Answer is (A)
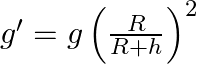
When ![]() then.
then.
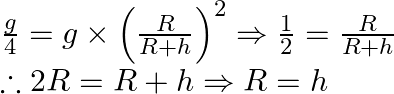
Home » The value of gravitational acceleration ‘ ‘ at a height ‘h’ above the earth’s surface is then radius of earth)A) B) C) D)
The value of gravitational acceleration ‘ 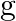 ‘ at a height ‘h’ above the earth’s surface is
‘ at a height ‘h’ above the earth’s surface is 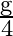 then
then 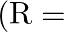 radius of earth)
radius of earth)
A)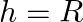
B)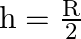
C)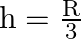
D)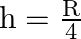
A)
B)
C)
D)
The value of gravitational acceleration ‘ 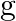 ‘ at a height ‘h’ above the earth’s surface is
‘ at a height ‘h’ above the earth’s surface is 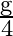 then
then 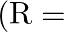 radius of earth)
radius of earth)
A)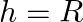
B)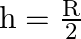
C)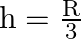
D)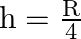
A)
B)
C)
D)
i
