Given:
Coefficient of volume expansion of glycerine, ![]()
Rise in temperature, ![]()
Fractional change in volume ![]()
We know that,
![]()
Which can also be written as, ![]()
If taken relation into consideration we have,
![]()
Where, ![]() mass of glycerine
mass of glycerine
![]() Final density at
Final density at ![]()
![]() Initial density at
Initial density at ![]()
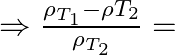 Fractional change in density
Fractional change in density
Therefore, Fractional change in density ![]()
