Solution: The difference in electronegativity between constituent atoms determines the ionic character of a molecule. As a result, the greater the difference, the greater the ionic character of a...
Arrange the bonds in order of increasing ionic character in the molecules: LiF,
Explain with the help of suitable example polar covalent bond.
Solution: The bond pair of electrons are not shared equally when two unique atoms with different electronegativities join to form a covalent bond. The bond pair is attracted to the nucleus of an...
Define electronegativity. How does it differ from electron gain enthalpy?
Solution: "Electronegativity refers to an atom's ability to attract a bond pair of electrons towards itself in a chemical compound." Sr. No Electronegativity Electron affinity 1 A tendency to...
Write the significance/applications of dipole moment.
Solution: There is a difference in electro-negativities of constituents of the atom in a heteronuclear molecule, which causes polarisation. As a result, one end gains a positive charge, while the...
Although both 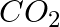 and
and 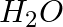 are triatomic molecules, the shape of the
are triatomic molecules, the shape of the 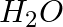 molecule is bent while that of
molecule is bent while that of 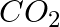 is linear. Explain this on the basis of dipole moment.
is linear. Explain this on the basis of dipole moment.
Solution: $CO_2$ has a dipole moment of 0 according to experimental results. And it's only possible if the molecule's shape is linear, because the dipole moments of the C-O bond are equal and...
Use Lewis symbols to show electron transfer between the following atoms to form cations and anions :(iii) Al and N.
Solution: Below is a list of Lewis symbols. To form a cation, a metal atom loses one or more electrons, while a nonmetal atom gains one or more electrons. Ionic bonds are formed between cations and...
Use Lewis symbols to show electron transfer between the following atoms to form cations and anions : (i) K and S (ii) Ca and O
Solution: Below is a list of Lewis symbols. To form a cation, a metal atom loses one or more electrons, while a nonmetal atom gains one or more electrons. Ionic bonds are formed between cations and...
Write the resonance structures for 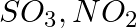 , and
, and 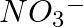
Solution: Resonance is the phenomenon that allows a molecule to be expressed in multiple ways, none of which fully explain the molecule's properties. The molecule's structure is called a resonance...
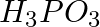 can be represented by structures 1 and 2 shown below. Can these two structures be taken as the canonical forms of the resonance hybrid representing
can be represented by structures 1 and 2 shown below. Can these two structures be taken as the canonical forms of the resonance hybrid representing 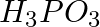 ? If not, give reasons for the same.
? If not, give reasons for the same.
Solution: The positions of the atoms remain constant in canonical forms, but the positions of the electrons change. The positions of atoms change in the given canonical forms. As a result, they...
Explain the important aspects of resonance with reference to the 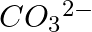 ion.
ion.
Solution: However, while the carbonate ion cannot be represented by a single structure, the properties of the ion can be described by two or more different resonance structures. The actual structure...
Define Bond length.
Solution: Bond length is defined as the equilibrium distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule.
How do you express the bond strength in terms of bond order?
Solution: During the formation of a molecule, the extent of bonding that occurs between two atoms is represented by the bond strength of the molecule. As the bond strength increases, the bond...
Although geometries of  and
and  molecules are distorted tetrahedral, bond angle in water is less than that of Ammonia. Discuss.
molecules are distorted tetrahedral, bond angle in water is less than that of Ammonia. Discuss.
Solution: Ammonia's central atom (N) has one lone pair and three bond pairs. In water, the central atom (O) has two lone pairs and two bond pairs. As a result, the two bond pairs repel the two lone...
Discuss the shape of the following molecules using the VSEPR model: 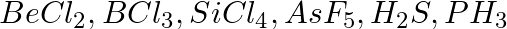
Solution: $BeCl_2$ The central atom does not have a lone pair, but it does have two bond pairs. As a result, its shape is AB2, or linear. $BCl_3$ The central atom has three bond pairs but no lone...
Write the favourable factors for the formation of an ionic bond.
Solution: Ionic bonds are formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another. As a result, the ability of neutral atoms to lose or gain electrons is required for the...
Define the octet rule. Write its significance and limitations
Solution: “Atoms can combine either by transferring valence electrons from one atom to another or by sharing their valence electrons in order to achieve the closest inert gas configuration by having...
Draw the Lewis structures for the following molecules and ions : 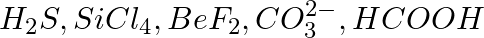
Solution: The lewis dot structures are:
Write Lewis symbols for the following atoms and ions: Sand 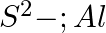 and
and 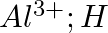 and
and 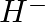
Solution: For S and S2- A sulphur atom has only 6 valence electrons, which is a very small number. As a result, the Lewis dot symbol for the letter S is The presence of a...
Write Lewis dot symbols for atoms of the following elements :e) N f) Br
Solution: Nitrogen atoms have only five valence electrons in total. As a result, the Lewis dot symbol for N is Bromine, because the atom has only seven valence electrons. As a result,...
Write Lewis dot symbols for atoms of the following elements :c) B d) O
Solution: Boron atoms have only three valence electrons, which is a very small number. As a result, the Lewis dot symbols for B are as follows: The oxygen atom has only six valence...
Write Lewis dot symbols for atoms of the following elements :
a) Mg
b) Na
Solution: Only two valence electrons exist in the magnesium atom. As a result, the Lewis dot symbols for Mg are as follows: Only one valence electron exists in the sodium atom. As a...
Explain the formation of a chemical bond.
Answer: "A chemical bond is an attractive force that holds a chemical species' constituents together." For chemical bond formation, many theories have been proposed, including valence shell electron...
If the starting material for the manufacture of silicones is RSiCl3, write the structure of the product formed.
Solution:
Elements of group 14 (a) exhibit oxidation state of 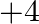 only (b) exhibit oxidation state of
only (b) exhibit oxidation state of 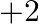 and
and 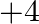 (c) form
(c) form 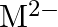 and
and 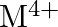 ion (d) form
ion (d) form 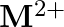 and
and 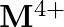 ions
ions
Solution: (b) Group 14 components have 4 valence electrons. Thus, bunch oxidation status is $+4$. In any case, the lower oxidation state turns out to be progressively steady because of the inactive...
An aqueous solution of borax is 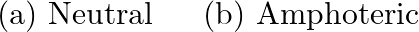

Solution: (b) Borax is a strong base salt (NaOH) and a feeble corrosive $\left(\mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{BO}_{3}\right)$. In this way, it is essential thing in nature.
Give one method for industrial preparation and one for laboratory preparation of CO and 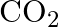 each.
each.
Solution: Carbon dioxide CO2 can be ready in the lab through the activity of weaken hydrochloric corrosive on calcium carbonate. Their response is as per the following: CO2 is industrially ready by...
Write balanced equations for: 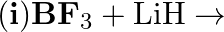 (ii)
(ii) 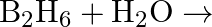 (iii)
(iii) 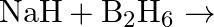 (iv)
(iv) 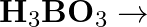 (v)
(v) 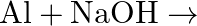 (vi)
(vi) 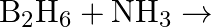
Solution: The balanced equations are as follow:
A certain salt 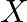 gives the following results. (i) Its aqueous solution is alkaline to litmus. (ii) It swells up to a glassy material
gives the following results. (i) Its aqueous solution is alkaline to litmus. (ii) It swells up to a glassy material 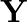 on strong heating. (iii) When conc.
on strong heating. (iii) When conc. 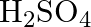 is added to a hot solution of
is added to a hot solution of 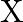 , a white crystal of an acid
, a white crystal of an acid 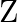 separates out Write equations for all the above reactions and identify X,
separates out Write equations for all the above reactions and identify X, 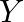 , and
, and 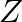 .
.
Solution: The salt given to litmus is antacid. $X$ is, subsequently, a salt with a solid base, and a feeble corrosive. When $X$ is warmed unnecessarily, it additionally enlarges to frame material...
When metal 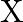 is treated with sodium hydroxide, a white precipitate (A) is obtained, which is soluble in excess of
is treated with sodium hydroxide, a white precipitate (A) is obtained, which is soluble in excess of 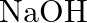 to give soluble complex (B). Compound (A) is soluble in dilute HCI to form compound (C). The compound (A) when heated strongly gives (D), which is used to extract the metal. Identify (X), (A), (B), (C) and (D). Write suitable equations to support their identities.
to give soluble complex (B). Compound (A) is soluble in dilute HCI to form compound (C). The compound (A) when heated strongly gives (D), which is used to extract the metal. Identify (X), (A), (B), (C) and (D). Write suitable equations to support their identities.
Solution: The given metal $X$ gives sodium hydroxide to a white accelerate, and the encourage breaks up surpassing sodium hydroxide. $X$ must, consequently, be made of aluminum. The acquired white...
(a) Classify the following oxides as neutral, acidic, basic or amphoteric. 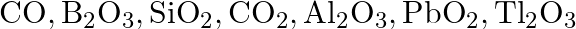 (B) Write suitable equations to show their nature.
(B) Write suitable equations to show their nature.
Solution: $\rightarrow$ CO $=$ Neutral $\rightarrow \mathrm{B}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}=$ Acidic Being acidic, it responds with bases to frame salts. It responds with $\mathrm{NaOH}$ to frame sodium...
What are allotropes? Sketch the structure of two allotropes of carbon namely diamond and graphite. What is the impact of structure on the physical properties of two allotropes?
Solution: Allotropy is the presence of a component in more than one structure, having diverse actual properties however similar substance properties. Diamond's solid 3-D construction makes it a...
How would you explain the lower atomic radius of Ga as compared to Al?
Solution: A tomic sweep (in pm) Aluminum Gallium In spite of the fact that Ga has more than one shell than Al, it is more modest in size than Al. This is on the grounds that the $3 \mathrm{~d}$...
Explain why is there a phenomenal decrease in ionization enthalpy from carbon to silicon?
Solution: Carbon ionizing enthalpy (the primary component in bunch 14 ) is exceptionally high $(1086 \mathrm{~kJ}/\mathrm{mol})$. That is normal on account of its little size. Nonetheless, there is...
Explain the following reactions (a) Silicon is heated with methyl chloride at high temperature in the presence of copper; (b) Silicon dioxide is treated with hydrogen fluoride; (c) CO is heated with ZnO; (d) Hydrated alumina is treated with aqueous 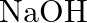 solution.
solution.
Solution: (a) Silicon is warmed with methyl chloride at high temperature within the sight of copper A class of organosilicon polymers called methyl-subbed chlorosilane $\mathrm{MeSiCl}_{3},...
What happens when (a) Borax is heated strongly (b) Boric acid is added to water (c) Aluminum is treated with dilute NaOH (d) 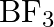 is reacted with ammonia?
is reacted with ammonia?
Solution: (a) Borax is warmed firmly Borax goes through different changes when warmed. It is losing atoms and expands of water right away. Then, at that point, it turns into a clear fluid, which...
Explain the structures of diborane and boric acid.
Solution: (a) Diborane $\mathrm{B}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{6}$ is a compound that does not have an electron. $\mathrm{B}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{6}$ just has 12 electrons $-6 \mathrm{e}^{-}$of $6 \mathrm{H}$...
Aluminium trifluoride is insoluble in anhydrous HF but dissolves when NaF is added. It precipitates out of the resulting solution when gaseous 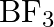 (boron trifluoride) is bubbled through. Give reasons.
(boron trifluoride) is bubbled through. Give reasons.
Solution: Hydrogen fluoride is a covalent compound with an exceptionally solid intermolecular clinging to hydrogen. Along these lines, it doesn't give particles and doesn't break up aluminum...
If B-CI bond has a dipole moment, explain why 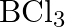 molecule has zero dipole moment.
molecule has zero dipole moment.
Solution: The $B-C l$ bond is normally polar as a result of the distinction in the electronegativities of $\mathrm{Cl}$ and $B$. However the particle of $\mathrm{BCl}_{3}$ is non-polar. That is on...
Suggest reasons why the B-F bond lengths in 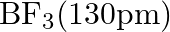 and
and 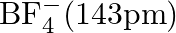 differ.
differ.
Solution; In $\mathrm{BF}_{3}$, the length of the $\mathrm{B}-\mathrm{F}$ bond is more limited than that of the $\mathrm{B}-\mathrm{F}$ bond in $\mathrm{BF}_{4}^{-} \cdot \mathrm{BF}_{3}$ is an...
Rationalize the given statements and give chemical reactions: – Lead (II) chloride reacts with 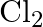 to give
to give 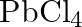 . – Lead (IV) chloride is highly unstable towards heat. – Lead is known not to form an iodide,
. – Lead (IV) chloride is highly unstable towards heat. – Lead is known not to form an iodide, 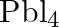 .
.
Solution: - Lead is an individual from bunch 14 of the occasional table. The two oxidation situations with bunch shows are $+2$ and $+4$. The $+2$ oxidation state turns out to be more steady when...
Explain the difference in properties of diamond and graphite on the basis of their structures.
Solution: Diamond: 1. It has a glasslike grid 2. In precious stone, every carbon molecule is sp3 hybridized and attached to four other carbon particles through a sigma bond. 3. It has an unbending...
What is the state of hybridisation of carbon in (a) 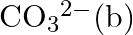 diamond (c) graphite?
diamond (c) graphite?
Solution: The condition of hybridization of carbon in: (a) $C O_{3}^{2-}$ c in $\mathrm{CO}_{3}^{2-}$ is sp $^{2}$ hybridized and is attached to 3 oxygen iotas. (b) Diamond Every precious stone...
Write the resonance structures of 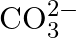 and
and 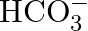 .
.
Solution: For $C O_{3}^{2-}$ There are just 2 resounding designs for the bicarbonate particle. For $\mathrm{HCO}_{3}^{-}$
Write reactions to justify amphoteric nature of aluminium
Solution: Amphoteric substances will be substances that display both acidic and essential characteristics. Since aluminum breaks up in the two acids and bases, it is said to have an amphoteric...
Describe the shapes of 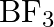 and
and 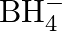 . Assign the hybridisation of boron in these species
. Assign the hybridisation of boron in these species
Solution: (I) $\mathbf{B} \boldsymbol{F}_{3}$ Boron will in general shape monomeric covalent halides in view of its little size and high electronegativity. These halides of boron generally have a...
Explain what happens when boric acid is heated .
Solution: After warming orthoboric corrosive at a temperature of $370 \mathrm{~K}$ or above, it is changed over into metaboric corrosive and, upon additional warming, yields boric oxide...
Is boric acid a protic acid? Explain.
Solution: Boric corrosive is a powerless monobasic corrosive which acts as a Lewis corrosive. In this way, it's anything but a protic corrosive. $\mathrm{B}(\mathrm{OH})_{3}+2 \mathrm{HOH}...
Consider the compounds, 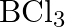 and
and 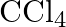 . How will they behave with water? Justify.
. How will they behave with water? Justify.
Solution: Since it is a Lewis corrosive, $\mathrm{BCl}_{3}$ promptly goes through hydrolysis to frame boric corrosive. $\mathrm{BCl}_{3}+3 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow 3...
Why does boron trifluoride behave as a Lewis acid?
Solution: The electronic arrangement of boron is $n s^{2} n p^{1}$. It contains 3 electrons in its valence shell. In this way, it can frame just 3 covalent bonds which imply that there are just 6...
How can you explain the higher stability of 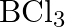 as compared to
as compared to 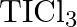 ?
?
Solution: Thallium and boron have a place with bunch 13 of the intermittent table and $+1$ oxidation state turns out to be more steady as we drop down the gathering. Boron is more steady than...
Discuss the pattern of variation in the oxidation states of (i) 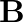 to
to 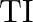 (ii)
(ii)  to
to 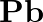
Solution: (I) $B$ to $\mathrm{TI}$ Gathering 13 components have their electronic design of $\mathrm{ns}^{2} \mathrm{np}^{1}$ and the oxidation state displayed by these components ought to be 3 ....
Depict the galvanic cell in which the reaction is:  Further show: (i) which of the electrode is negatively charged? (ii) the carriers of the current in the cell. (iii) individual reaction at each electrode.
Further show: (i) which of the electrode is negatively charged? (ii) the carriers of the current in the cell. (iii) individual reaction at each electrode.
Solution: The galvanic cell relating to the given redox response can be displayed as: $\mathrm{Zn}\left|Z n_{(a q)}^{2+} \| A g_{(a q)}^{+}\right| \mathrm{Ag}$ (I) Zn anode is contrarily charged on...
Given the standard electrode potentials, 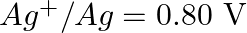
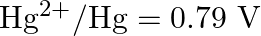
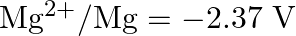
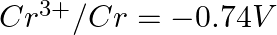 Arrange these metals in their increasing order of reducing power.
Arrange these metals in their increasing order of reducing power.
Solution: The diminishing specialist is more grounded as the terminal potential declines. Subsequently, the expanding request of the lessening force of the given metals is as given underneath: Ag...
Arrange the given metals in the order in which they displace each other from the solution of their salts. Al, Fe, Cu, Zn, Mg
Solution: A metal with more grounded diminishing force uproots one more metal with more vulnerable lessening power from its answer of salt. The request for the expanding diminishing force of the...
Predict the products of electrolysis in each of the following: (i) An aqueous solution of 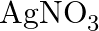 with silver electrodes (ii) An aqueous solution
with silver electrodes (ii) An aqueous solution 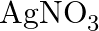 with platinum electrodes (iii) A dilute solution of
with platinum electrodes (iii) A dilute solution of 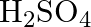 with platinum electrodes (iv) An aqueous solution of
with platinum electrodes (iv) An aqueous solution of 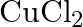 with platinum electrodes.
with platinum electrodes.
Solution: (I) In fluid arrangement, AgNO3 ionizes to give Ag+(aq) and NO3–(aq) particles. \[AgN03\left( aq \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }Ag+\left( aq \right)\text{ }+\text{ }NO3\left( aq...
Using the standard electrode potentials given in Table 8.1, predict if the reaction between the following is feasible: (a) 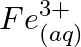 and
and 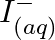 (b)
(b) 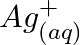 and
and 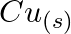 (c)
(c) 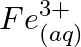 and
and 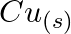 (d)
(d) 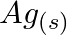 and
and 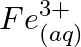 (e)
(e) 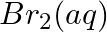 and
and 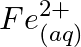
Solution: (a) $F e_{(a q)}^{3+}$ and $I_{(a q)}^{-}$ $2 F e_{(a q)}^{3+}+2 I_{(a q)}^{-} \rightarrow 2 F e_{(a q)}^{2+}+I_{2(s)}$ Oxidation half response: $2 I_{(a q)}^{-} \rightarrow I_{2}(s)+2...
In Ostwald’s process for the manufacture of nitric acid, the first step involves the oxidation of ammonia gas by oxygen gas to give nitric oxide gas and steam. What is the maximum weight of nitric oxide that can be obtained starting only with 10.00 g. of ammonia and 20.00 g of oxygen?
Solution: The reasonable response is as given underneath: $4 \mathrm{NH}_{3(g)}+5 \mathrm{O}_{2}(g) \rightarrow 4 \mathrm{NO}_{(g)}+6 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(g)}$ $4 N H_{3}=4 \times 17...
Refer to the periodic table given in your book and now answer the following questions: (a) Select the possible non – metals that can show disproportionation reaction? (b) Select three metals that show disproportionation reaction?
Solution: One of the responding components consistently has a component that can exist in somewhere around 3 oxidation numbers. (I) The non - metals which can show disproportionation responses are...
Chlorine is used to purify drinking water. Excess of chlorine is harmful. The excess of chlorine is removed by treating with sulphur dioxide. Present a balanced equation for this redox change taking place in water.
Solution: The redox response is as given beneath: Cl2(s)+SO2(aq)+H2O(l)→Cl(aq)-+SO4(aq)2- The oxidation half response: SO2(aq)→SO4(aq)2- Add 2 electrons to adjust the oxidation no. :...
The 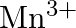 ion is unstable in solution and undergoes disproportionation to give
ion is unstable in solution and undergoes disproportionation to give 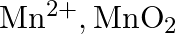 , and
, and 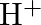 ion. Write a balanced ionic equation for the reaction.
ion. Write a balanced ionic equation for the reaction.
Solution: The response is as given beneath: $\mathrm{Mn}_{(a q)}^{3+} \rightarrow \mathrm{Mn}_{(a q)}^{2+}+\mathrm{MnO}_{2(s)}+\mathrm{H}_{(a q)}^{+}$ The oxidation half response: $\mathrm{Mn}_{(a...
What sorts of informations can you draw from the following reaction? 
Solution: The oxidation no. of $\mathrm{C}$ in $(C N)_{2}, C N^{-}$and $C N O^{-}$are $+3,+2$ and $+4$ separately. Let the oxidation no. of $\mathrm{C}$ be $\mathrm{y}$. $(C N)_{2}$ $2(y-3)=0$ Along...
Balance the following equations in basic medium by ion-electron method and oxidation number methods and identify the oxidising agent and the reducing agent. (a) 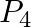 (s)
(s) 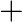
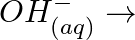
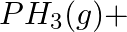
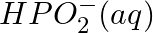 (b)
(b) 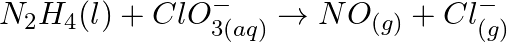 (c)
(c) 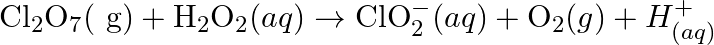
Solution:
Balance the following redox reactions by ion – electron method : (a) 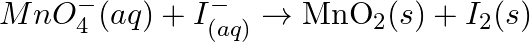 (Basic medium) (b)
(Basic medium) (b) 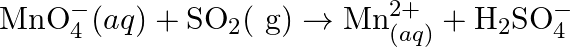 (Acidic medium) (c)
(Acidic medium) (c) 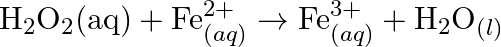 (Acidic medium) (d)
(Acidic medium) (d) 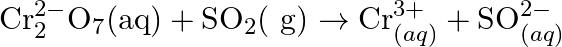 (Acidic medium)
(Acidic medium)
Solution: (a) $M n O_{4}^{-}(a q)+I_{(a q)}^{-} \rightarrow \operatorname{MnO}_{2}(s)+I_{2}(s)$ Stage 1 The two half responses are given beneath: Oxidation half response: $I_{(a q)} \rightarrow...
Consider the reactions: (a) 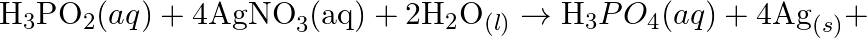
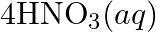 (b)
(b) 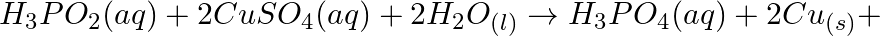
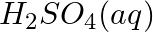 (c)
(c) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{CHO}_{(l)}+2\left[\mathrm{Ag}\left(\mathrm{NH}_{3}\right)_{2}\right]_{(a q)}^{+}+3 \mathrm{OH}_{(a q)}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{COO}_{(a q)}^{-}+2 \mathrm{Ag}_{(s)}+](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7aa1b43808014d89aabd5bf76808b357_l3.png)
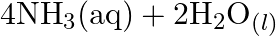 (d)
(d) 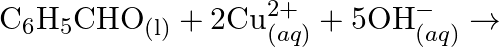 No change is observed What inference do you draw about the behavior of
No change is observed What inference do you draw about the behavior of 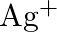 and
and 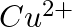 from these reactions?
from these reactions?
Solution: $\mathrm{Ag}^{+}$and $C u^{2+}$ acts as oxidizing specialist in responses (I) and (ii) individually. In response (iii), $\mathrm{Ag}^{+}$oxidizes $\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{5}...
Why does the following reaction occur?  What conclusion about the compound
What conclusion about the compound 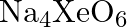 (of which
(of which 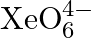 is a part) can be drawn from the reaction?
is a part) can be drawn from the reaction?
Solution: $X e O_{6(a q)}^{4-}+2 F_{(a q)}^{-}+6 H_{(a q)}^{+} \rightarrow X e O_{3(g)}+F_{2(g)}+3 H_{2} O_{(l)}$ The oxidation no. of Xe decreases from $+8$ in $\mathrm{XeO}_{6}^{4-}$ to $+6$ in...
Justify giving reactions that among halogens, fluorine is the best oxidant and among hydrohalic compounds, hydroiodic acid is the best reductant.
Solution: $F_{2}$ can oxidize $C l^{-}$to $C l_{2}, B r^{-}$to $B r_{2}$, and $I^{-}$to $I_{2}$ as: $F_{2(a q)}+2 C l_{(s)}^{-} \rightarrow 2 F_{(a q)}^{-}+C l_{2(g)}$ $F_{2}(a q)+2 B r_{(a q)}^{-}...
Consider the reactions : 
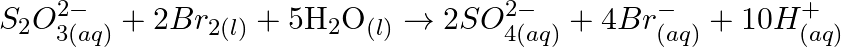 Why does the same reductant, thiosulphate react differently with iodine and bromine?
Why does the same reductant, thiosulphate react differently with iodine and bromine?
Solution: The normal oxidation no. of $\mathrm{S}$ in $\mathrm{S}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}^{2-}$ is $+2$. The normal oxidation no. of $\mathrm{S}$ in $S_{4} \mathrm{O}_{6}^{2-}$ is $+2.5$. The oxidation...
Identify the substance oxidised, reduced, oxidising agent and reducing agent for each of the following reactions: (a)  (b)
(b) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com H C H O_{(l)}+2\left[A g\left(N H_{3}\right)_{2}\right]_{(a q)}^{+}+3 O H_{(a q)}^{-} \rightarrow 2 A g_{(s)}+H C O O_{(a q)}^{-}+](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b8e4956dd6ca01b2ee5147606a038527_l3.png)
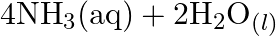 (c)
(c) 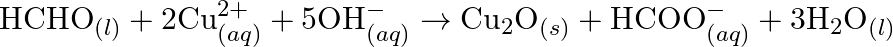 (d)
(d) 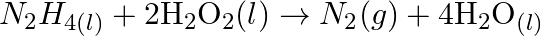 (e)
(e) 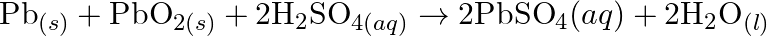
Solution: (a) $2 \mathrm{AgBr}_{(s)}+C_{6} H_{6} O_{2}(a q) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{Ag}_{(s)}+2 \mathrm{HBr}_{(a q)}+C_{6} \mathrm{H}_{4} O_{2}(a q)$ $\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{6}...
How do you count for the following observations? (a) Though alkaline potassium permanganate and acidic potassium permanganate both are used as oxidants, yet in the manufacture of benzoic acid from toluene we use alcoholic potassium permanganate as an oxidant. Why? Write a balanced redox equation for the reaction. (b) When concentrated sulphuric acid is added to an inorganic mixture containing chloride, we get colourless pungent smelling gas HCl, but if the mixture contains bromide then we get red vapour of bromine. Why?
Solution: (a) While producing benzoic corrosive from toluene, alcoholic potassium permanganate is utilized as an oxidant because of the given reasons. (I) In an impartial medium, $O H^{-}$ions are...
Whenever a reaction between an oxidisina adent and a reducina aqent is carried out, a compound of lower oxidation state is formed if the reducing agent is in excess and a compound of higher oxidation state is formed if the oxidising agent is in excess. J ustify this statement giving three illustrations. Justify the above statement with three examples.
Solution: When there is a response between lessening specialist and oxidizing specialist, a compound is framed which has lower oxidation number if the diminishing specialist is in abundance and a...
The compound 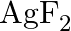 is unstable compound. However, if formed, the compound acts as a very strong oxidising agent. Why?
is unstable compound. However, if formed, the compound acts as a very strong oxidising agent. Why?
Solution: The oxidation no. of $A g$ in $A g F_{2}$ is $+2$. Be that as it may, $+2$ is entirely unsound oxidation no. of Ag. Consequently, when $A g F_{2}$ is framed, silver acknowledges an...
Consider the reactions: (a)  (b)
(b) 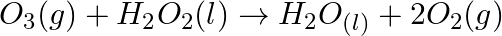 Why it is more appropriate to write these reactions as : (a)
Why it is more appropriate to write these reactions as : (a) 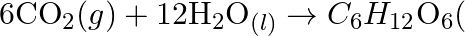 aq
aq 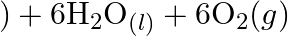 (b)
(b) 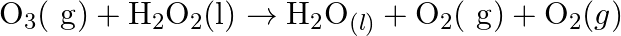 Also suggest a technique to investigate the path of the above (a) and (b) redox reactions
Also suggest a technique to investigate the path of the above (a) and (b) redox reactions
Solution: (a) Stage 1: $\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}$ breaks to give $\mathrm{H}_{2}$ and $\mathrm{O}_{2}$. $2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(\mathrm{l})} \rightarrow 2...
While sulphur dioxide and hydrogen peroxide can act as oxidising as well as reducing agents in their reactions, ozone and nitric acid act only as oxidants. Why?
Solution: In sulfur dioxide $\left(S O_{2}\right)$ the oxidation no. of $\mathrm{S}$ is $+4$ and the scope of oxidation no. of sulfur is from $+6$ to $-2$. Consequently, $S O_{2}$ can go about as a...
Suggest a list of substances where carbon can exhibit oxidation states from -4 to +4 and nitrogen from -3 to +5.
Solution: The compound where carbon has oxidation number from -4 to +4 are given below in the table:
Write formulas for the following compounds: (a) Mercury (II) chloride (b) Nickel (II) sulphate (c) Tin (IV) oxide (d) Thallium (I) sulphate (e) Iron (III) sulphate (f) Chromium (III) oxide
Solution: Formulas are: (a) Mercury (II) chloride $H g C l_{2}$ (b) Nickel (II) sulphate $\mathrm{NiSO}_{4}$ (c) Tin (IV) oxide $\mathrm{SnO}_{2}$ (d) Thallium (I) sulphate $\mathrm{Tl}_{2}...
Calculate the oxidation number of sulphur, chromium and nitrogen in H2SO5, Cr2O2 and NOT. Suggest structure of these compounds. Count for the fallacy. nitrogen in H2SO5, Cr2O2 and NOT. Suggest structure of these compounds. Count for the fallacy.
Solution: O.N. of S in H2SO5. By traditional strategy, the O.N. of S in H2SO5 is 2 (+1) + x + 5 (- 2) = 0 or x = +8 This is outlandish on the grounds that the most extreme O.N. of S can't be more...
Fluorine reacts with ice and results in the change:  Justify that this reaction is a redox reaction
Justify that this reaction is a redox reaction
Solution: $H_{2} O_{(s)}+F_{2}(g) \rightarrow H F_{(g)}+H O F_{(g)}$ In the above response, Oxidation no. of $\mathrm{H}$ and $\mathrm{O}$ in $\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}$ is $+1$ and $-2$...
Justify that the reactions is redox reactions: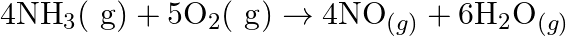
Solution: $4 \mathrm{NH}_{3(g)}+5 \mathrm{O}_{2}(g) \rightarrow 4 \mathrm{NO}_{(g)}+6 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(g)}$ In the above response, Oxidation no. of $\mathrm{N}$ and $\mathrm{H}$ in $N...
Justify that the reactions is redox reactions: 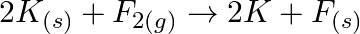
Solution: $2 K_{(s)}+F_{2(g)} \rightarrow 2 K+F_{(s)}$ In the above response, Oxidation no. of $\mathrm{K}$ is 0 . Oxidation no. of $F$ is 0 . Oxidation no. of $\mathrm{K}$ and $\mathrm{F}$ in...
Justify that the reactions is redox reactions: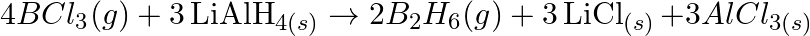
Solution: $4 \mathrm{BCl}_{3(g)}+3 \mathrm{LiAlH}_{4(s)} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{~B}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{6}(\mathrm{~g})+3 \mathrm{LiCl}_{(s)}+3 \mathrm{AlCl}_{3}(s)$ the above response, Oxidation no. of...
Justify that the reactions is redox reactions: 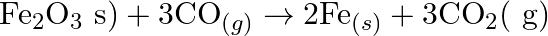
Solution: $\mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3(s)}+3 \mathrm{CO}_{(g)} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{Fe}_{(s)}+3 \mathrm{CO}_{2}(g)$ In the above response, Oxidation no. of Fe and $\mathrm{O}$ in $\mathrm{Fe}_{2}...
Justify that the reactions is redox reactions: 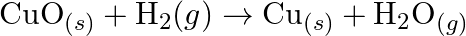
Solution: $\mathrm{CuO}_{(s)}+\mathrm{H}_{2}(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{Cu}_{(s)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(g)}$ Oxidation no. of $\mathrm{Cu}$ and $\mathrm{O}$ in $C u O$ is $+2$ and $-2$...
What are the oxidation number of the underlined elements and how do you rationalise your results?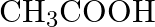
Solution: $\underline{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_{3} \underline{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{OOH}$ C2x+14O2 \mathrm{C}_{2}^{\mathrm{x}}+1_{4} \mathrm{O}_{2} Let $x$ be the oxidation no. of $C$. Oxidation...
What are the oxidation number of the underlined elements and how do you rationalise your results?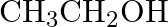
Solution: $\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{C} \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{OH}$ $$ $$ Let $x$ be the oxidation no. of $C$. Oxidation no. of $\mathrm{O}=-2$ Oxidation no. of $\mathrm{H}=+1$ Then, at that...
What are the oxidation number of the underlined elements and how do you rationalise your results?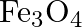
Solution: $\mathrm{Fe}_{3} \mathrm{O}_{4}$ Let $x$ be the oxidation no. of Fe. Oxidation no. of $0=-2$ Then, at that point, $3(x)+4(- 2)=0$ $3 x-8=0$ $x=\frac{8}{3}$ Oxidation no. can't be partial....
What are the oxidation number of the underlined element and how do you rationalise your results?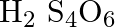
Solution: H2S4O6: Let x be the oxidation number of S. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Oxidation\text{ }no.\text{ }of\text{ }H\text{ }=\text{ }+1 \\ Oxidation\text{ }no.\text{ }of\text{ }O\text{ }=\text{...
What are the oxidation number of the underlined elements and how do you rationalise your results? 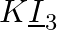
Solution: KI3: In KI3, the oxidation number (O.N.) of K is +1. Consequently, the normal oxidation number of I is Ncert Solutions Cbse Class 11-science Chemistry Chapter - Redox Reactions. In any...
Following results are observed when sodium metal is irradiated with different wavelengths. Calculate threshold wavelength and Planck’s constant.
If the threshold wavelength is $\lambda_{0} n m\left(=\lambda_{0} \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{~m}\right)$, the K.E. of the radiation would be: $ h\left(\nu-\nu_{0}\right)=\frac{1}{2} m \nu^{2} $ Three...
The work function for the caesium atom is 1.9 eV. Calculate
(a) the threshold wavelength and
(b) the threshold frequency of the radiation. If the caesium element is irradiated with a wavelength of 500 nm,(c) calculate the kinetic energy and the velocity of the ejected photoelectron.
Given, the work function of caesium $\left(W_{0}\right)=1.9 \mathrm{eV}$ (a)From the $W_{0}=\frac{h c}{\lambda_{0}}$ expression, we get: $\lambda_{0}=\frac{h c}{W_{0}}$ Where, $\lambda_{0}$ is the...
In astronomical observations, signals observed from the distant stars are generally weak. If the photon detector receives a total of  from the radiations of
from the radiations of 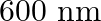 , calculate the number of photons received by the detector.
, calculate the number of photons received by the detector.
From the expression of energy of one photon (E), $ E=\frac{h c}{\lambda} $ Where, $\lambda$ denotes the wavelength of the radiation $\mathrm{h}$ is Planck's constant c denotes the velocity of the...
Neon gas is generally used in the signboards. If it emits strongly at 616 nm, calculate the number of quanta presents if it produces 2 J of energy.
No. quanta in $2 \mathrm{~J}$ of energy $\frac{2 J}{32.27 \times 10^{-20} J}$ $ =6.19 \times 10^{18} $ $ =6.2 \times 10^{18} $
Neon gas is generally used in the signboards. If it emits strongly at 616 nm, calculate the energy of quantum
Energy of one quantum $(E)=h v$ $ =\left(6.626 \times 10^{-34} \mathrm{Js}\right)\left(4.87 \times 10^{14} \mathrm{~s}^{-1}\right) $ Energy of one quantum $(\mathrm{E})=32.27 \times 10^{-20}...
Neon gas is generally used in the signboards. If it emits strongly at 616 nm, calculate distance travelled by this radiation in 30 s
Speed of the radiation, $\mathrm{c}=3 \times 10^{8} \mathrm{~ms}^{-1}$ Distance travelled by the radiation in a timespan of $30 \mathrm{~s}$ $ \begin{array}{l} =\left(3 \times 10^{8}...
Neon gas is generally used in the signboards. If it emits strongly at 616 nm, calculate the frequency of emission,
Wavelength of the emitted radiation $=616 \mathrm{~nm}=616 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{~m}$ (Given) (a)Frequency of the emission $(\nu)$ $ \nu=\frac{c}{\lambda} $ Where, $c=$ speed of the radiation...
Nitrogen laser produces radiation at a wavelength of 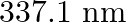 . If the number of photons emitted is
. If the number of photons emitted is 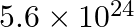 , calculate the power of this laser.
, calculate the power of this laser.
Energy with which it emits photons=Power of laser Power $=E=\frac{N h c}{\lambda}$ Where, $N=$ number of photons emitted $\mathrm{h}=$ Planck's constant $\mathrm{c}=$ velocity of radiation...
An ion with mass number 56 contains 3 units of positive charge and 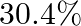 more neutrons than electrons. Assign the symbol to this ion.
more neutrons than electrons. Assign the symbol to this ion.
Let us consider the total no. electrons present in $A^{3+}$ be $x$. Now, total no. neutrons in it $=x+30.4 \%$ of $x=1.304 x$ Since the ion has a charge of $+3, \Rightarrow$ no. electrons in neutral...
An ion with mass number 37 possesses one unit of negative charge. If the ion contains 11.1% more neutrons than the electrons, find the symbol of the ion.
The number of electrons in a negatively charged ion be $x$. Then, no. neutrons present $=x+11.1 \%$ of $x=x+0.111 x=1.111 x$ No. electrons present in the neutral atom $=(x-1)$ (When an ion carries...
An element with mass number 81 contains 31.7% more neutrons as compared to protons. Assign the atomic symbol.
Let us consider that the No.of protons in the element be $x$. No. of neutrons $=x+31.7 \%$ of $x$ $=x+0.317 x$ $=1.317 x$ According to the question, Mass number of the element $=81$, which...
Symbols 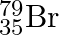 and
and 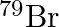 can be written, whereas symbols
can be written, whereas symbols 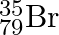 and
and 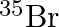 are not acceptable. Answer briefly.
are not acceptable. Answer briefly.
The general convention followed while representing elements along with their atomic masses (A), and their atomic numbers $(Z)$ is ${ }_{Z}^{A} \mathrm{X}$. Therefore, ${ }_{35}^{79} \mathrm{Br}$ is...
In Rutherford’s experiment, generally the thin foil of heavy atoms, like gold, platinum etc. have been used to be bombarded by the α-particles. If the thin foil of light atoms like Aluminium etc. is used, what difference would be observed from the above results?
The findings obtained with a foil made up of heavy atoms will differ from those obtained with a foil made up of comparatively light atoms. The magnitude of positive charge in the nucleus of a...
In Milikan’s experiment, the static electric charge on the oil drops has been obtained by shining 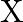 rays. If the static electric charge on the oil drop is
rays. If the static electric charge on the oil drop is  , calculate the number of electrons present on it.
, calculate the number of electrons present on it.
Charge held by the oil drop $=1.282 \times 10^{-18} C$ Charge held by one electron $=1.6022 \times 10^{-19} C$ Therefore, No. electrons present in the drop of oil $\frac{1.282 \times 10^{-18}...
A certain particle carries 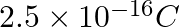 of static electric charge. Calculate the number of electrons present in it.
of static electric charge. Calculate the number of electrons present in it.
Charge held by one electron $=1.6022 \times 10^{-19} C \Rightarrow 1.6022 \times 10^{-19} C$ charge is held by one electron. Therefore, electrons carrying charge of $2.5 \times 10^{-16} C \quad...
The diameter of the zinc atom is 2.6Å. Calculate (a) radius of zinc atom in pm and (b) number of atoms present in a length of 1.6 cm if the zinc atoms are arranged side by side lengthwise.
Radius of carbon atom$ =\frac{2.6}{2} $ $ \begin{array}{l} =1.3 \times 10^{-10} \mathrm{~m} \\ =130 \times 10^{-12} \mathrm{~m}=130 \mathrm{pm} \end{array} $ (b) Length of the arrangement $=1.6...
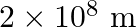 atoms of carbon are arranged side by side. Calculate the radius of carbon atom if th length of this arrangement is
atoms of carbon are arranged side by side. Calculate the radius of carbon atom if th length of this arrangement is 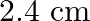 .
.
Length of the arrangement $=2.4 \mathrm{~cm}$ No. carbon atoms present $=2 \times 10^{8}$ The diameter of the carbon atom $=\frac{2.4 \times 10^{-2} m}{2 \times 10^{8} m}$ $=1.2 \times 10^{-10} m...
If the diameter of a carbon atom is 0.15 nm, calculate the number of carbon atoms which can be placed side by side in a straight line across the length of the scale of length 20 cm long.
We know that$ 1 \mathrm{~cm}=10^{-2} \mathrm{~m} $ Length of the scale $=20 \mathrm{~cm}=20 \times 10^{-2} \mathrm{~m}$ Diameter of one carbon atom $=0.15 \mathrm{~nm}=0.15 \times 10^{-9}...
Calculate the energy required for the process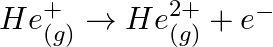 The ionization energy for the
The ionization energy for the  atom in the ground state is
atom in the ground state is 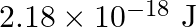 atom
atom 
The energy associated with hydrogen-like species is: $ E_{n}=-2.18 \times 10^{-18}\left(\frac{Z^{2}}{n^{2}}\right) J $ For the ground state of the hydrogen atom, $ \begin{array}{l} \Delta...
What transition in the hydrogen spectrum would have the same wavelength as the Balmer transition n = 4 to n = 2 of He+ spectrum?
The wave number associated with the Balmer transition for the He+ ion (n = 4 to n = 2 ) is given by: $ \bar{\nu}=\frac{1}{\lambda}=R Z^{2}\left(\frac{1}{n_{1}^{2}}-\frac{1}{n_{2}^{2}}\right) $...
Show that the circumference of the Bohr orbit for the hydrogen atom is an integral multiple of the de Broglie wavelength associated with the electron revolving around the orbit.
Only one electron exists in hydrogen atoms. The angular momentum of this electron, according to Bohr's postulates, is: $m v r=n \frac{h}{2 \pi} \quad \ldots .(1)$ Where, $n=1,2,3, \ldots$ As per de...
How many electrons in an atom may have the following quantum numbers?a) n = 4, 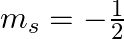 b)n = 3, l = 0
b)n = 3, l = 0
(a)The total number of electrons in the atom =$2n^2$ if n is the primary quantum number. Hence, For n = 4, Total no. electrons = 2 (16) = 32 An atom with 32 electrons has the following electron...
Using s, p and d notations, describe the orbital with the following quantum numbers.
(a)n = 1, l = 0;
(b)n = 3; l =1
(c) n = 4; l = 2;
(d) n = 4; l =3.
(a)n = 1, l = 0 implies a 1s orbital. (b)n = 3 and l = 1 implies a 3p orbital. (c)n = 4 and l = 2 implies a 4d orbital. (d)n = 4 and l = 3 implies a 4f orbital.
(I)An atomic orbital has n = 3. What are the possible values of l and ml ? (II)List the quantum numbers (ml and l) of electrons for 3d orbital. (III) Which of the following orbitals are possible? 1p, 2s, 2p and 3f
(I) The range of potential values for 'l' is 0 to (n – 1). As a result, the possible values of l for n = 3 are 0, 1, and 2. The total number of potential ml = (2l + 1) values. It has a range of...
Give the number of electrons in the species , 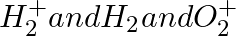
The number of electrons in H2 is 1 + 1 = 2. 2 – 1 = 1 number of electrons in H2+ H2: The number of electrons in H2 equals 1 + 1 = 2. Number of electrons in O2 = 8 + 8 = 16. In O2+, the number of...
An atom of an element contains 29 electrons and 35 neutrons. Deduce (i) the number of protons and (ii) the electronic configuration of the element.
(i)No.protons = no.electrons in a neutral atom. The number of protons in the atoms of the element is 29. (ii)The electronic configuration of this element (atomic number 29) is 1s...
An electron is in one of the 3d orbitals. Give the possible values of n, l and ml for this electron.
For the 3d orbital: Principal quantum number ,possible values (n) = 3 Azimuthal quantum number, possible values(l) = 2 Magnetic quantum number ,possible values(ml) = – 2, – 1, 0, 1, 2
(III) Which atoms are indicated by the following configurations? (a) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com [\mathrm{He}]{2} \mathrm{~s}^{1}](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-949e215e254ffdae25444046a6badfbf_l3.png)
 Ne]
Ne] 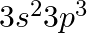 (c)
(c) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com [\mathrm{Ar}] 4 \mathrm{~s}^{2} 3 \mathrm{~d}^{1}](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c46b18eb49590f81f622e0747e88d18b_l3.png)
$(I I I)(a)[H e] 2 s^{1}$ Complete electronic configuration: $1 \mathrm{~s}^{2} 2 \mathrm{~s}{ }^{1}$. $\therefore$ the element's atomic number is 3 . The element is lithium (Li) (b) $[\mathrm{Ne}]...
(I)Write the electronic configurations of the following ions:(a) 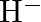 (b)
(b) 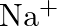 (c)
(c) 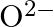 (d)
(d) 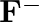
The electronic configuration of the Hydrogen atom (in its ground state) $1 \mathrm{~s}^{1}$. The single negative charge on this atom indicates that it has gained an electron. Hence, the electronic...
The mass of an electron is 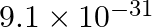 kg. If its K.E. is
kg. If its K.E. is J, calculate its wavelength.
J, calculate its wavelength.
As per de Broglie’s equation, $ \lambda=\frac{h}{m v} $ Given, K.E of electron $=3.0 \times 10^{-25} \mathrm{~J}$ $ \begin{array}{l} \text { Since K.E.= } \frac{1}{2} m v^{2} \therefore...
Calculate the wavelength of an electron moving with a velocity of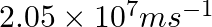
As per de Broglie’s equation, $ \lambda=\frac{h}{m v} $ Where, $\lambda$ denotes thr wavelength of the moving particle $\mathrm{m}$ is the mass of the particle $v$ denotes the velocity of the...
(i) The energy associated with the first orbit in the hydrogen atom is 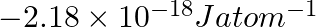 . What is the energy associated with the fifth orbit? (ii) Calculate the radius of Bohr’s fifth orbit for the hydrogen atom.
. What is the energy associated with the fifth orbit? (ii) Calculate the radius of Bohr’s fifth orbit for the hydrogen atom.
(i) Energy associated with the fifth orbit of hydrogen atom is calculated as: $E_{5}=\frac{-\left(2.18 \times 10^{-18}\right)}{(5)^{2}}=\frac{-\left(2.18 \times 10^{-18}\right)}{25}=-8.72 \times...
Why is Wurtz reaction not preferred for the preparation of alkanes containing odd number of carbon atoms? Illustrate your answer by taking one example
Solution: For the union of balanced alkanes (for example alkanes with a significantly number of carbon particles), the Wurtz response is restricted. Two comparative alkyl halides are taken as...
Out of benzene, m–dinitrobenzene and toluene, state the increasing order of nitration. Justify your answer?
Solution: The simplicity of nitration relies upon the presence of electron thickness on the compound to shape nitrates. Nitration responses are instances of electrophilic replacement responses where...
List the names of some Lewis acid which can be used during ethylation of benzene in a Friedel-Craft alkylation reaction.
Solution: The response of benzene to the presence of Lewis acids (AlCl3) with an acyl halide or corrosive anhydride yields acyl benzene (or benzene ring). A Friedel-Craft alkylation response is...
Arrange the following set of compounds in order of their increasing relative reactivity with an electrophile, E+ : p – H3C – C6H4 – NO2, Toluene, p-O2N – C6H4 – NO2.
Solution: Electrophiles are reagents that take part in a response by tolerating a couple of electrons to tie to nucleophiles. The higher the thickness of electrons on a benzene ring, the more...
Arrange the following set of compounds in order of their increasing relative reactivity with an electrophile, E+ p-nitrochlorobenzene, Chlorobenzene, 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene,
Solution: Electrophiles are reagents that take part in a response by tolerating a couple of electrons to tie to nucleophiles. The higher the thickness of electrons on a benzene ring, the more...
Write structures of all the alkenes which on hydrogenation give 2-methylbutane.
Solution: The fundamental design of 2-methylbutane is displayed beneath: Based on the above structure, different alkenes that will give 2-methylbutane on hydrogenation are displayed beneath: a) b)...
How would you convert the Hexane into benzene?
Solution: Hexane into benzene: When vapours of hexane are passed over heated catalyst consisting of Cr₂O3 MO₂O3, and V₂O5, at 773 K under 10-20 atm pressure, cyclization and aromatization occurs...
How would you convert the Ethene into benzene?
Solution: Ethene into benzene: Ethene is first converted inti Ethyne and then into benzene.
How would you convert Ethyne into benzene?
Solution: Ethyne into benzene:
What do you understand by the term : Fuel cell?
Solution: Fuel cell: Energy components are gadgets for creating power from fuel within the sight of an electrolyte. Dihydrogen can be utilized as a fuel in these cells. It is liked over different...
What do you understand by the term :Water-gas shift reaction
Solution: Water-gas shift response: It is a response of carbon monoxide of syngas blend with steam within the sight of an impetus as: $\mathrm{CO}_{(g)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(g)} \rightarrow...
What do you understand by the term :‘syngas’
Solution: 'syngas': Syngas is a combination of carbon monoxide and dihydrogen. Since the combination of the two gases is utilized for the blend of methanol, it is called syngas amalgamation gas, or...
What do you understand by the term :Hydrogenation
Solution: Hydrogenation: The method involved with adding dihydrogen to one more reactant is known as hydrogenation. It is utilized to decrease a compound within the sight of appropriate impetus. For...
What do you understand by the terms: Hydrogen economy ?
Solution: Hydrogen economy: Dihydrogen delivers more energy than petroleum and is more eco-accommodating. Subsequently, it tends to be utilized in energy units to create electric force. Hydrogen...
Do you expect different products in solution when aluminium (III) chloride and potassium chloride treated separately with (i) alkaline water (ii) acidified water, and (iii) normal water. Write equations wherever necessary.
Solution: Potassium chloride $(\mathrm{KCl})$ is the salt of a solid corrosive $(\mathrm{HCl})$ and solid base (KOH). Consequently, it is nonpartisan in nature and doesn't go through hydrolysis in...
What do you expect the nature of hydrides is, if formed by elements of atomic numbers 15,19, 23 and 44 with dihydrogen? Compare their behaviour with water.
Solution: The components of nuclear numbers 15 is phosphorus, 19 potassium, 23 is vanadium and 44 is ruthenium Hydride of Phosphorus Hydride of phosphorus $\left(\mathrm{PH}_{3}\right.$ ) is...
How can saline hydrides remove traces of water from organic compounds?
Solution: Normally, saline hydrides are ionic. Saline hydrides responds with water which brings about the arrangement of metal hydroxide alongside hydrogen gas freedom. It is addressed as, $A...
What is the difference between the terms ‘hydrolysis’ and ‘hydration’?
Solution: Hydration: The expansion of at least 1 atoms to a particle or particle which brings about arrangement of hydrated mixtures is known as hydration. For example $\mathrm{CuSO}_{4}+5...
Write chemical reactions to justify that hydrogen peroxide can function as an oxidising as well as reducing agent.
Solution: Hydrogen peroxide goes about as an oxidizing specialist just as diminishing specialist in both basic medium and acidic medium. The response which are associated with oxidizing activities...
Write chemical reactions to show the amphoteric nature of water
Solution: The amphoteric idea of water can be depicted based on the accompanying responses: 1) Reaction with $\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S}$ The response happens as: $\mathrm{H}_{2}...
Discuss the principle and method of softening of hard water by synthetic ionexchange resins.
Solution: The method involved with treating extremely durable hardness of water utilizing engineered saps commonly based or trade of anions and cations present in water by $\mathrm{OH}^{-}$and...
Complete the following chemical reactions. (i) 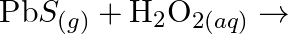 (ii)
(ii) 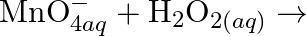 (iii)
(iii) 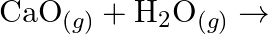 (iv)
(iv) 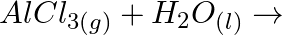 (v)
(v) 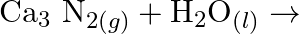 Classify the above into (a) Hydrolysis, (b) Redox and (c) Hydration reactions.
Classify the above into (a) Hydrolysis, (b) Redox and (c) Hydration reactions.
Solution: (I) $\mathrm{PbS}_{(g)}+4 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2(a q)} \rightarrow \mathrm{PbSO}_{4(s)}+4 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(l)}$ $\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2}$ is going about as an...
Consider the reaction of water with 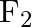 and suggest, in terms of oxidation and reduction, which species are oxidized/reduced.
and suggest, in terms of oxidation and reduction, which species are oxidized/reduced.
Solution: The response among water and fluorine can be addressed as: $2 F_{2(g)}+2 H_{2} O_{(l)} \rightarrow 4 H_{(a q)}^{+}+4 F_{(a q)}^{-}+O_{2(g)}$ This is an illustration of redox response $2...
What do you understand by the term ‘auto-protolysis’ of water? What is its significance?
Solution: Auto-protolysis (self-ionization) of water is a compound response wherein 2 water atoms respond to deliver a hydroxide particle $\left(\mathrm{OH}^{-}\right)$and a hydronium particle...
Saline hydrides are known to react with water violently producing fire. Can 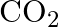 , a well known fire extinguisher, be used in this case? Explain.
, a well known fire extinguisher, be used in this case? Explain.
Solution: Saline hydrides [i.e.,LiH, NaH etc.] respond with water to shape hydrogen gas Furthermore, a base. The synthetic condition to address this response is $M H_{(g)}+H_{2} O_{(a q)}...
What characteristics do you expect from an electron-deficient hydride with respect to its structure and chemical reactions?
Solution: To shape an ordinary bond, an electron-lacking hydride doesn't have adequate electrons in which 2 electrons are shared by 2 particles. e.g., $B_{2} H_{6}$ $\mathrm{Al}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{6}$...
Complete the following reactions: (i) 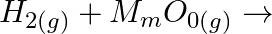 (ii)
(ii) 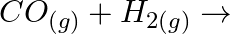 (iii)
(iii) 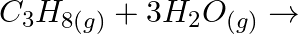 (iv)
(iv) 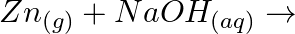
Solution: (i) $H_{2(g)}+M_{m} O_{0(g)} \rightarrow m M_{(s)}+H_{2} O_{(l)}$ (ii) $\mathrm{CO}_{(g)}+\mathrm{H}_{2(g)} \rightarrow \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{OH}_{(l)}$ (iii) $\mathrm{C}_{3}...
Describe the bulk preparation of dihydrogen by electrolytic method. What is the role of an electrolyte in this process?
Solution: The readiness of di hydrogen is by the electrolysis of fermented or soluble water utilizing platinum anodes Generally, $15-20 \%$ of a corrosive $\left(\mathrm{H}_{2}...
Write the names of isotopes of hydrogen. What is the mass ratio of these isotopes?
Solution: 3-isotopes are: (i) tritium ${ }_{1}^{3} H$ or $\mathrm{T}$ (ii) protium ${ }_{1}^{3} H$ (iii) deuterium ${ }_{1}^{2} H$ or $\mathrm{D}$ Mass Ratio: Tritium : Protium : deuterium $=1: 2:...
Explain the terms inductive and electromeric effects. Which electron displacement effect explain the following correct orders of acidity of the carboxylic acids? (a) Cl3CCOOH > Cl2CHCOOH > ClCH2 COOH (b) CH3CH2COOH > (CH3)2 CHCOOH > (CH3)3CCOOH
Solution: Inductive Effect: The inductive impact alludes to the extremity delivered in a particle because of higher electronegativity of one molecule contrasted with another.Atoms or gatherings...
For the following bond cleavage, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
Solution: The bond cleavage can be displayed as: It goes under heterolytic cleavage since the common remaining parts with one of the sections. A carbocation is framed as the response middle.
For the following bond cleavage, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
Solution: The bond cleavage can be displayed as: It goes under heterolytic cleavage since the common remaining parts with the bromine particle. A carbocation is framed as the response...
For the following bond cleavage, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
Solution: The bond cleavage can be displayed as: It goes under heterolytic cleavage since the common remaining parts with the carbon molecule of propanone. A carbanion is framed as the response...
For the following bond cleavage, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
Solution: The bond cleavage can be displayed as: It goes under homolytic cleavage since one of the common pair in a covalent bond goes with the reinforced molecule. A free revolutionary is framed as...
What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of structures? Are they structural or geometrical isomers or resonance contributors?
Solution: The given mixtures are a pair of contributing constructions or authoritative structures. They don't address any genuine particle and are absolutely speculative. They are additionally...
What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of structures? Are they structural or geometrical isomers or resonance contributors?
Solution: The given mixtures are a pair of mathematical isomers since they have a similar molecular formulas, succession of covalent bonds and a similar constitution yet vary in the general...
What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of structures? Are they structural or geometrical isomers or resonance contributors? following pairs of structures? Are they structural or geometrical isomers or resonance contributors?
Solution: The given mixtures are a pair of primary isomers since they have a similar molecular formula yet have various structures. These mixtures vary in the situation of the ketone bunch. For the...
Draw the resonance structures for ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{C}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{3}}}\mathbf{CH}=\mathbf{CHCH}2\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6637624364ee1ee04d838ff239050994_l3.png)
. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
Solution: \[\mathbf{C}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{3}}}\mathbf{CH}=\mathbf{CHCH}2\] Resonating structures:
Draw the resonance structure for the compound C6H5CH2. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
Solution: C6H5CH2 Resonating structures:
Draw the resonance structure for the compound C6H5—CHO. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
Solution: structure of C6H5CHO: Resonating structures:
Draw the resonance structure for the compound CH3CH=CHCHO. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
Solution: \[C{{H}_{3}}CH\text{ }=\text{ }CH\text{ }\text{ }CHO\] Resonating structures:
Draw the resonance structure for the compound C6H5N02. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
Solution: structure of C6H5NO2: Resonating structures:
Draw the resonance structure for the compound C6H5OH . Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
Solution: structure of C6H5OH : Resonating structures:
Explain why alkyl groups act as electron donors when attached to a π system.
Solution: Because of hyperconjugation, an alkyl bunch acts as an electron-benefactor bunch when joined to a π framework. For instance, take a gander at propene. The sigma electrons of the C-H bond...
Identify the functional groups in the compound:
Solution: Nitro (–NO2), C=C Ethylenic Alkene
Identify the functional groups in the compound:
Solution: \[~Ester\text{ }-\left( O\text{ }=\text{ }C\text{ }\text{ }O \right)-,\text{ }{{1}^{o}}Amino\text{ }\left( N{{H}_{2}} \right)\text{ }\left( aromatic \right),\text{ }Diethylamine\text{...
Identify the functional groups in the compound.
Solution: Hydroxyl (–OH), Aldehyde (–CHO), Methoxy (–OMe), C=C double bond
Give condensed and bond line structural formulas and identify the functional group(s) present, if any, for: Hexanedial.
Solution: Hexanedial Condensed Formula: \[\left( CHO \right){{\left( C{{H}_{2}} \right)}_{4}}\left( CHO \right)\] Bond line formula: Functional groups: Aldehyde (-CHO) group
Give condensed and bond line structural formulas and identify the functional group(s) present, if any, for: 2-Hydroxy-l, 2, 3-propanetricarboxylic acid
Solution: 2–hydroxy–1, 2, 3–propanetricarboxylic acid Condensed Formula: \[\left( COOH \right)C{{H}_{2}}C\left( OH \right)\text{ }\left( COOH \right)C{{H}_{2}}\left( COOH \right)\] Bond line...
Give condensed and bond line structural formulas and identify the functional group(s) present, if any, for : 2,2,4-Trimethylpentane
Solution: 2, 2, 4–trimethylpentane Condensed formula: \[{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}CHC{{H}_{2}}C\text{ }{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}\] Bond line formula : Functional group: no functional...
Give the IUPAC name of the compound :Cl2CHCH2OH
Solution: 2, 2–dichloroethanol
Give the IUPAC name of the compound :
Solution: 3–chloropropanal
Give the IUPAC name of the compound :
Solution: 3–bromo–3–chloroheptane
Give the IUPAC name of the compound :
Solution: 2, 5–dimethyl heptane
Give the IUPAC name of the compound :
Solution: 3–methylpentanenitrite
Give the IUPAC name of the compound:
Solution: Propylbenzene
Write bond line formula for : Heptan–4–one
Solution: Bond line formula for Heptan–4–one:
Write bond line formula for : 2, 3–dimethyl butanal
Solution: Bond line formula for 2, 3–dimethyl butanal :
Write bond line formula for :Isopropyl alcohol
Solution: Bond line formula for Isopropyl alcohol:
Indicate sigma (σ) and pi (Π) bonds in the molecule :HCONHCH3
Solution: HCONHCH3 There are four C–H sigma bonds, two C–N sigma bond, one N–H sigma bond, and one C=O pi bond in the given compound.
Indicate sigma (σ) and pi (Π) bonds in the molecule :CH3NO2
Solution: CH3NO2 There are three C–H sigma bonds, one C–N sigma bond, one N–O sigma bond, and one N=O pi bond in the given compound.
Indicate sigma (σ) and pi (Π) bonds in the molecule :CH2 = C = CH2
Solution: CH2 = C = CH2 There are two C–C sigma bonds, four C–H sigma bonds, and two C=C pi bonds in the given compound.
Indicate sigma (σ) and pi (Π) bonds in the molecule :CH2Cl2
Solution: CH2Cl2 There are two C – Cl sigma bonds and two C–H sigma bonds in the given compound.
Indicate the σ and π bonds in the molecule:C6H12
Solution: C6H12 There are six C – C sigma bonds and twelve C–H sigma bonds in the given compound.
Indicate the σ and π bonds in the following molecules:C6H6
Solution: C6H6 There are six C – C sigma bonds, six C–H sigma bonds, and three C=C pi resonating bonds in the given compound.
Using the definition, prove that the function f : A→ B is invertible if and only if f is both one-one and onto.
Let us consider f: A → B be many-one function. Let us consider f(a) = p and f(b) = p So, for inverse function we will have \[{{f}^{-1}}\left( p \right)\text{ }=\text{ }a\] and \[{{f}^{-1}}\left( p...
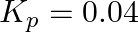 atm at
atm at 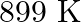 for the equilibrium shown below. What is the equilibrium concentration of
for the equilibrium shown below. What is the equilibrium concentration of  when it is placed in a flask at
when it is placed in a flask at 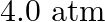 pressure and allowed to come to equilibrium?
pressure and allowed to come to equilibrium? 
Answer: At equilibrium, the pressure exerted by ethane and hydrogen gas (each) is given by the symbol p. Now, according to the reaction, C2H6 (g) ↔ C2H4 (g) + H2 (g) Initial conc. 4.0atm ...
What is the equilibrium concentration of each of the substances in the equilibrium when the initial concentration of ICI was 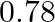 M?
M? 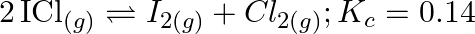
Answer: The equilibrium constant, Kc, is defined as the product of the equilibrium concentrations of products over the equilibrium concentrations of reactants, each raised to the power of the...
At 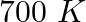 , equilibrium constant for the reaction
, equilibrium constant for the reaction 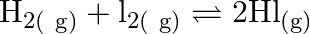 is
is 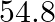 . If
. If  of
of 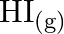 is present at equilibrium at
is present at equilibrium at 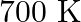 , what are the concentration of
, what are the concentration of 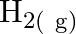 and
and 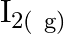 assuming that we initially started with
assuming that we initially started with 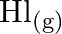 and allowed it to reach equilibrium at
and allowed it to reach equilibrium at 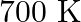 ?
?
Answer: It is given that equilibrium constant $\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{c}}$ for the reaction $\mathrm{H}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}+\mathrm{I}_{2(\mathrm{~g})} \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{HI}_{(\mathrm{g})}$ is...
One mole of 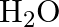 and one mole of
and one mole of 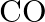 are taken in
are taken in 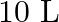 vessel and heated to
vessel and heated to 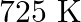 . At equilibrium,
. At equilibrium, 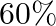 of water (by mass) reacts with
of water (by mass) reacts with 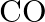 according to the equation,
according to the equation, 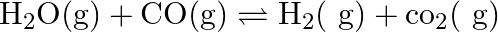 Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction.
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction.
Answer: As we know that the equilibrium constant, Kc, is defined as the product of the equilibrium concentrations of products over the equilibrium concentrations of reactants, each raised to the...
At 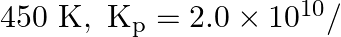 bar for the given reaction at equilibrium.
bar for the given reaction at equilibrium. 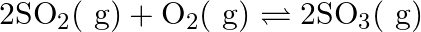 What is
What is 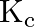 at this temperature?
at this temperature?
Answer: For the given reaction, we have been given the information, $\Delta \mathrm{n}=2-3=-1$ $\mathrm{T}=450 \mathrm{~K}$ $\mathrm{R}=0.0831$ bar $\mathrm{L}$ bar $\mathrm{K}^{-1}...
Nitric oxide reacts with  and gives nitrosyl bromide as per reaction given below:
and gives nitrosyl bromide as per reaction given below: 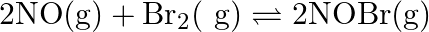 When
When  mol of NO and
mol of NO and 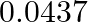 mol of
mol of  are mixed in a closed container at a constant temperature,
are mixed in a closed container at a constant temperature, 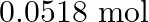 of NOBr is obtained at equilibrium. Calculate the equilibrium amount of NO and
of NOBr is obtained at equilibrium. Calculate the equilibrium amount of NO and  .
.
Answer: The given reaction is: $2 \mathrm{NO}_{(\mathrm{g})}+\mathrm{Br}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}$ $\rightarrow$ $2 \mathrm{NOBr}_{(\mathrm{g})}$ Now, $2 \mathrm{~mol}$ of $\mathrm{NOBr}$ is formed...
The reaction between 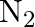 and
and 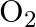 takes place as follows:
takes place as follows: 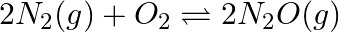 If a solution of
If a solution of 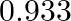 mol of oxygen and
mol of oxygen and 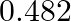 mol of nitrogen is placed in a
mol of nitrogen is placed in a 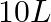 reaction vessel and allowed to form
reaction vessel and allowed to form 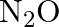 at a temperature for which
at a temperature for which 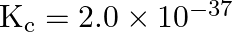 , determine the composition of the equilibrium solution.
, determine the composition of the equilibrium solution.
Answer: Assuming the concentration of $\mathrm{N}_{2} \mathrm{O}$ at equilibrium be $\mathrm{x}$ The given reaction is: $2 \mathrm{~N}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})$+$\mathrm{O}_{2}(\mathrm{~g}) \quad...
Explain why solids and pure liquids can be ignored while writing the equilibrium constant expression.
Answer: The equilibrium constant statement does not include pure solids or pure liquids since they are inert. Because they have no effect on the quantity of reactant present at equilibrium in the...
Find out the value of 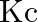 for each of the following equilibria from the value of
for each of the following equilibria from the value of 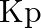 :(i)
:(i)  at
at 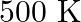 (ii)
(ii) 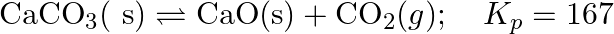 at
at 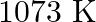
Answer: Kp and Kc are equilibrium constants for reversible reactions. The equilibrium constant Kp is stated in terms of atmospheric pressure, whereas Kc is expressed in terms of concentrations...
Write the expression for the equilibrium constant, 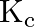 for each of the following reactions: (v)
for each of the following reactions: (v) 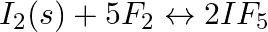
Answer: The equilibrium constant, Kc, is defined as the product of the equilibrium concentrations of products over the equilibrium concentrations of reactants, each raised to the power of the...
Write the expression for the equilibrium constant, 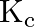 for each of the following reactions:(iii)
for each of the following reactions:(iii) 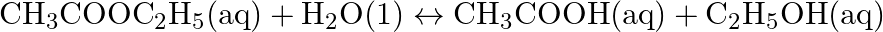 (iv)
(iv) 
Answer: The equilibrium constant, Kc, is defined as the product of the equilibrium concentrations of products over the equilibrium concentrations of reactants, each raised to the power of the...
At a certain temperature and total pressure of  , iodine vapour contains
, iodine vapour contains 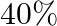 by volume of
by volume of 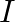 atoms
atoms 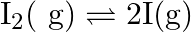 Calculate
Calculate 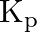 for the equilibrium
for the equilibrium
Answer: Evaluating Partial pressure of lodine atoms (I) $p_{I}=\frac{40}{100} \times p_{\text {total }}$ $=\frac{40}{100} \times 10^{5}$ $=4 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~Pa}$ Similarly, Partial pressure...
What is 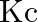 for the following equilibrium when the equilibrium concentration of each substance is:
for the following equilibrium when the equilibrium concentration of each substance is: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \left[\mathrm{SO}_{2}\right]=0.60 \mathrm{M},\left[\mathrm{O}_{2}\right]=0.82 \mathrm{M}](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-93a7d012ef84aab39a01900d902571f6_l3.png) and
and ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \left[\mathrm{SO}_{3}\right]=1.90 \mathrm{M} ?](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ae729162596e2357e0b3fef8b31901e2_l3.png)
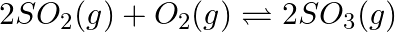
Answer: Given information in the question, $2 S O_{2}(g)+O_{2}(g) \rightleftharpoons 2 S O_{3}(g)$ As we know that, $K_{c}=\frac{\left[S O_{3}\right]^{2}}{\left[S...
A liquid is in equilibrium with its vapour in a sealed container at a fixed temperature. The volume of the container is suddenly increased.c) What happens when equilibrium is restored finally and what will be the final vapour pressure?
Answer: Equality of rates of forward and backward processes restores equilibrium. However, the vapour pressure will stay unchanged because it is temperature dependent and not container volume....
A liquid is in equilibrium with its vapour in a sealed container at a fixed temperature. The volume of the container is suddenly increased. a) What is the initial effect of the change on vapour pressure? b) How do rates of evaporation and condensation change initially?
Answer: (a) As the container's capacity increases, the vapor pressure decreases due to the increased distribution of vapors. (b) Increasing the container's capacity increases evaporation rates...
