Solution:
General solution for the differential equation in the form of ![]() Qis given by,
Qis given by,
![]()
Where, integrating factor,
![]()
The slope of the tangent to the curve ![]()
The slope of the tangent to the curve is equal to the sum of the coordinates of the point.
![]() differential equation
differential equation ![]()
![]()
In equation (1)
![]() and
and ![]()
Therefore, integrating factor is
![]()
General solution is
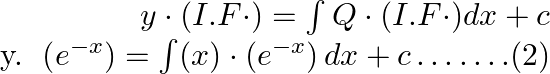
![]()
Let, ![]() and
and ![]()
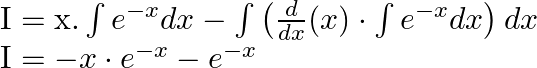
Substituting I in (2),
![]()
Dividing above equation by ![]() ,
,
![]()
The curve passes through origin, therefore the above equation satisfies for ![]() and
and ![]()
![]()
Substituting c in general solution,
![]()
