Given, n coins are two headed coins and the remaining
![]()
coins are fair.
Let
![]()
: the event that unfair coin is selected
![]()
: the event that the fair coin is selected
E: the event that the toss results in a head
So,
![]()
![]()
(As it’s a sure event)
![]()
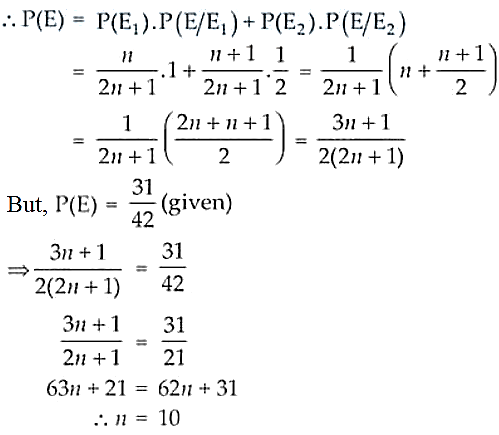
Therefore, the required value of n is
![]()
.
