Given : Here probability of ![]() and
and ![]() that can solve the same problem is given, i.e.,
that can solve the same problem is given, i.e., ![]() and
and ![]()
![]() and
and ![]()
Also, ![]() and
and ![]() are independent. not
are independent. not ![]() and not
and not ![]() are independent.
are independent.
i) atleast one of ![]() and B will solve the problem
and B will solve the problem
Now, P(atleast one of them will solve the problem) ![]() – P(both are unable to solve)
– P(both are unable to solve)
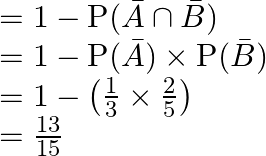
Therefore, atleast one of ![]() and
and ![]() will solve the problem is
will solve the problem is ![]()
ii) none of the two will solve the problem
Now, ![]() (none of the two will solve the problem)
(none of the two will solve the problem) ![]()
![]()
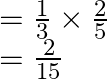
Therefore, none of the two will solve the problem is ![]()
Given the probability that A can solve a problem is 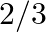 , and the probability that B can solve the same problem is \%, find the probability that
, and the probability that B can solve the same problem is \%, find the probability that
(i)at least one of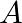 and
and 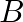 will solve the problem
will solve the problem
(ii)none of the two will solve the problem
(i)at least one of
(ii)none of the two will solve the problem
Given the probability that A can solve a problem is 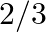 , and the probability that B can solve the same problem is \%, find the probability that
, and the probability that B can solve the same problem is \%, find the probability that
(i)at least one of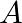 and
and 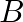 will solve the problem
will solve the problem
(ii)none of the two will solve the problem
(i)at least one of
(ii)none of the two will solve the problem
