Solution:
As per the question it is given that,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Assume there be a system of n simultaneous linear equations and with n unknown given by
![]()
![]()
![]()
 Let
Let ![]() be the determinant obtained from D after replacing the
be the determinant obtained from D after replacing the ![]() column by
column by
![]() Then,
Then,
![]() provided that
provided that ![]()
Then, here we get
![]()
![]()
![]()
So by comparing with the theorem, let’s find ![]()
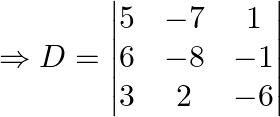
Solving for the determinant, expanding along 1st row
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Now, solve ![]() formed by replacing
formed by replacing ![]() Colum by B matrices
Colum by B matrices
Here,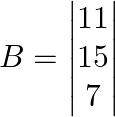
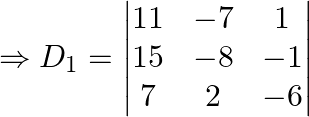
Solving for the determinant, expanding along 1st row
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \Rightarrow {{D}_{1}}=11\left[ (-8)(-6)-(2)(-1) \right]-(-7)\left[ (15)(-6)-(-1)(7) \right]+1\left[ (15)2-(7)(-8) \right]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-315f21107b7285c10aced024d74c4fe0_l3.png)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Then, solve ![]() formed by replacing
formed by replacing ![]() column by B matrices
column by B matrices
Here,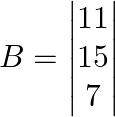
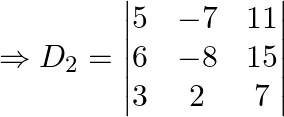
Solving for the determinant, expanding along 1st row
![]()
⇒ ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() `
`
Then, solve ![]() formed by replacing
formed by replacing ![]() column by B matrices
column by B matrices
Here, 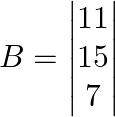
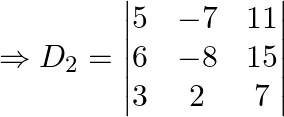
Solving for the determinant, expanding along 1st row
![]()
⇒ ![]()
![]()
⇒ ![]()
![]()
Therefore, by Cramer’s Rule, we will get
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
