Solution:
(i) Given that ![]()
![]()
![]()
For ![]() now we have to find critical point, we must have
now we have to find critical point, we must have
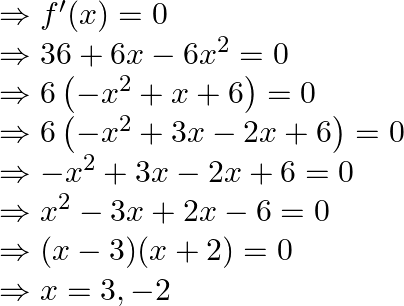
So, ![]() if
if ![]() and
and ![]() if
if ![]() and
and ![]()
Therefore, ![]() increases on
increases on ![]() and
and ![]() is decreasing on interval
is decreasing on interval ![]() ,
,
(ii) Given that ![]()
On differentiating with respect to ![]() we get,
we get,
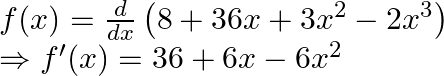
For ![]() we have to find critical point, we must have
we have to find critical point, we must have
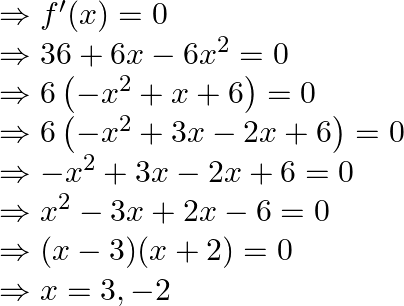
So, ![]() if
if ![]() and
and ![]() if
if ![]() and
and ![]()
Therefore, ![]() increases on
increases on ![]() and
and ![]() is decreasing on interval
is decreasing on interval ![]()
