal field splitting than octahedral complex.
Solution: (b, c) Aqueous pink arrangement of cobalt (II) chloride is because of electronic progress of electron from t2g to eg energy level of [Co(H2O)6]2+ complex. At the point when overabundance...
Which of the following options are correct for [Fe(CN)6]3- complex? (a) d2sp3 hybridisation (b) sp3d2 hybridisation (c) Paramagnetic (d) Diamagnetic
Solution: hence, option a and c are correct for [Fe(CN)6]3- complex
Atomic number of Mn, Fe, Co and Ni are 25, 26 27 and 28 respectively. Which of the following outer orbital octahedral complexes have same number of unpaired electrons? (a) [MnCl6]3- (b) [FeF6]3- (c) [CoF6]3- (d) [Ni(NH3)6]2+
Solution: so, option a and c are the correct answer
The atomic number of Mn, Fe and Co are 25, 26 and 27 respectively. Which of the following inner orbital octahedral complexions are diamagnetic? (a) [Co(NH3)6]3+ (b) [Mn(CN)6]3– (c) [Fe(CN)6]4– (d) [Fe(CN)6]3–
Solution: hence , a and c are the correct answer
IUPAC name of [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)] is (a) platinum diaminechloronitrite (b) chloronitrito-N-ammineplatinum (II) (c) diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum (II) (d) diamminechloronitrito-N-platinate (II).
Solution: (c) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)] is diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum (II)
What kind of isomerism exists between [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 (violet) and [Cr(H2O)5Cl)Cl2.H2O (greyish- green)? (a) Linkage isomerism (b) Solvate isomerism (c) Ionisation isomerism (d) Coordination isomerism
Solution: (b) The given mixtures have diverse number of water atoms inside and outside the organize circle.
Which of the following species is not expected to be a ligand? (a) NO (b) NH4– (c) NH2CH2CH2NH2 (d) CO
Solution: (b) Ligand should give a pair of electrons or inexactly held electron pair to metal and shape a M – L bond,
A chelating agent has two or more than two donor atoms to bind to a single metal ion. Which of the following is not a chelating agent? (a) Thiosulphate (b) Oxalato (c) Glycinato (d) Ethane-1, 2-diamine
Solution: (a) Thiosulphate or S2O3–isn't a chelating specialist since it is a monodentate ligand.
The compounds [Co(SO4)(NH3)5]Br and [CO(SO4)(NH3)5]Cl represent (a) linkage isomerism (b) ionization isomerism (c) coordination isomerism (d) no isomerism.
Solution: (d) [Co(SO4)(NH3)5]Br and [CO(SO4)(NH3)5]Cl address no isomerism since they are different compounds.
Due to the presence of ambidentate ligands coordination compounds show isomerism. Palladium complexes of the type [Pd(C6H5)2(SCN)2] and [Pd(C6H5)2(NCS)2] are (a) linkage isomers (b) coordination isomers (c) ionisation isomers (d) geometrical isomers
Solution: (a) The ligands having two distinctive holding locales are known as ambident ligands e.g., NCS, NO2, and so forth Here, NCS has two restricting locales at N and S. Subsequently, NCS...
The CFSE for octahedral [CoCl6]4– is 18,000 cm–1. The CFSE for tetrahedral [CoCl4]2– will be (a) 18,000 cm–1 (b) 16,000 cm–1 (c) 8,000 cm–1 (d) 20,000 cm–1
Solution:
Indicate the complex ion which shows geometrical isomerism. (a) [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]+ (b) [Pt(NH3)3 Cl] (c) [Co(NH3)6]3+ (d) [Co(CN)5(NC)]3–
Solution:
The stabilisation of coordination compounds due to chelation is called the chelate effect. Which of the following is the most stable complex species? (a) [Fe(CO)5] (b) [Fe(CN)6]3– (c) [Fe(C2O4)3]3– (d) [Fe(H2O)6]3+
Solution: (c) arrangement of cycle by linkage between metal particle and ligand balances out the coordination compound. The ligand which chelates the metal particle are known as chelating ligand....
The correct IUPAC name of [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] is (a) diamminedichloridoplatinum (II) (b) diamminedichloridoplatinum (IV) (c) diamminedichloridoplatinum (I) (d) dichloridodiammineplatinum (IV)
Solution: (a) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] is diamminedichloridoplatinum (II) .
When 1 mol CrCl3.6H2O is treated with an excess of AgNO3, 3 mol of AgCl are obtained. The formula of the complex is : (a) [CrCl3 (H2O)3].3H2O (b) [CrCl2(H2O)4]Cl.2H2O (c) [CrCl(H2O)5]Cl2.H2O (d) [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3
Solution: (d) 3 mol of AgCl implies 3Cl are given in the arrangement henceforth, the equation of the complex will be [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3.
When 0.1 mol COCl3(NH3)5 is treated with excess of AgNO3, 0.2 mol of AgCl are obtained. The conductivity of solution will correspond to (a) 1:3 electrolyte (b) 1:2 electrolyte (c) 1:1 electrolyte (d) 3:1 electrolyte
Solution: (b) One mole of AgNO3 accelerates one mole of chloride particle. In the above response, when 0.1 mole COCl3(NH3)5 is treated with abundance of AgNO3, 0.2 mole of AgCl are obtained hence,...
The colour of the coordination compounds depends on the crystal field splitting. What will be the correct order of absorption of wavelength of light in the visible region, for the complexes, [Co(NH3)6]3+, [Co(CN)6]3–, [Co(H2O)6]3+ (a) [Co(CN)6]3–> [Co(NH3)6]3+>[Co(H2O)6]3+ (b) [Co(NH3)6]3+> [Co(H2O)6]3+> [Co(CN)6]3– (c) [Co(H2O)6]3+> [Co(NH3)6]3+> [Co(CN)6]3– (d) [Co(CN)6]3–> [Co(NH3)6]3+> [Co(H2O)6]3+
Solution:
Which of the following complexes formed by Cu2+ ions is most stable?
Solution: (b) The greater the value of log K, the more prominent will be strength of complicated compound shaped. For response, For this response, log K has most elevated worth among the...
For what reason do compounds having comparable calculation have an alternate attractive second?
Solution: They vary in the quantity of combined and unpaired electrons. A solid field ligand will cause blending of electrons while a feeble field ligand won't cause matching. Blending or not...
Mastermind following complex particles in expanding request of precious stone field parting energy (DO) : [Cr(Cl)6]3–, [Cr(CN)6]3–, [Cr(NH3)6]3+.
Solution: The expanding request of gem field energy is [Cr(Cl)6]3–<[Cr(NH3)6]3+ <[Cr(CN)6]3– This is additionally the request for field strength of the ligands as indicated by the...
Clarify why [Fe(H2O)6]3+ has an attractive second worth of 5.92 BM while [Fe(CN)6]3–has a worth of just 1.74 BM.
Solution: For [Fe(H2O)6]3+, H2O is a powerless field ligand will not cause matching of electrons. Along these lines, the quantity of unpaired electrons will be 5. [Fe(CN)6]3–, Fe3+ has six unpaired...
Why are low twist tetrahedral edifices not framed?
Solution: For tetrahedral edifices, the gem field parting energy is excessively low. It is lower than blending energy in this way, the matching of electrons isn't supported and consequently the...
In view of gem field hypothesis clarify why Co(III) structures a paramagnetic octahedral complex with feeble field ligands though it frames a diamagnetic octahedral complex with solid field ligands.
Solution: The electronic design will be t42g e2g. It has 4 unpaired electron and paramagnetic. With weal ligand Δ0 < p. The design with solid field ligand will be t62g e0g. the Δ0 > p and...
The attractive snapshot of [MnCl4]2–is 5.92 BM. Clarify giving an explanation.
Solution: An attractive snapshot of 5.92 BM implies there are 5 unpaired electrons in light of the fact that \[Attractive\text{ }Moment\text{ }=\text{ }\surd \text{ }n\left( n+2 \right)\] The...
A complex of the kind [M(AA)2X2]n+is known to be optically dynamic. What does this demonstrate about the design of the complex? Give one illustration of such complicated.
Solution: The design must be cis-octahedral. Model for a particularly mind boggling is [Co(en)2Cl2]+ which is optically dynamic.
A coordination compound CrCl3.4H2O hastens silver chloride when treated with silver nitrate. The molar conductance of its answer relates to a sum of two particles. Compose the primary recipe of the compound and name it.
Solution: Assuming it structures silver chloride, there is without one chlorine iota outside the coordination circle. The primary recipe must be [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl. The name of this complex is...
Organize the accompanying buildings in the expanding request of conductivity of their answer: [Co(NH3)3Cl3], [Co(NH3)4Cl2] Cl, [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 , [Cr(NH3)5Cl]Cl2
Solution: The expanding request of conductivity is as per the following: [Co(NH3)3Cl3]<[Co(NH3)4Cl2]Cl< [Cr(NH3)5Cl]Cl2<[Co(NH3)6]Cl3
Reactivity of change components diminishes routinely from Sc to Cu. Clarify.
Solution: Viable atomic charge increments as we move along the period from left to right. Because of the explanation, the size likewise lessens. Subsequently the electrons will be held all the more...
While topping off of electrons in the nuclear orbitals, the 4s orbital is filled before the 3d orbital yet the opposite occurs during the ionization of the molecule. Clarify why?
Solution: Electrons are filled by the n+l rule. Assuming an orbital has lower n+l esteem, the electron will enter that orbital. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} For\text{ }3d,\text{ }n+l=\text{...
The halides of progress components become more covalent with expanding oxidation condition of the metal. Why?
Solution: Halides become more covalent with expanding oxidation state. As the oxidation state expands, the charge on the iota increments and the size of the particle of progress component...
E° of Cu is + 0.34V while that of Zn is – 0.76V. Clarify.
Solution: The decreased type of Cu2+ is more steady than the oxidized type of Cu. In this manner, the worth of E° is positive for Cu. Eliminating two electrons gives a steady setup [Ar]3d10 with...
An answer of KMnO4 on decrease yields either lackluster arrangement or an earthy colored encourage or a green arrangement relying upon the pH of the arrangement. What various phases of the decrease do these address and how are they completed?
Solution: In acidic medium, permanganate changes to manganous particle which is lackluster. \[MnO4-+8H+\text{ }+\text{ }5e-\to \text{ }Mn2+\text{ }+\text{ }4H2O\] (drab) In basic...
At the point when an orange arrangement containing Cr2O72–particle is treated with an antacid, a yellow arrangement is framed and when H+ particles are added to a yellow arrangement, an orange arrangement is acquired. Clarify for what reason does this occur?
Solution: At the point when Cr2O72–is treated with an antacid: \[\left( orange \right)\text{ }Cr2O72+\text{ }OH-\to \text{ }2CrO42-\left( yellow \right)\] At the point when the yellow...
Clarify why the shade of KMnO4 vanishes when oxalic corrosive is added to its answer in acidic medium.
Solution: This is a redox titration. The profound purple shade of KMnO4 vanishes because of the development of MnSO4. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} ~ \\ 5H2C2O4\text{ }+\text{ }2KMnO4\text{...
At the point when an earthy colored compound of manganese (A) is treated with HCl it gives a gas (B). The gas taken in abundance responds with NH3 to give an unstable compound (C). Distinguish intensifies A, B and C.
Solution: At the point when earthy colored co pound of manganese (A) is treated with HCl it gives chlorine gas. \[MnO2\text{ }+\text{ }4HCl\text{ }\to \text{ }MnCl2\text{ }+\text{ }Cl2\text{...
At the point when Cu2+ particle is treated with KI, a white hasten is shaped. Clarify the response with the assistance of the compound condition.
Solution: \[~2Cu2+\text{ }+\text{ }4I-\to \text{ }Cu2I2\text{ }+\text{ }I2\] Cu2+ gets decreased to Cu+, and I–gets oxidized to I2.
Why first ionization enthalpy of Cr is lower than that of Zn?
Solution: The electronic setup of chromium and zinc are separately: \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Cr\text{ }\left( 24 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\left[ Ar \right]\text{ }3d54s2 \\ ~Zn\text{ }\left(...
In spite of the fact that +3 is the trademark oxidation state for lanthanoids however cerium additionally shows +4 oxidation state in light of the fact that (a) it has variable ionization enthalpy (b) it tends to accomplish respectable gas design (c) it tends to accomplish f° arrangement (d) it looks like Pb4+
Solution: (b, c) Cerium shows +4 oxidation state likewise on the grounds that it tends to accomplish respectable gas setup and achieve f° design. Ce – 4f15d'6s2 (Ce4+–4f°)
Which of the accompanying won’t go about as oxidizing specialists? (a) CrO3 (b) MoO3(c) WO3 (d) CrO42-
Solution: (b, c) An animal types can go about as an oxidizing specialist just when metal is available in high oxidation state however lower oxidation state show strength. As higher oxidations...
Change components structure double mixtures with incandescent lamp. Which of the accompanying components will frame MF3 type compounds? (a) Cr (b) Co (c) Cu (d) Ni
Solution: (a, b) Cr and Co structure MF3 kind of mixtures. The capacity of fluorine to balance out the most elevated oxidation state is because of higher grid energy in CoF3 and higher bond enthalpy...
Which of the accompanying particles show higher twist just attractive second worth? (a) Ti3+ (b) Mn2+ (c) Fe2+ (d) Co3+
Solution: (b, c) Mn2+ (3d5) and Fe2+ (3d6) have 5 and 4 unpaired electrons thus higher upsides of twist just attractive second when contrasted with Ti3+ (3d1) and Co2+ (3d7).
Which of the accompanying lanthanoids show +2 oxidation state other than the trademark oxidation state +3 of lanthanoids? (a) Ce (b) Eu (c) Yb (d) Ho
Solution: (b, c)
General electronic arrangement of actinoids is (n – 2)f1-14 (n – 1 )d0-2 ns2. Which of the accompanying actinoids have one electron in 6d orbital? (a) U (Atomic no. 92) (b) Np (Atomic no. 93) (c) Pu (Atomic no. 94) (d) Am (Atomic no. 95)
Solution:
Which of the accompanying actinoids show oxidation states up to +7? (a) Am (b) Pu (c) U (d) Np
Solution: (b, d) Np and Pu show +7 oxidation state.
As dichromate, Cr (VI) is a solid oxidizing specialist in acidic medium however, Mo (VI) in MoO3 and W (VI) in WO3 are not on the grounds that (a) Cr (VI) is more steady than Mo(VI) and W(VI) (b) Mo(VI) and W(VI) are more steady than Cr(VI) (c) higher oxidation conditions of heavier individuals from bunch 6 of change series are more steady (d) lower oxidation conditions of heavier individuals from bunch 6 of change series are more steady
Solution: (b, c) In d-block components, for heavier components, the higher oxidation states are more steady. Thus, Mo(VI) and W(VI) are more steady than Cr (VI). That is the reason, Cr (VI) as...
Change components show attractive second because of twist and orbital movement of electrons. Which of the accompanying metallic particles have practically same twist just attractive second? (a) Co2+ (b) Cr2+ (c) Mn2+ (d) Cr3+
Solution: (a, d) Co2+ (3d7) and Cr3+ (3d3) have 3 unpaired electrons. Thus they have practically same twist just attractive second.
For the most part, progress components and their salts are shaded because of the presence of unpaired electrons in metal particles. Which of the accompanying mixtures are hued? (a) kMnO4 (b) Ce(SO4)2 (c) TiCl4 (d) Cu2Cl2
Solution: (a, b) KMnO4 and Ce(S04)2 are shaded because of charge move
For what reason is HCl not used to make the medium acidic in oxidation responses of KMnO4 in acidic medium? (a) Both HCl and KMn04 go about as oxidizing specialists. (b) KMnO4 oxidizes HCl into Cl2 which is likewise an oxidizing specialist. (c) KMnO4 is a more fragile oxidizing specialist than HCl. (d) KMnO4 goes about as a decreasing specialist within the sight of HCl.
Solution: (b) HCl isn't utilized to make the medium acidic in oxidation responses of KMnO4 in acidic medium. The explanation is that in case HCl is utilized, the oxygen delivered from KMnO4 + HCl is...
In spite of the fact that zirconium has a place with 4d change series and hafnium to 5d change series and still, after all that they show comparative physical and substance properties in light of the fact that (a) both have a place with d-block (b) both have same number of electrons (c) both have comparative nuclear span (d) both have a place with a similar gathering of the intermittent table
Solution: (c) Zirconium and hafnium have comparable nuclear range thus they show comparable physical and synthetic properties.
Most elevated oxidation condition of manganese in fluoride is +4 (MnF4) however most noteworthy oxidation state in oxides is +7 (Mn2O7) in light of the fact that (a) fluorine is more electronegative than oxygen (b) fluorine doesn’t have d-orbitals (c) fluorine settles lower oxidation state (d) in covalent mixtures fluorine can frame single bond just while oxygen shapes twofold bond
Solution: (d) The most noteworthy oxidation condition of manganese in fluoride is +4 (MnF4) yet in oxides it is +7 (Mn2O7) in light of the fact that in covalent mixtures fluorine can frame single...
