 Answer:
Answer:
b) total internal reflection of light in the air during a mirage
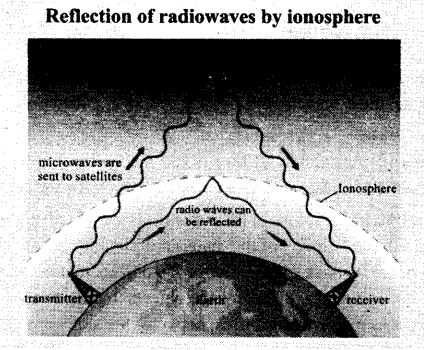
The ionosphere, a layer of the atmosphere, reflects radio waves, allowing them to reach far-flung portions of the globe. Total internal reflection causes radio signals to be reflected by the ionosphere. The angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, which is the same as the total internal reflection of light in the air during a mirage.
Important note: The ionosphere is the ionized portion of the Earth’s atmosphere. The sun’s ultraviolet radiation collides with the atoms in this region, knocking electrons loose. Ions, or atoms with missing electrons, are formed as a result of this process. The free electrons are what produce the reflection and absorption of radio waves, and this is what gives the Ionosphere its name.
