A solenoid is a large coil of insulated copper wire looped in a circular pattern. When current is passed through the solenoid, the magnetic field produced around it is comparable to that produced around the bar magnet. When electricity is conducted through a solenoid, magnetic fields are formed around it, as shown in the diagram below.
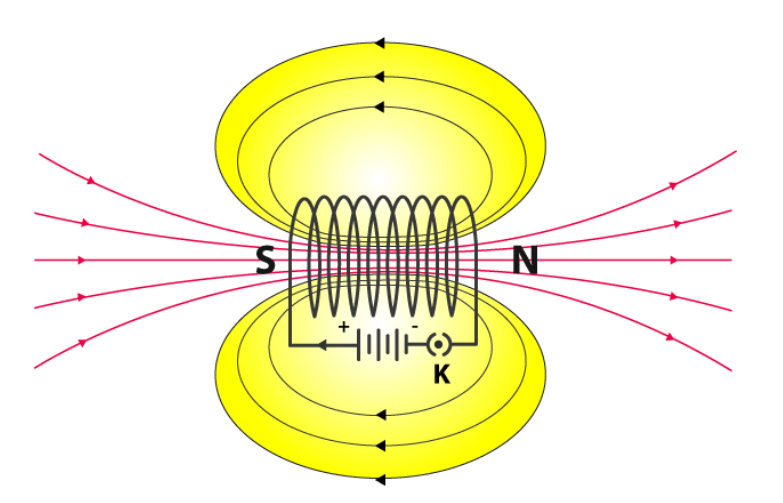
When the north pole of the bar magnet is brought close to the end of the battery’s negative terminal, the solenoid repels the battery. The end connected to the negative terminal is referred to as a north pole, whereas the end connected to the positive terminal is referred to as a south pole.
