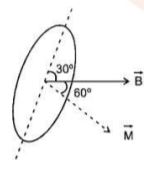
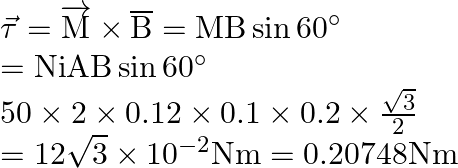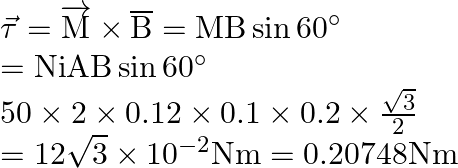A rectangular coil of length
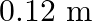
and width
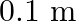
having 50 turns of wire is suspended vertically in a uniform magnetic field of strength
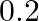
Weber
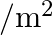
. The coil carries a current of
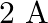
. if the plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of
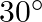
with the direction of the field, the torque required to keep coil in stable equilibrium will be: (1)
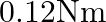
(2)
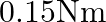
(3)
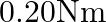
(4)
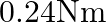
.