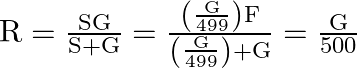The correct option is C
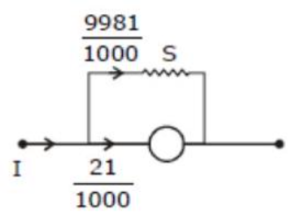
Potential drop is same for both, so on equating,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Total resistan ce of ammeter R can be calculated as,
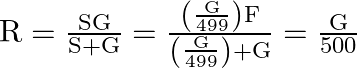
The correct option is C

Potential drop is same for both, so on equating,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Total resistan ce of ammeter R can be calculated as,