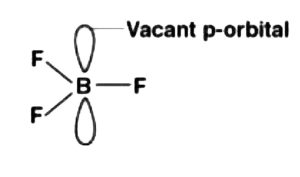
Solution:
The electronic arrangement of boron is ![]() . It contains 3 electrons in its valence shell. In this way, it can frame just 3 covalent bonds which imply that there are just 6 electrons around boron and its octet stays inadequate. At the point when 1 of the boron’s iota consolidates with 3 fluorine particles, its octet (8) stays fragmented. In this way, boron trifluoride remains electron-lacking and goes about as Lewis corrosive.
. It contains 3 electrons in its valence shell. In this way, it can frame just 3 covalent bonds which imply that there are just 6 electrons around boron and its octet stays inadequate. At the point when 1 of the boron’s iota consolidates with 3 fluorine particles, its octet (8) stays fragmented. In this way, boron trifluoride remains electron-lacking and goes about as Lewis corrosive.